Beyazıt Tower Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Travel Tips
Date: 17/08/2024
Introduction
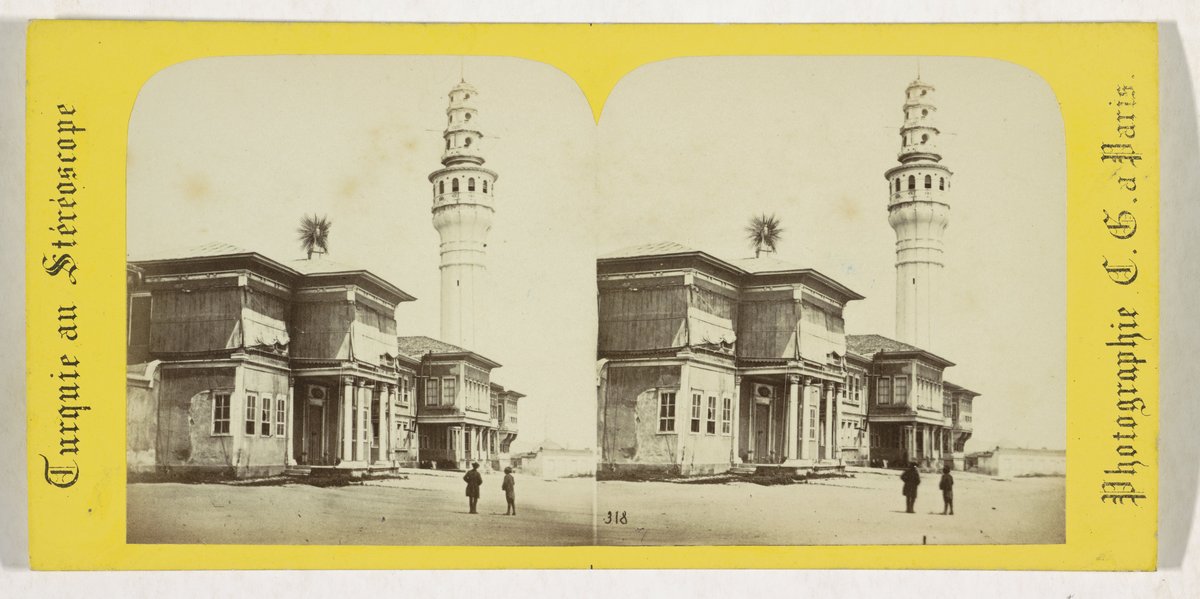
Beyazıt Tower, also known as Serasker (Seraskier) Tower, is a prominent symbol of Istanbul’s architectural and historical legacy. Rising above the Beyazıt district and the Istanbul University campus, this 85-meter stone tower was constructed in 1828 by the renowned Armenian-Ottoman architect Senekerim Balyan during Sultan Mahmud II’s reign. Once a vital fire-watch post, Beyazıt Tower has witnessed many of Istanbul’s dramatic moments and continues to fascinate locals, historians, and visitors, even though entry remains restricted. This guide explores the tower’s history, architecture, current status, and practical tips for those wishing to admire this iconic structure (Istanbul Clues, Turkey Travel Planner).
Table of Contents
- History of Beyazıt Tower
- Modern Use and Restoration
- Visiting Beyazıt Tower
- Cultural and Educational Significance
- Interesting Facts
- FAQ
- Conclusion
- References
History of Beyazıt Tower
Origins and Construction
The site of Beyazıt Tower has hosted fire-watch structures since the 18th century, but the wooden predecessors were destroyed by fires and uprisings. The current stone tower was commissioned by Sultan Mahmud II and completed in 1828 after previous towers were lost during the Janissary uprisings and the Great Fire of Cibali. The design by Senekerim Balyan, a distinguished member of the Balyan architectural family, reflects both resilience and innovation in Ottoman architecture (Istanbul Clues, Wikipedia).
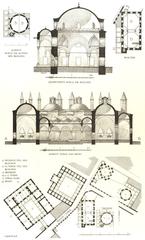
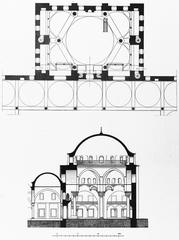
Architectural Design
Beyazıt Tower is a striking example of Ottoman Baroque architecture. Standing 85 meters (279 feet) tall, it features a cylindrical stone body with intricately carved details, a domed roof, and several balconies for observation. A wooden spiral staircase of 256 steps leads to the top. The east side bears Sultan Mahmud II’s tughra (imperial signature), marking its royal connection (Turkey Travel Planner, Visiting Istanbul).
Role in Fire Surveillance
In the 19th century, frequent fires threatened Istanbul’s wooden neighborhoods. Beyazıt Tower became the city’s main fire-watch post, with sentinels using colored flags (by day) and torches (by night) to signal fire locations to the city’s fire brigades. The tower’s vantage point allowed rapid communication, helping to save lives and property during emergencies (Istanbul Guide).
Major Historical Events
Beyazıt Tower played a crucial role during the Great Fire of Pera in 1870, one of Istanbul’s most devastating disasters. Despite the efforts of the fire-watchers, the fire caused extensive damage, highlighting the challenges of urban fire management in the Ottoman era (Historical Istanbul).
Modern Use and Restoration
With the advent of modern firefighting, Beyazıt Tower’s role shifted. Today, it is used as a meteorological hub, its lights displaying weather forecasts with a color-coded system: blue for clear skies, green for rain, yellow for fog, and red for snow. Restoration efforts—most notably in the 1990s—have preserved the tower’s structure and aesthetic, ensuring its continued presence on the Istanbul skyline (Istanbul Municipality, Tourwix).
Visiting Beyazıt Tower
Visiting Hours & Ticket Information
Public Access:
Currently, Beyazıt Tower is not open to the general public. Special visits are occasionally organized by Istanbul University and must be arranged in advance with the university’s Corporate Communications Coordination. Only small groups (maximum 10 people) are allowed at a time for safety and preservation (Istanbul University, Istanbul University Museum).
Tickets:
No tickets are required to view the exterior. Special tours or academic visits may require advance permission but are rare.
How to Get There
The tower is centrally located in Beyazıt Square, easily accessible by public transportation.
- Tram: T1 line, Beyazıt-Kapalıçarşı stop
- Bus: Multiple lines serve Beyazıt area
- On Foot: Short walk from the Grand Bazaar, Sultanahmet, and Süleymaniye districts (Lonely Planet).
Nearby Attractions & Things to Do
- Grand Bazaar: One of the world’s oldest and largest covered markets.
- Süleymaniye Mosque: A masterpiece of Ottoman architecture.
- Beyazıt Mosque & Square: Historic religious and civic sites.
- Istanbul University: The main campus features beautiful gates and gardens.
- Beyazıt Library: A major research library with rich collections (Forever Vacation).
Photography Tips
- Best Light: Visit at sunrise or sunset for warm, dramatic photos.
- Vantage Points: Capture the tower from Beyazıt Square or nearby rooftops for panoramic city shots.
- Detail Shots: Zoom in on the carved stonework and domed roof for architectural details (Trip.com).
Cultural and Educational Significance
Beyazıt Tower is not only a historical monument but also a symbol of Istanbul’s resilience and innovation. It features prominently in literature, art, and photography, and is a subject of academic research at Istanbul University. Its weather signaling system remains a unique feature, continuing to serve city residents (Cultural Istanbul, Tourwix).
Interesting Facts
- The tower’s predecessors were repeatedly destroyed by fires and uprisings.
- Its colored light system is used to forecast the next day’s weather.
- The tower’s wooden staircase has 256 steps.
- It was designed by Senekerim Balyan, part of the family responsible for many of Istanbul’s landmarks.
- The tughra of Sultan Mahmud II is still visible on its eastern side (Wikipedia, Visiting Istanbul).
FAQ
Q: Can I enter Beyazıt Tower?
A: No, regular public access is not available. Occasional group visits may be possible by prior arrangement with Istanbul University.
Q: Are tickets required?
A: No tickets are needed to view the tower from outside. Special academic or group visits require permission.
Q: What is the tower used for today?
A: It is used for meteorological signaling and as an iconic landmark.
Q: What are the best nearby attractions?
A: The Grand Bazaar, Süleymaniye Mosque, and Istanbul University campus are all within walking distance.
Q: Is it safe to visit the area?
A: Beyazıt Square and surroundings are generally safe, but like any major city, be mindful of pickpockets in crowded areas (Travellers Worldwide).
Conclusion
Beyazıt Tower is a unique testament to Istanbul’s blend of history, culture, and architectural innovation. While the tower itself is not generally open to visitors, its presence in Beyazıt Square and proximity to major historical sites make it a must-see for anyone exploring the city. For updates on potential opening, check the Istanbul University website. In the meantime, enjoy the vibrant surroundings and immerse yourself in the stories and sights that make this area of Istanbul so special (Cultural Istanbul, Lonely Planet).
References
- Istanbul Clues. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower. Istanbul Clues
- Turkey Travel Planner. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower. Turkey Travel Planner
- Istanbul Guide. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower History. Istanbul Guide
- Historical Istanbul. (n.d.). Great Fire of Pera. Historical Istanbul
- Istanbul Municipality. (n.d.). Restoration of Beyazıt Tower. Istanbul Municipality
- Istanbul University. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower. Istanbul University
- Istanbul University Museum. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower Monumental Museum. Istanbul University Museum
- Cultural Istanbul. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower Significance. Cultural Istanbul
- Lonely Planet. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower. Lonely Planet
- Wikipedia. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower. Wikipedia
- Tourwix. (n.d.). Towers of Istanbul and Their Unforgettable Stories. Tourwix
- Forever Vacation. (n.d.). Beyazıt. Forever Vacation
- Visiting Istanbul. (n.d.). Beyazıt Tower. Visiting Istanbul
- Trip.com. (n.d.). Tower of Beyazıt. Trip.com
- Travellers Worldwide. (n.d.). Best Time to Visit Istanbul. Travellers Worldwide
For more travel tips and updates on Istanbul’s landmarks, follow us on social media or download the Audiala mobile app.