Villa of the Mysteries Pompeii: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Travel Guide
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
The Villa of the Mysteries (Villa dei Misteri), located just outside the ancient city walls of Pompeii, Italy, is one of the most remarkable and best-preserved Roman suburban villas. Renowned globally for its stunning Dionysian frescoes, the villa provides visitors with a vivid window into the religious rites, luxurious lifestyles, and artistic achievements of Pompeii’s elite on the eve of the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE. Founded in the 2nd century BCE and expanded through later centuries, the villa is a superb example of Roman architecture that blends residential grandeur with agricultural functionality, notably featuring wine production facilities.
This comprehensive guide delivers everything you need to plan your visit, including opening hours, ticketing information, accessibility, travel tips, and a detailed exploration of the villa’s art and recent archaeological discoveries. Whether you are a history enthusiast, an art lover, or a curious traveler, this resource prepares you for a captivating journey into one of Pompeii’s most iconic sites. For up-to-date details, consult the Pompeii Archaeological Park website, TheTravel, and SeePompeii.
Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background & Archaeological Significance
- Layout and Architectural Features
- The Dionysian Frescoes: Artistic and Religious Significance
- Recent Archaeological Discoveries
- Visiting Information
- Hours & Tickets
- Accessibility
- Getting There
- Guided Tours and Special Events
- Nearby Attractions
- Visuals and Media Recommendations
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
- Sources
Historical Background & Archaeological Significance
Origins and Historical Development
The Villa of the Mysteries stands as a testament to the prosperity and sophistication of Pompeii’s elite. Archaeological evidence points to its origins in the 2nd century BCE, with significant expansion and renovation during the late Roman Republic (80–70 BCE), a time when affluent citizens sought opulent estates outside the city walls (TheTravel). Its location, just 400 meters from the Herculaneum Gate, offered privacy and proximity to Pompeii’s urban amenities.
Initially, the villa served as a luxurious retreat for a prominent Roman family. Following the earthquake of 62 CE, the estate was partially reconstructed and repurposed, with evidence suggesting an increased focus on agricultural production, especially wine, as indicated by installed wine presses and storage vats (SeePompeii).
Eruption and Preservation
The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE buried the villa under volcanic ash, effectively preserving its architectural layout, artwork, and even some organic materials. Since the beginning of systematic excavations in 1909, archaeologists have uncovered not only the villa’s structure and frescoes but also poignant evidence of those who perished within its walls (TheTravel).
Layout and Architectural Features
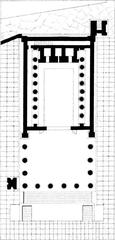
Site Plan and Key Spaces
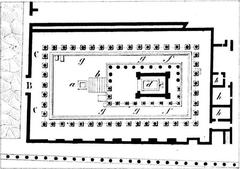
The villa’s main entrance faces the ancient road to Herculaneum, with a layout centered on a grand atrium (with an impluvium), peristyles (columned courtyards), multiple triclinia (dining rooms), cubicula (bedrooms), service quarters, baths, and expansive gardens (pompeiiinpictures.com; ermakvagus.com).
- Atrium: The villa’s core, featuring marble thresholds and sunken rainwater collection, flanked by bedrooms and corridors. Plaster casts of eruption victims are displayed here.
- Peristyle Garden: A tranquil, column-surrounded courtyard that links the residential and service areas.
- Triclinium (Dining Room): The famed Room 5, housing the Dionysian frescoes, was used for banquets and ceremonial gatherings.
- Service Quarters and Baths: Including a kitchen (with a preserved hearth), storerooms, and bathing facilities, reflecting Roman daily routines.
- Gardens and Exedra: Elevated terraces and a large exedra (semi-circular gathering space) overlook the countryside, blending leisure with agricultural activity.
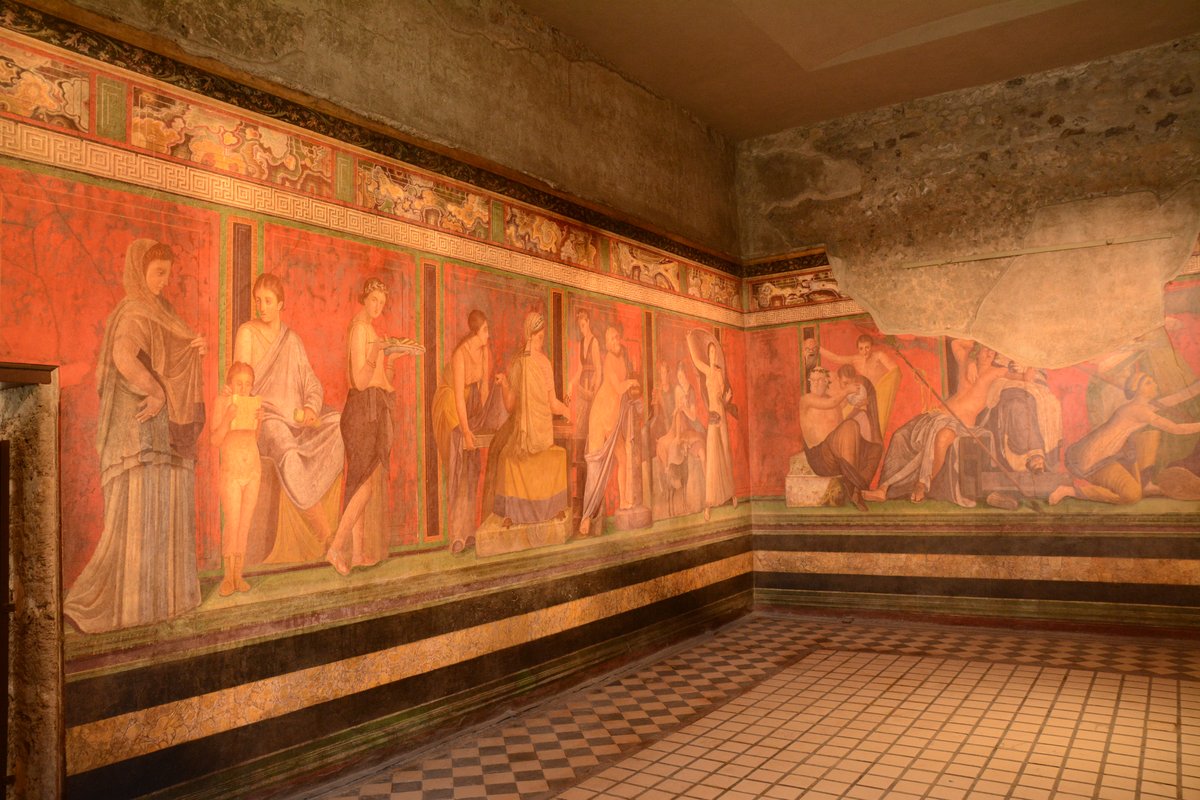
The Dionysian Frescoes: Artistic and Religious Significance
The Initiation Chamber
The villa’s international fame rests on the extraordinary frescoes of Room 5 (the triclinium), painted in the late 1st century BCE in the so-called Second Style of Roman wall painting (Smithsonian Magazine). The nearly life-size figures, set against a deep red background, create a dramatic and immersive frieze over 17 meters long.
- Subject Matter: The frescoes depict an initiation into the Dionysian Mysteries—a secretive cult dedicated to Dionysus, god of wine, ecstasy, and transformation.
- Iconography: Key scenes show women in various ritual acts, accompanied by satyrs, maenads, and Dionysus himself, blending mythological and mortal realms.
- Symbolism: The ritual processions, ecstatic dances, and acts of purification symbolize spiritual rebirth, the transition from girlhood to womanhood, and the duality of the Roman female experience (Smithsonian Magazine).
- Artistic Technique: The use of perspective, foreshortening, and illusionistic space demonstrates the technical mastery of Roman painters.
Social and Religious Context
The frescoes reflect the popularity of mystery cults in Roman society, offering secret knowledge distinct from Rome’s public religion. Despite periodic suppression by Roman authorities, the continued presence of Dionysian imagery in elite homes attests to the enduring appeal of these rites (Smithsonian Magazine).
Recent Archaeological Discoveries
New excavations at Pompeii, including the Villa of the Mysteries, have revealed even more about the social and ritual life of Pompeii’s inhabitants. In early 2025, archaeologists discovered a new fresco cycle in Region IX, featuring Dionysian initiation scenes similar to those at the villa (Pompeii Archaeological Park). Additional finds include bakeries, laundries, and bath complexes, deepening our understanding of the city’s urban fabric (Artnet News).
Preservation efforts leverage advanced technology such as 3D scanning and drone imaging to monitor and protect the frescoes (The Archaeologist).
Visiting Information
Hours & Tickets
- Opening Hours: Daily, 9:00 AM – 7:00 PM (last entry at 6:00 PM). Seasonal variations may apply.
- Tickets: Admission to the Villa of the Mysteries is included with the Pompeii archaeological park ticket (approx. €18 for adults, with discounts for youth and free entry for children under 18).
- Advance Purchase: Tickets can be purchased online to avoid queues.
Accessibility
- The villa is part of the “Pompeii for All” initiative, offering improved access. Some ancient surfaces remain uneven; wheelchair users should consult the official accessibility guide before visiting.
Getting There
- By Train: Pompeii is accessible from Naples and Rome. From Pompeii train station, the villa is a 15–20 minute walk or short bus ride.
- By Car/Bus: Paid parking and shuttle services are available near the site entrances.
Guided Tours and Special Events
- Guided Tours: Available on-site and via authorized providers, tours offer expert insights into the villa’s art, history, and recent discoveries.
- Special Events: Pompeii occasionally hosts night tours, exhibitions, and educational programs—check the official calendar for updates.
Nearby Attractions
- Explore Pompeii’s Forum, Amphitheatre, House of the Faun, and the House of the Vettii. Consider a visit to nearby Herculaneum or the ancient vineyards for a broader experience.
Visuals and Media Recommendations
- Images: Use high-resolution photos of the Dionysian frescoes, architectural details, and the villa’s gardens.
- Maps: Provide a site map with the location of the Villa of the Mysteries clearly marked.
- Alt Text Examples: “Villa of the Mysteries frescoes depicting Dionysian initiation rites,” “Pompeii archaeological site map with Villa of the Mysteries.”
- Virtual Tours: Link to the official Pompeii virtual tour platform for remote exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the Villa of the Mysteries’ opening hours?
A: Daily from 9:00 AM to 7:00 PM (last entry at 6:00 PM); check the official site for seasonal updates.
Q: How can I buy tickets?
A: Tickets are included with Pompeii archaeological park admission and can be purchased online or at the gate.
Q: Is the Villa accessible for visitors with disabilities?
A: Accessibility is improving, though some areas remain challenging. Consult the official accessibility guide.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, both in-person and audio-guided tours are available and highly recommended.
Q: Can I take photos?
A: Photography is allowed without flash; tripods and selfie sticks are not permitted.
Conclusion
The Villa of the Mysteries stands as a captivating testament to ancient Roman artistry, spirituality, and daily life. Its world-renowned Dionysian frescoes, architectural sophistication, and recent archaeological discoveries make it an essential destination for anyone interested in exploring the mysteries of Pompeii. Plan your visit by securing tickets in advance, consider a guided tour for deeper insights, and explore nearby attractions for a comprehensive experience. Stay informed about ongoing preservation and new finds through official resources and trusted publications.
For more in-depth exploration, download the Audiala app for guided audio tours and consult our related articles on Roman history and Pompeii’s archaeological wonders.
Sources and Further Reading
- Villa of the Mysteries Pompeii: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Insights, TheTravel
- Pompeii In Pictures – Villa of the Mysteries
- Smithsonian Magazine: Dionysian Cult Frescoes
- Pompeii Archaeological Park – Discovery of Dionysian Frescoes
- World Travel Connector: Pompeii Guide
- SeePompeii Official Site
- The Archaeologist: Preserving Pompeii
- Artnet News: New Pompeii Discoveries
- Pompeii Tickets