Stabian Baths Pompeii: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Significance
Date: 15/06/2025
Introduction
The Stabian Baths (Terme Stabiane) stand as the oldest and one of the most significant public bath complexes in Pompeii, Italy. As a testament to Roman engineering, social life, and architectural achievement, the baths offer a unique window into ancient daily rituals and communal activities. This comprehensive guide explores the baths’ history, layout, cultural importance, and provides essential information for visitors, including up-to-date details on visiting hours, ticketing, accessibility, and travel tips.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Overview
- Architectural Layout and Features
- Social and Cultural Importance
- Impact of the 62 CE Earthquake and Later Restorations
- Preservation and Archaeological Insights
- Visiting Information
- Practical Visitor Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion and Travel Advice
- References
Historical Overview
The Stabian Baths were constructed shortly after 125 BCE, making them the oldest surviving public baths in Pompeii (Archaeology Magazine; History Skills). Their strategic location at the intersection of major city streets underscores their centrality in urban life. Originally supplied by a well-fed rooftop reservoir, the baths underwent significant transformation with the introduction of aqueduct-supplied running water in the 1st century CE, elevating them to new standards in comfort and hygiene (Academia.edu).
The devastating earthquake of 62 CE prompted extensive renovations, modernizing the baths and expanding their facilities. This resilience reflects Pompeii’s civic pride and commitment to public welfare (Archaeology Magazine).
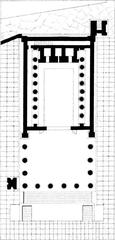
Architectural Layout and Features
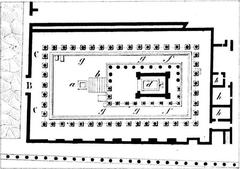
Covering approximately 3,500 square meters, the Stabian Baths occupy an entire city block (insula) in Regio VII (ermakvagus.com). The complex is organized around a large palaestra (exercise yard), with bathing facilities along the northern and western edges. Separate sections for men and women reflect Roman social norms, with the men’s area being larger and more elaborately decorated.
Key Bathing Areas
- Apodyterium (Changing Room): Served as the entry point where bathers would undress and store belongings. Decorated with benches and wall niches.
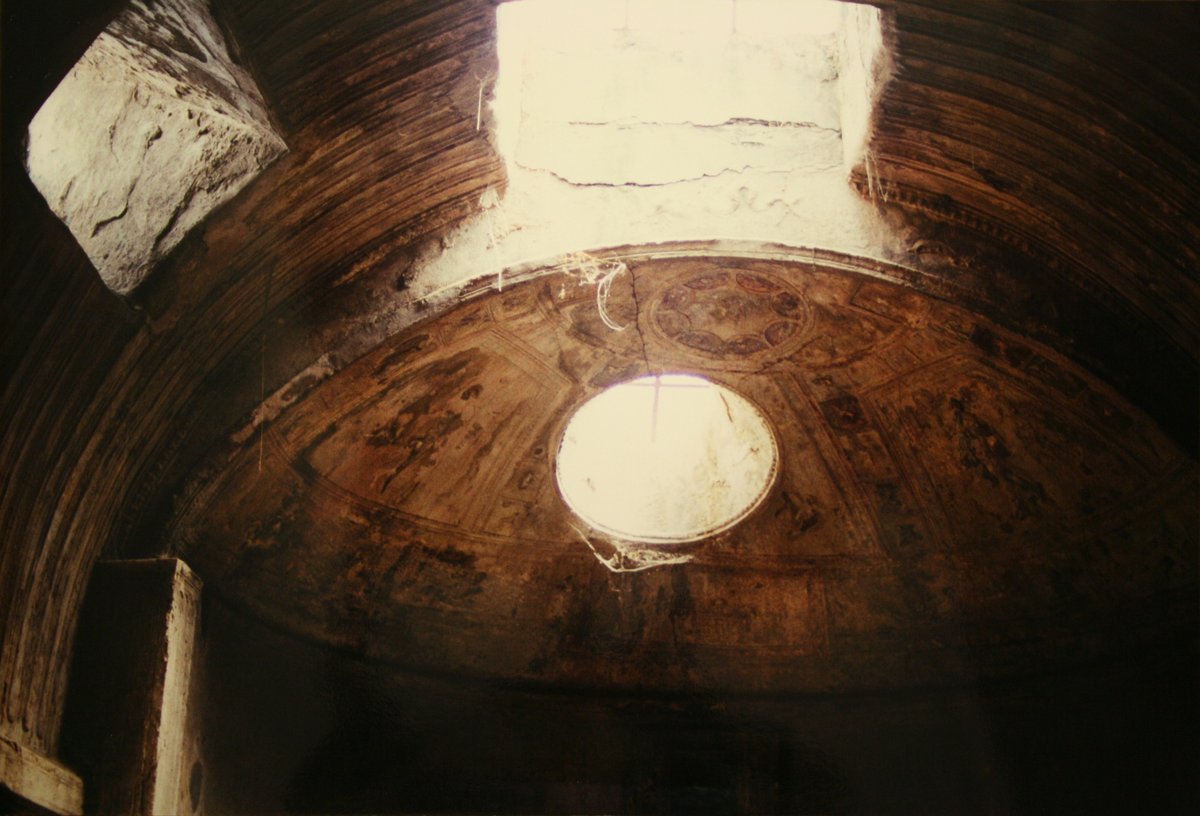
- Frigidarium (Cold Room): A domed chamber with a marble-lined cold-water pool, featuring stucco and frescoes.
- Tepidarium (Warm Room): A transitional space with heated floors, barrel vaults, and marble benches.
- Caldarium (Hot Room): The hottest area, equipped with a large hot-water pool, a cold-water basin (labrum), and advanced underfloor and wall heating (Academia.edu).
- Laconicum (Sweating Room): Functioned much like a modern sauna.
- Palaestra: The open-air gymnasium for exercise and socializing.
- Natatio (Swimming Pool): Outdoor pool for swimming and cooling down.
Engineering Innovations
- Hypocaust System: An advanced heating network circulating hot air beneath floors and within hollow wall tiles, ensuring comfort in the caldarium and tepidarium (Italy Sights).
- Water Supply and Drainage: Fed by aqueducts, with lead pipes and settling tanks for clean water and efficient waste removal.
Decorative Elements
The Stabian Baths are renowned for their vibrant frescoes, intricate mosaics, and stucco reliefs—many illustrating mythological scenes and geometric motifs (The Geographical Cure). Statues of deities such as Apollo and Venus further highlight the baths’ cultural and spiritual significance.
Social and Cultural Importance
Communal Bathing and Gender Segregation
The baths were open to all social classes for a modest fee, with free admission on public holidays (Pompeii Tours). Gender segregation was observed, with separated entrances and bathing suites for men and women. While the men’s section was larger and more ornate, both areas allowed for the communal rituals central to Roman society (shorthistory.org; pompeionline.net).
Daily Life and Recreation
Bathing was a daily routine intertwined with exercise, relaxation, and socialization. The palaestra hosted athletic activities, while various rooms enabled conversation, business dealings, and leisure (italyguides.it). The baths also featured amenities like gardens and sometimes libraries or taverns, making them vibrant centers of community life.
Economic and Commercial Role
The Stabian Baths were economic hubs, with vendors selling oils, refreshments, and bathing tools. Proximity to major roads and integration with local businesses made the baths well-connected within the urban landscape (pompeiitravel.com).
Impact of the 62 CE Earthquake and Later Restorations
The earthquake of 62 CE caused significant damage to Pompeii, spurring a major restoration of the Stabian Baths. Authorities expanded and modernized the complex, introducing new decorative schemes and facilities to rival other public baths (Archaeology Magazine). These efforts underscore the baths’ centrality to civic identity and urban renewal.
Preservation and Archaeological Insights
Thanks to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE, the Stabian Baths are remarkably well-preserved. Archaeological excavations have revealed an array of artifacts—strigils, oil flasks, coins—and preserved rooms with original mosaics, frescoes, and hypocaust remains (Italy Sights). The site provides invaluable evidence for understanding Roman engineering, social customs, and daily life.
Visiting Information
Hours and Tickets
- Opening Hours: Typically open daily from 9:00 AM to 7:00 PM, with the last entry at 6:00 PM. Always check the official Pompeii Archaeological Park website for seasonal updates.
- Tickets: Included in the general admission to Pompeii Archaeological Park. Standard adult tickets are approximately €16, with discounts for EU citizens aged 18–25 and free entry for children under 18. Advance booking online is recommended during peak seasons (Travel With Kinsley).
Accessibility
While improvements have been made, the ancient stone surfaces and steps can challenge visitors with mobility issues. A designated accessible route exists, but some areas remain difficult to navigate. It is advisable to contact the park in advance for the latest accessibility information (Travel With Kinsley).
Guided Tours and Tips
- Guided Tours: Available from various operators and highly recommended for in-depth historical context.
- Audio Guides: Rentable at the site or downloadable via the official Pompeii app, offering detailed commentary and maps.
- Best Times to Visit: Early morning or late afternoon to avoid crowds and midday heat. Spring and autumn are optimal for milder weather (World Travel Connector).
Nearby Attractions
Combine your visit with other notable sites, such as the Pompeii Forum, Amphitheater, House of the Faun, and Villa of the Mysteries. All are within walking distance and accessible via the main site pathways.
Practical Visitor Tips
- Footwear: Wear sturdy, comfortable shoes for uneven ancient pavements.
- What to Bring: Lightweight clothing, sun protection, refillable water bottle, and a small backpack (large bags may be restricted).
- Facilities: Restrooms are located at main entrances and throughout the park (not inside the baths). Water fountains are available outside the baths.
- Photography: Non-flash photography is permitted; tripods and flash may be restricted. Do not touch or lean on decorated surfaces (The Geographical Cure).
- Etiquette: Stay on marked paths, avoid loud conversations, and respect the preservation of the ruins.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the Stabian Baths’ visiting hours?
A: Typically 9:00 AM to 7:00 PM, last entry at 6:00 PM. Confirm on the official website before visiting.
Q: How do I get tickets?
A: Included with Pompeii Archaeological Park admission. Book online for convenience, especially in high season.
Q: Is the site accessible for those with mobility challenges?
A: Partial accessibility is provided via designated routes, but some areas are still difficult due to original Roman construction.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, and they are highly recommended for an enriched experience. Audio guides are also available.
Q: Are children and families welcome?
A: The site is suitable for families, though supervision is advised due to uneven surfaces.
Q: Can I take photos?
A: Photography is permitted without flash; check for restrictions on tripods.
Conclusion and Travel Advice
The Stabian Baths embody the innovative spirit and social vibrance of ancient Pompeii. Their sophisticated engineering, grand architecture, and role as centers of community life make them a highlight of any visit to Pompeii. By planning your visit—checking hours, securing tickets, considering accessibility, and following practical tips—you can fully appreciate this remarkable archaeological treasure.
For the best experience, consider using audio guides or joining expert-led tours, and explore nearby landmarks to immerse yourself in Pompeii’s rich historical landscape. Download the Audiala app for personalized tours and stay updated via social media for the latest travel tips and offers.
References
- Archaeology Magazine
- Academia.edu
- Pompeionline.net
- Pompeii Archaeological Park
- Italy Sights
- Pompeii Tours
- Travel With Kinsley
- ermakvagus.com
- The Geographical Cure
- World Travel Connector
- History Skills
- shorthistory.org
- italyguides.it
- pompeiitravel.com
- Holidify