Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Comprehensive Paris Historical Sites Guide
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction: The Significance of Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet
Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet, situated in the heart of Paris’s 5th arrondissement, is an exceptional testament to the city’s religious, artistic, and cultural evolution. Famed for its harmonious blend of Baroque and Classical architectural features, the church attracts visitors with its rich history, remarkable artistic program, and ongoing role in religious and cultural debates. Established on land once covered by thistle fields (“chardons”), the church’s origins date back to a 13th-century chapel. The current edifice, constructed between 1656 and 1763, features a classical façade completed in 1934. Inside, masterpieces by Charles Le Brun, Antoine Coysevox, and Jean-Baptiste Corneille highlight the triumph of Catholic art during the Counter-Reformation (Wikipedia; Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet Official Site).
Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet is also notable for its contemporary history. In 1977, the Society of Saint Pius X (SSPX) occupied the church and introduced the Traditional Latin Mass, establishing the church as a hub for traditionalist Catholic worship. This event, both significant and controversial, adds a unique layer to the church’s identity, drawing visitors interested in its spiritual, artistic, and societal relevance (Nouvel Obs; english.katholisch.de).
With free admission, accessible visiting hours, and proximity to other Parisian landmarks like Notre-Dame Cathedral and the Latin Quarter, Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet is an ideal destination for travelers seeking to experience Paris’s layered heritage (France Voyage; paris-promeneurs.com).
Historical Overview
Early Origins and Medieval Development
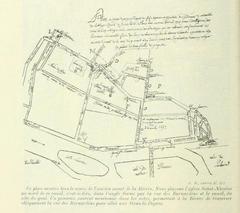
The church’s roots extend to the early 13th century, when the area—known as the “clos du Chardonnet”—was part of the holdings of the Abbey of Saint Victor. In 1230, a chapel was constructed to serve the Left Bank’s growing population, marking the foundation of a parish that would expand through the Middle Ages (official website). Over time, the original chapel was enlarged and rebuilt, reflecting the community’s increasing prominence (Wikipedia; paris-promeneurs.com).
Building the Present Church: 1656–1763
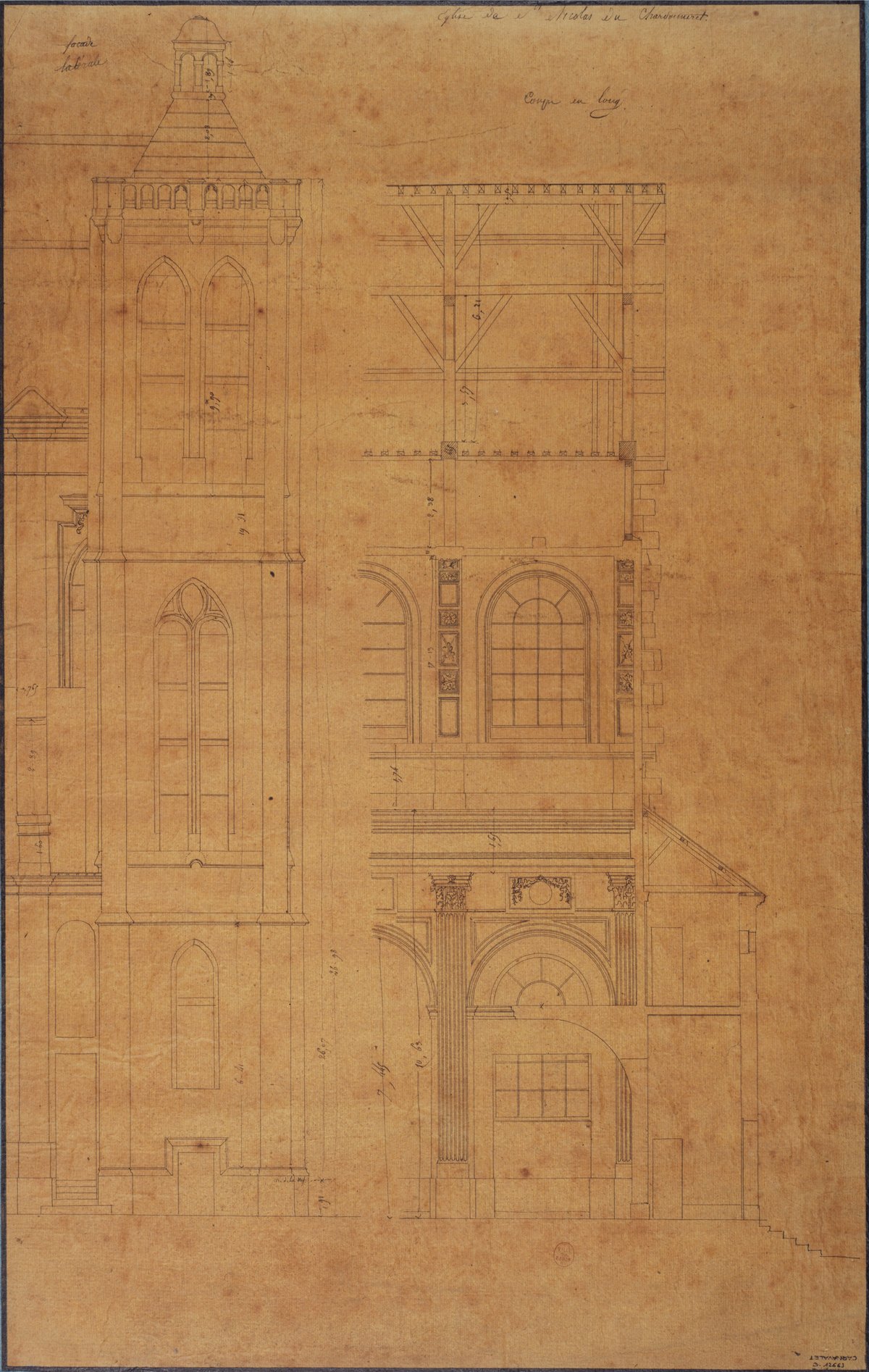
The current structure was begun in 1656 to accommodate a larger congregation and embody the architectural aspirations of the era. The project, led by architects Michel Noblet and François Levé with artistic direction from Charles Le Brun, progressed slowly due to financial constraints. The distinctive bell tower, dating from 1625, is the only surviving element from the earlier church (paris-promeneurs.com). The main building was finally completed in 1763 (Wikipedia).
Artistic and Architectural Heritage
Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet is a prime example of Parisian Baroque architecture with classical elements, particularly in its 1934 façade (english.katholisch.de). Its interior features restored 19th-century artwork and funerary monuments by Antoine Coysevox and Jean Collignon, based on Le Brun’s designs. Paintings such as Le Brun’s “Martyrdom of Saint John Porte Latine” and Corneille’s “Charles Borromee Communicating the Plague Victims” are among the highlights (France Voyage).
Revolutionary Turmoil and 19th-Century Restoration
The French Revolution brought closure and confiscation: the church was stripped of its art and used for secular purposes. Restoration and renewal began after the 1801 Concordat, with new commissions and careful conservation (official website).
Modern History: Secularization and the 1977 Occupation
After the 1905 separation of Church and State, the church became city property but continued to serve as a Catholic place of worship (Wikipedia). The pivotal event of 1977 saw the SSPX occupy the church, restoring the exclusive use of the Traditional Latin Mass and sparking ongoing legal and ecclesiastical debates (paris-promeneurs.com; english.katholisch.de).
Notable Figures
Saint Vincent de Paul and Saint Francis de Sales are reputed to have prayed here. Composer Jean-Nicolas Geoffroy served as organist, and numerous artists, including Charles Le Brun, are interred within the church (Wikipedia).
Architectural and Artistic Highlights
Exterior and Interior Design
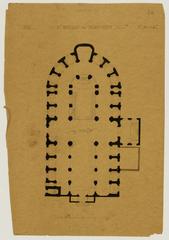
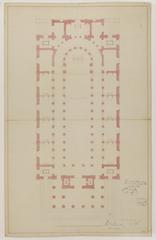
The church’s façade, completed in 1934, features classical symmetry and restrained ornamentation, with a 45-meter bell tower punctuating the Latin Quarter skyline (Structurae). Inside, the Latin cross plan, lofty nave, and luminous clerestory windows create an atmosphere of reverence and grandeur.
Artistic Treasures
- Paintings: Key works include “Le Martyre de Saint Nicolas” by Jean-Baptiste de Champaigne and “La Vierge et l’Enfant apparaissant à Saint Nicolas” by Charles Le Brun (Louvre.fr).
- Sculptures and Altars: The monumental high altar and Rococo pulpit by Louis Regnier are masterworks of 18th-century French religious art (Petit Patrimoine).
- Stained Glass: 19th-century stained glass by Émile Hirsch illuminates the chapels with vibrant biblical scenes (Vitraux de France).
Organ and Liturgical Furnishings
The François-Henri Clicquot organ (1771), one of Paris’s most celebrated, is housed in a Louis XVI-style case (Orgues de France). The church also preserves historic chalices, reliquaries, and vestments.
Visiting Information: Hours, Tickets, and Access
Location and Getting There
- Address: 23 Rue des Bernardins, 75005 Paris
- Metro: Maubert–Mutualité (Line 10), Saint-Michel (Line 4, RER B)
- Bus: Lines 24, 63, 86
- Nearby: Notre-Dame Cathedral, Jardin des Plantes, Sorbonne University, Panthéon
Visiting Hours
- Daily: 7:00 AM – 8:00 PM
- Guided Tours: Sundays at 3:30 PM (check official website for updates and holiday hours)
Admission and Tickets
- Entry: Free of charge, no tickets required. Donations are welcome.
Accessibility
- Wheelchair Access: Main entrance is accessible; some chapels have steps.
- Assistance: Staff available for visitors with mobility needs.
Visitor Policies
- Dress Code: Modest attire recommended.
- Photography: Permitted outside of services; no flash. Respect during religious ceremonies.
- Guided Tours: Available on Sundays and by advance booking.
- Virtual Tours and Media: Explore online tours and galleries on the official website.
Noteworthy Features and Events
- Ceiling Frescoes: 17th-century frescoes depicting scenes from the life of Saint Nicholas and the Virgin Mary.
- Side Chapels: Fourteen chapels, each with unique devotional art and atmospheres.
- Music and Concerts: The church’s acoustics make it a venue for sacred music and organ recitals (Musique Sacrée à Saint-Nicolas).
- Restoration Efforts: Ongoing projects preserve the church’s artistic and architectural legacy (Fondation du Patrimoine).
Religious and Cultural Significance
Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet serves as a focal point for traditionalist Catholic worship in Paris, celebrating the Tridentine Mass in Latin with Gregorian chant. The church’s administration by the SSPX gives it a distinctive identity, attracting pilgrims and visitors interested in pre-Vatican II liturgical forms (Wikipedia).
Controversy and Modern History
The 1977 occupation by the SSPX has made Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet a symbol of ongoing debates within the Catholic Church. Despite legal rulings, the traditionalist group remains in control, and the church continues to host events that occasionally draw political attention (Nouvel Obs; english.katholisch.de).
FAQ: Practical Visitor Information
Q: Is there an entrance fee?
A: No, entry is free. Donations are encouraged.
Q: What are the church’s visiting hours?
A: Open daily from 7:00 AM to 8:00 PM, with tours on Sundays at 3:30 PM.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, regular tours are offered on Sundays. Additional tours can be arranged by contacting the church.
Q: Is the church accessible for visitors with disabilities?
A: The main entrance is accessible, though some areas have steps.
Q: Can I attend Mass?
A: Yes, daily Masses are celebrated in Latin according to the Tridentine rite.
Q: Is photography allowed?
A: Yes, except during services and with no flash.
Nearby Attractions and Travel Tips
- Notre-Dame Cathedral: Gothic masterpiece a short walk away.
- Jardin des Plantes: Paris’s historic botanical garden.
- Panthéon: Resting place of France’s national heroes.
- Latin Quarter: Bustling historic district with cafes, bookstores, and markets.
Travel Tips:
Arrive early for guided tours or Mass. Combine your visit with nearby sites for a full day in Paris’s historic center.
Visual and Interactive Elements
Explore virtual tours, photo galleries, and interactive maps on the official website. Descriptive alt text is provided for images, such as “Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet façade Paris” and “Baroque paintings inside Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet.”
Summary and Recommendations
Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet is a multifaceted jewel in Paris’s cultural and religious landscape. Its origins in the 13th century, layered architectural evolution, and role as a center for traditionalist Catholic worship make it a compelling destination for visitors. The church’s rich artistic program, accessible location, and free admission provide a memorable experience for those interested in history, art, and living tradition (Wikipedia; Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet Official Site; Nouvel Obs; english.katholisch.de).
For the most up-to-date information on visiting hours, events, and access, consult the official Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet website. Enhance your visit with digital tools like the Audiala app for guided tours and audio content, and explore related Paris historical sites for a deeper appreciation of the city’s heritage.
Sources and Further Reading
- Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet Wikipedia
- Official Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet Website
- Nouvel Obs: “Les trente ans de l’occupation de Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet”
- English Katholisch.de: “A Church Under Siege Between Tradition and Extremism”
- France Voyage: “Church Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet”
- Paris Promeneurs: “L’église Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet”
Plan your visit and immerse yourself in the rich heritage of Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet! For more travel guides, download the Audiala app and follow us on social media for exclusive content and updates.