Visiting Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge in Moscow, Russia: Hours, Tickets, and Historical Insights
Date: 18/07/2024
Introduction
This article delves into the historical background, architectural significance, and the transformative impact of the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge on Moscow’s urban landscape and transportation network. It also provides practical visitor information, highlighting the bridge’s role as both a historical landmark and a modern marvel.
Table of Contents
- [History and Significance](#history-and-significancehistory-and-significance)
- [Early Crossings and the Quest for Permanence](#early-crossings-and-the-quest-for-permanenceearly-crossings-and-the-quest-for-permanence)
- [The Dawn of the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge](#the-dawn-of-the-bolshoy-ustinsky-bridgethe-dawn-of-the-bolshoy-ustinsky-bridge)
- [A Symbol of Resilience and Transformation](#a-symbol-of-resilience-and-transformationa-symbol-of-resilience-and-transformation)
- [Visitor Information](#visitor-informationvisitor-information)
- [Visiting Hours and Tickets](#visiting-hours-and-ticketsvisiting-hours-and-tickets)
- [Travel Tips](#travel-tipstravel-tips)
- [Nearby Attractions](#nearby-attractionsnearby-attractions)
- [Special Events and Tours](#special-events-and-toursspecial-events-and-tours)
- [Architectural and Engineering Insights](#architectural-and-engineering-insightsarchitectural-and-engineering-insights)
- [Design and Structure](#design-and-structuredesign-and-structure)
- [Deck and Support System](#deck-and-support-systemdeck-and-support-system)
- [Photographic Spots](#photographic-spotsphotographic-spots)
- [Integration with Surroundings](#integration-with-surroundingsintegration-with-surroundings)
- [Impact on Urban Landscape and Transportation](#impact-on-urban-landscape-and-transportationimpact-on-urban-landscape-and-transportation)
- [Urban Development](#urban-developmenturban-development)
- [Transportation Improvements](#transportation-improvementstransportation-improvements)
- [Conclusion](#conclusionconclusion)
- [FAQ](#faqfaq)
- [References](#referencesreferences)
History and Significance
Early Crossings and the Quest for Permanence
Before the rise of the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge, the river crossing at this location was marked by a history of temporary structures. The earliest records point to a pontoon bridge erected in the 15th century, serving as a vital link between the city center and the Tagansky district. This early bridge, however, was a far cry from the permanent structures that would later define the crossing.
The late 19th century ushered in a new era for Moscow, marked by industrial expansion and a burgeoning population. This growth necessitated a more robust solution for the Ustinsky crossing. In 1887, the city saw the construction of a truss bridge, a significant upgrade from its predecessor. This bridge, while a step towards permanence, still fell short of the city’s aspirations for a truly iconic structure.
The Dawn of the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge
The early 20th century brought with it a wave of architectural innovation, and Moscow was eager to embrace the possibilities. The existing Ustinsky bridge, while functional, was deemed outdated and inadequate for the city’s grand vision. This led to the decision to construct a new bridge, one that would embody both functionality and aesthetic grandeur.
The task of designing this new bridge fell upon the renowned engineer V.M. Kuznetsov, a figure known for his innovative approach to bridge building. Kuznetsov envisioned a structure that would not only accommodate the growing traffic but also serve as a symbol of Moscow’s progress. His design, a graceful arch bridge crafted from steel, was a testament to the era’s fascination with industrial materials and bold architectural statements.
Construction of the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge commenced in 1936, marking a pivotal moment in Moscow’s architectural history. The project, however, was not without its challenges. The outbreak of World War II in 1941 cast a long shadow over the construction, leading to significant delays and resource constraints. Despite these setbacks, the bridge was completed in 1938, a testament to the resilience and determination of the city and its people.
A Symbol of Resilience and Transformation
The Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge stands as a symbol of Moscow’s ability to adapt and thrive amidst adversity. Its completion during the tumultuous war years underscored the city’s unwavering spirit and commitment to progress. The bridge quickly became a vital artery, facilitating the movement of people and goods within the city, even as the war raged on.
In the postwar years, the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge continued to play a crucial role in Moscow’s development. It witnessed the city’s transformation from a war-torn landscape to a thriving metropolis, its steel arches standing as silent witnesses to the city’s resilience and growth.
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Tickets
The Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge is open to pedestrians and vehicles 24/7, making it accessible at any time of the day. There is no ticket required to visit the bridge, making it a free attraction for all visitors.
Travel Tips
- Best Time to Visit: Early mornings or late evenings offer the best views and fewer crowds.
- Safety: While the bridge is safe, always be cautious of traffic if you’re walking.
- Photography: The bridge offers stunning views of the Moskva River and the city skyline, especially at sunset.
Nearby Attractions
- Red Square: Just a short distance away, this historic square is a must-visit.
- St. Basil’s Cathedral: Famous for its colorful, onion-shaped domes, located near Red Square.
- Kremlin: The seat of Russian power, filled with historic buildings and museums.
Special Events and Tours
While there are no regular guided tours of the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge, the area often hosts special events and festivals. Keep an eye on local event listings for any upcoming activities that might coincide with your visit.
Architectural and Engineering Insights
Design and Structure
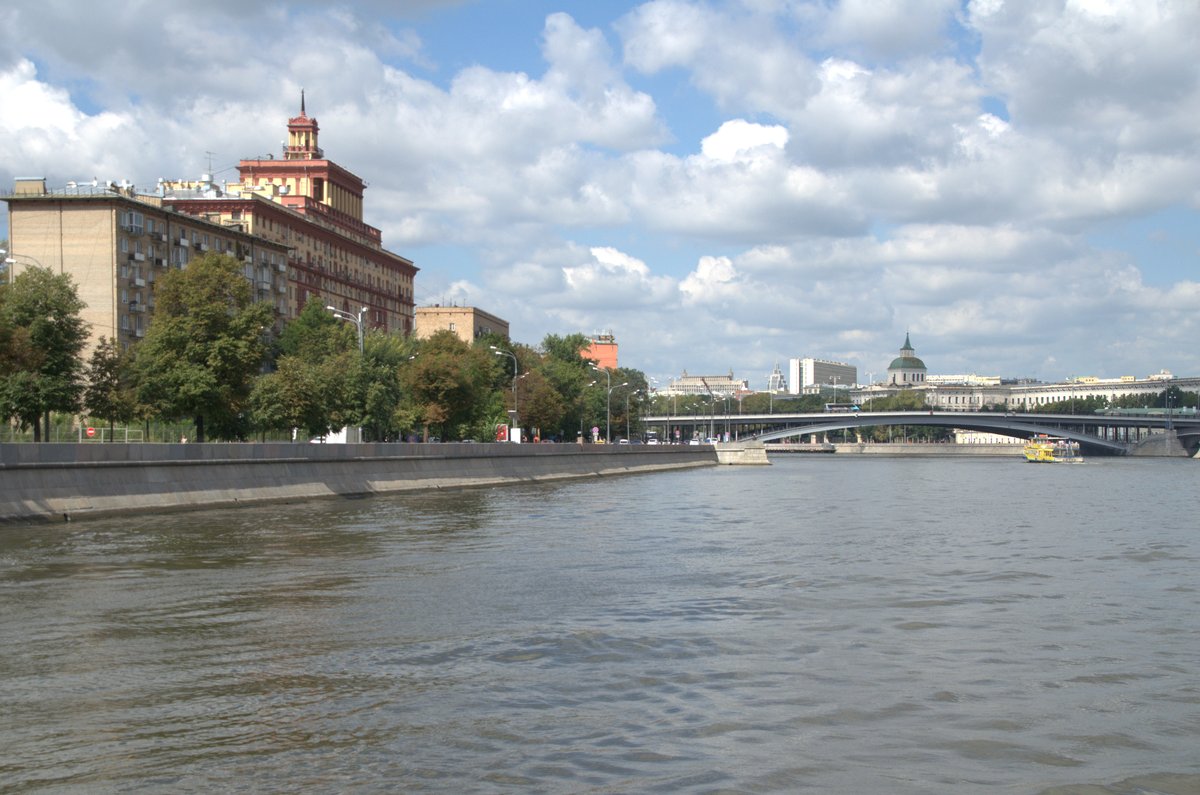
Designed by architects A.V. Shcherbina, P.Y. Yurin, and the Transmost engineering group, the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge reflects a contemporary approach to bridge construction. The bridge boasts an impressive total length of 135 meters (443 feet), with a main span of 90 meters (295 feet) achieved using a unique steel arch design. This arch, painted a striking red, rises 29 meters (95 feet) above the waterline, providing ample clearance for river traffic.
Deck and Support System
The bridge deck, suspended from the arch by steel cables, carries three lanes of traffic in each direction. This suspension system allows for a relatively lightweight deck structure while maintaining strength and stability. The deck itself is constructed using orthotropic steel plates, known for their high strength-to-weight ratio.
Photographic Spots
For photography enthusiasts, the bridge offers numerous spots for capturing the vibrant red arch against the backdrop of the Moskva River and the city skyline. Evening visits are particularly recommended for capturing the bridge illuminated against the night sky.
Integration with Surroundings
The relatively low profile of the arch minimizes visual intrusion on the surrounding cityscape, while the pedestrian walkways on either side offer panoramic views. The bridge’s lighting design enhances its integration, illuminating the structure at night and creating a captivating visual experience.
Impact on Urban Landscape and Transportation
Urban Development
-
Revitalization of Riverfront Areas: The bridge has played a crucial role in rejuvenating the formerly industrial areas along the Moskva River. It has spurred the development of new residential complexes, office buildings, and recreational spaces, transforming the riverfront into a vibrant and desirable location.
-
Connectivity and Accessibility: By connecting previously isolated districts, the bridge has improved accessibility and connectivity within the city. This has led to increased property values and economic growth in the surrounding areas, particularly in the Zamoskvorechye district.
-
Aesthetic Enhancement: The bridge’s unique architectural design has become a recognizable landmark in Moscow’s skyline. Its aesthetic appeal has contributed to the city’s visual identity and enhanced the overall urban landscape.
Transportation Improvements
-
Traffic Flow and Congestion Relief: The Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge has significantly improved traffic flow in central Moscow by providing an alternative route across the Moskva River. This has helped to alleviate congestion on other major thoroughfares, such as the Third Ring Road.
-
Public Transportation Integration: The bridge accommodates various modes of public transportation, including dedicated lanes for buses and trolleybuses. This integration has made it easier and more efficient for commuters to travel across the city, reducing reliance on private vehicles.
-
Pedestrian and Cycling Infrastructure: The bridge features dedicated pedestrian walkways and bike paths, promoting alternative modes of transportation and enhancing the city’s walkability. This has encouraged a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle among residents.
-
Future Development: The Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge serves as a catalyst for future urban development and transportation projects in Moscow. Its construction has paved the way for similar infrastructure initiatives aimed at improving the city’s connectivity, accessibility, and overall quality of life.
Conclusion
FAQ
Q - What are the visiting hours for the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge?
A - The bridge is open 24/7 for both pedestrians and vehicles.
Q - Is there an entrance fee to visit the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge?
A - No, visiting the bridge is free of charge.
Q - What are some nearby attractions?
A - Nearby attractions include Red Square, St. Basil’s Cathedral, and the Kremlin.
Q - Are there any special events held on or near the bridge?
A - While there are no regular guided tours, the area often hosts special events and festivals. Check local listings for more information.
Q - Is the Bolshoy Ustinsky Bridge accessible for people with disabilities?
A - Yes, the bridge includes ramps and accessible pathways for people with disabilities.
Q - Can I take photos on the bridge?
A - Yes, the bridge offers excellent photographic spots, especially during sunset.