Thermopolium VII.4.4 Pompeii: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Site Guide
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
Thermopolium VII.4.4 in Pompeii stands as a remarkable testament to ancient Roman street food culture and social life. Serving as a “fast-food” establishment, this thermopolium was essential for Pompeii’s working class and travelers, especially those without private cooking facilities. With more than 80 such establishments identified in Pompeii before the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE, thermopolia were not only centers for quick meals but also for social interaction and commerce. The name “thermopolium” itself means “a place where something hot is sold,” reflecting its primary function (All That’s Interesting; Artnet News).
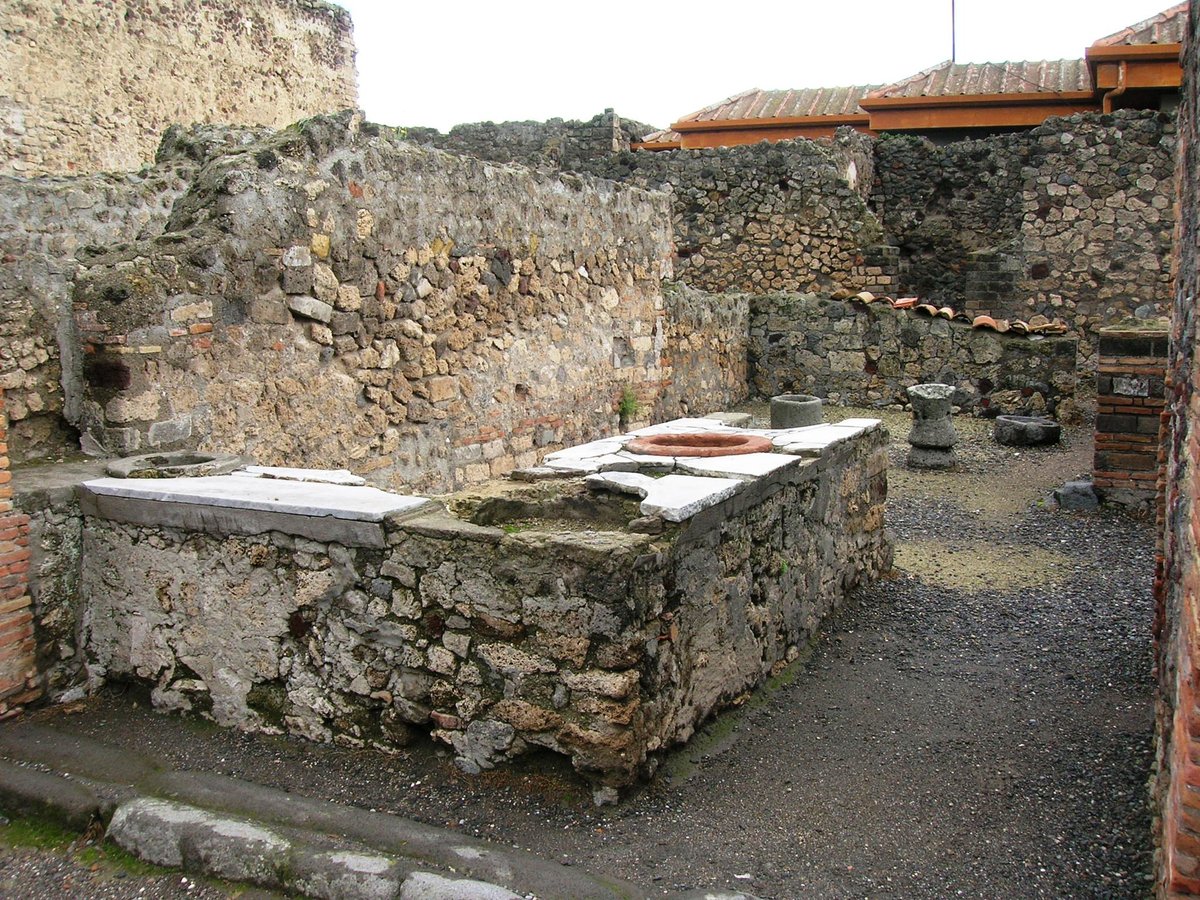
Located on Via del Foro, one of Pompeii’s busiest streets, Thermopolium VII.4.4—also known as the Thermopolium of Regio V—offers visitors a vivid window into Roman daily life. Its well-preserved masonry counter with embedded dolia (large terracotta storage jars), colorful frescoes, kitchen hearth, and latrine provide a unique archaeological and cultural experience (pompeii.uk; Pompeii Archaeological Park). Recent discoveries and restorations have illuminated the diverse diets of Pompeii’s inhabitants, revealing a menu of stews, olives, wine, and spices like saffron (pompeiisites.org).
This guide provides essential information for potential visitors, including historical context, practical travel tips, ticketing and accessibility updates, and insider recommendations to enhance your visit to Thermopolium VII.4.4 and the wider Pompeii archaeological park.
Table of Contents
- What is a Thermopolium?
- Historical and Cultural Significance
- Location and Layout
- Construction and Archaeological Features
- Decorative Elements and Artefacts
- Preservation and Recent Discoveries
- Visiting Hours and Ticket Information
- Accessibility and Facilities
- Nearby Attractions
- Tips for Visitors
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Summary and Recommendations
- References
What is a Thermopolium?
A thermopolium (plural: thermopolia) was a type of ancient Roman eatery where hot food and drinks were sold to the public. Primarily catering to those without private kitchens, these establishments were widespread in Pompeii—between 80 and 150 are estimated to have existed before 79 CE (All That’s Interesting; Artnet News). Thermopolia became social hubs for the working class and travelers, providing affordable, ready-to-eat meals.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Thermopolia were essential to the urban lifestyle of Pompeii’s citizens, serving as both eateries and social gathering points. While Roman elites dined at home, the majority relied on these establishments for daily nourishment. Counters with embedded dolia stored hot and cold food, and the walls often featured vibrant frescoes and mosaics—sometimes advertising menu items or showcasing mythological scenes.
Recent excavations at Regio V have uncovered lively frescoes of animals and mythological figures, as well as graffiti that reveal the personalities of ancient vendors and patrons (Artnet News). The food discovered—ranging from stews and lentils to exotic dishes—reflects the diversity of Roman cuisine.
Location and Layout
Site Location
Thermopolium VII.4.4 is located in Regio V, along Via del Foro, in close proximity to Pompeii’s Forum and other key landmarks (pompeii.uk). The site is accessible from the main entrances, particularly Porta Marina, and is well-signposted on official maps (Mashable; My Modern Met).
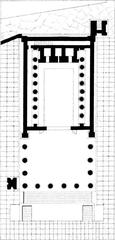
Layout
The thermopolium’s compact ground-floor space is divided into distinct functional areas:
- Sales Counter: A two-sided masonry counter with embedded dolia for serving food and drinks.
- Customer Area: Small space behind the counter, possibly for storage or seating.
- Kitchen: Equipped with a hearth for cooking and a latrine for sanitation.
- Latrine: Located in the kitchen’s southwest corner for waste management.
- Storage Room: Adjacent small room likely used for supplies.
Construction and Archaeological Features
Construction Techniques
Built in the 1st century CE, the thermopolium employs the opus incertum technique—irregular stones set in mortar. Walls are coated with lime plaster, often decorated with painted scenes. The counter features marble and stone finishes with holes for dolia (pompeiiarchaeologicalpark.com).
Key Archaeological Features
- Counter and Dolia: Three large dolia and a smaller jar were used to store and serve stews, olives, wine, and more (pompeii.uk).
- Kitchen Hearth: A cooking area at the rear enabled quick meal preparation.
- Latrine: Efficient use of space, typical of Roman commercial buildings.
- Storage/Staff Room: Likely for supplies or resting workers.
Decorative Elements and Artefacts
While Thermopolium VII.4.4 is more utilitarian than some others, remnants of painted plaster still brighten the interior. Other thermopolia in Pompeii display elaborate frescoes with food and mythological themes (historylearning.com). Artefacts recovered include cooking pots, amphorae for wine and garum, and food remains such as lentils, nuts, olives, chicken, peppercorns, and saffron (pompeiisites.org; wantedinrome.com). Animal bones and shells point to a varied diet.
Preservation and Recent Discoveries
Excavated in the 19th century and recently restored, Thermopolium VII.4.4 owes its preservation to the ash from the 79 CE eruption. Conservation efforts have focused on stabilizing wall surfaces and analyzing food residues, providing new insights into ancient culinary practices (Pompeii Archaeological Park).
Visiting Hours and Ticket Information
- Opening Hours: Pompeii Archaeological Park is typically open daily from 9:00 AM to 7:00 PM (last entry varies by season, usually 5:00–6:00 PM). Always consult the official website for current information.
- Tickets: Standard admission (€15–€20) covers all open sites, including Thermopolium VII.4.4. Advance online purchase is strongly recommended to avoid queues, especially during peak months (Krista the Explorer). Discounts are available for EU residents, students, and seniors.
- Guided Tours: Official guides and audio guides are available at the entrance; many tours focus on food culture and the thermopolium.
- Entry Policy: Small bags only; large bags must be checked. Photography is permitted without flash or tripods.
Accessibility and Facilities
- Wheelchair Access: Pompeii’s “Pompeii per tutti” (Pompeii for All) route enables wheelchair users to access main areas, including the Forum and nearby streets. Some uneven terrain remains, and some interior spaces of the thermopolium may be difficult to access (Disabled Accessible Travel).
- Accessible Toilets: Located at Porta Marina Superiore, Porta Marina Inferiore, Villa Imperiale, and Piazza Anfiteatro. Staff can assist with access.
- Restrooms and Seating: Facilities are available at main entrances; seating is limited on site.
Nearby Attractions
- Forum: Pompeii’s civic heart, near the thermopolium.
- House of the Faun: The city’s largest residence.
- Macellum: The main Roman market.
- Temple of Jupiter: Central religious monument.
These sites are within walking distance and enrich your understanding of Pompeii’s urban life (Mapcarta).
Tips for Visitors
- Timing: Visit early or late to avoid crowds and midday heat.
- Footwear: Wear sturdy, comfortable shoes for uneven, sometimes slippery surfaces.
- Sun Protection: Bring a hat, sunglasses, and sunscreen; shade is minimal.
- Hydration: Carry a refillable water bottle; fountains are available.
- Guided Tours: Consider joining a tour for deeper insights.
- Maps: Download or collect a map at the entrance for navigation.
- Respect: Do not touch artifacts or frescoes; stay behind barriers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the visiting hours for Pompeii and the Thermopolium?
A: Typically 9:00 AM to 7:00 PM, with last entry by 5:00–6:00 PM, depending on the season. Confirm on the official website.
Q: How can I buy tickets?
A: Purchase tickets online through the official ticketing page for guaranteed entry and shorter queues.
Q: Is the thermopolium wheelchair accessible?
A: The main areas of Pompeii are accessible via marked routes; some uneven surfaces remain. Interior access to the thermopolium may be limited.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, official guides and audio guides are available in multiple languages.
Q: Can I bring food and drink?
A: Food options are limited inside Pompeii; bring water and snacks.
Summary and Recommendations
Thermopolium VII.4.4 offers a captivating insight into the foodways and social life of ancient Pompeii. Its preserved counter, kitchen, frescoes, and artifacts reveal the vibrancy of Roman street food culture. Visitors can enhance their experience by booking tickets in advance, joining guided tours, wearing suitable clothing, and following accessibility and preservation guidelines.
For those seeking a comprehensive visit, plan your route to include nearby attractions like the Forum and House of the Faun. Accessibility improvements make the site more inclusive, though some challenges remain for those with limited mobility. Stay updated by consulting the official Pompeii Archaeological Park website and trusted travel resources.
References
- All That’s Interesting
- Artnet News
- pompeii.uk
- Pompeii Archaeological Park
- pompeiisites.org
- Krista the Explorer
- Disabled Accessible Travel
- Mashable
- My Modern Met
- Helen on Her Holidays
- Finding the Universe
- The Geographical Cure
- The GenX Travels
- Nomad Epicureans
- SeePompeii
- wantedinrome.com
- historylearning.com
- Mapcarta