Eumachia Building Pompeii: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Visitor Guide
Date: 04/07/2025
Introduction
The Eumachia Building is one of Pompeii’s most impressive and significant ancient monuments, offering visitors a deep insight into the city’s social, economic, religious, and architectural life. Located prominently on the eastern side of Pompeii’s Forum, this grand structure was commissioned by Eumachia, a wealthy priestess and benefactress, during the reign of Emperor Tiberius. The building’s history and architecture not only reflect the economic vitality of Pompeii, particularly its textile industry, but also highlight the unique and influential role of elite women in Roman society—a rarity in the ancient world (ItalyGuides; Wisdom Words).
This guide will provide an in-depth exploration of the Eumachia Building’s origins, architectural features, cultural and social functions, as well as practical information on visiting, tickets, accessibility, travel tips, and nearby attractions. Whether you’re a history enthusiast or a traveler planning your Pompeii itinerary, this comprehensive resource is designed to enhance your experience.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Origins and Patronage
- Architectural Features and Layout
- Cultural, Economic, and Social Role
- Historical Significance and Archaeological Discoveries
- Visiting the Eumachia Building
- Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Guided Tours and Visitor Experience
- Visuals and Media
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion and Call to Action
- References
Origins and Patronage
The Eumachia Building was inaugurated by Eumachia, a prominent priestess and benefactress in Pompeii during the Tiberian era (14–37 AD). Her wealth, derived from the thriving textile industry, enabled her to commission this monumental structure. Eumachia’s patronage was significant not only for its scale but for its dedication to Concordia Augusta, symbolizing harmony within the imperial family and the Roman state (ItalyGuides).
The building’s dedication, inscribed on the architrave above the porch, intertwined civic, religious, and imperial interests, reflecting Eumachia’s ambition and the status of her family within Pompeian society. The marble façade was added after the earthquake of 62 AD, during Pompeii’s period of reconstruction.
Architectural Features and Layout
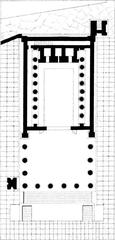
Location and Structure
The Eumachia Building is strategically located on the eastern side of the Forum, adjacent to key civic buildings. Its rectangular footprint (approximately 70 by 30 meters) makes it one of the largest non-religious structures in Pompeii (planetpompeii.com; madainproject.com).
Main Components
- Chalcidicum: The vestibule or entrance hall, opening onto the Forum.
- Porticus: A colonnaded courtyard surrounded by elegant Corinthian columns and paved with stone slabs.
- Crypta: A covered corridor at the rear, separated by a wall with windows for light and ventilation.
The marble-clad façade features niches that once held statues of Rome’s legendary founders and imperial ancestors—Aeneas, Romulus, Julius Caesar, and Augustus—linking Pompeii to broader Roman identity (planetpompeii.com).
Cultural, Economic, and Social Role
Headquarters of the Fullers’ Guild
Archaeological and epigraphic evidence points to the Eumachia Building serving as the headquarters for the fullones, or fabric dyers and launderers, a guild central to Pompeii’s economy (ItalyGuides). The building hosted guild meetings, business transactions, and potentially religious ceremonies linked to the trade.
Female Patronage and Civic Engagement
Eumachia’s role as a benefactor is underscored by the statue dedicated to her by the fullers’ guild, emphasizing the rare but impactful agency of elite women in Roman public and economic life (Wisdom Words).
Symbolic Function
The building’s dedication to Concordia Augusta and the presence of imperial statues highlight its role in promoting imperial ideology and reinforcing the connection between Pompeii’s elite and the emperor (ItalyGuides).
Historical Significance and Archaeological Discoveries
The Eumachia Building was constructed during a period of prosperity, fueled by Pompeii’s strategic trade position and the textile industry. After the earthquake of 62 AD, the building underwent substantial restorations, notably the addition of its marble façade.
Excavations have revealed decorative marble flooring, niches for statues, dedicatory inscriptions, and the remains of Eumachia’s statue, now housed in the National Archaeological Museum of Naples. These findings provide valuable insight into the civic, economic, and religious life of ancient Pompeii (planetpompeii.com).
Visiting the Eumachia Building
Location and Accessibility
The Eumachia Building is located on the eastern side of the Forum, with its main entrance facing the civic heart of Pompeii. The rear entrance opens onto Via dell’Abbondanza, Pompeii’s principal commercial street (trek.zone).
Accessibility: The Forum area is mostly flat, though uneven surfaces and steps may challenge those with mobility issues. Wheelchair users should consult official accessibility maps and may request assistance at the site.
Visiting Hours
Pompeii Archaeological Park is generally open daily from 9:00 AM to 7:00 PM (last admission at 5:30–6:00 PM, depending on the season). Confirm current hours before visiting (Pompeii Archaeological Park).
Tickets and Admission
Admission to the Eumachia Building is included with the general Pompeii site ticket (approx. €16–18 for adults, discounts for EU citizens aged 18–25, free for children under 18). Advance purchase is recommended, especially during peak seasons (thegeographicalcure.com).
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Getting There: Pompeii is accessible by train from Naples or Sorrento (Pompeii Scavi–Villa dei Misteri station).
- Nearby Landmarks: House of the Faun, Temple of Jupiter, Basilica, Temple of Apollo, Lupanar, and the Amphitheatre are all within a short walk (trek.zone).
- Best Time to Visit: Early morning or late afternoon for cooler temperatures and fewer crowds.
- Facilities: Public restrooms and refreshment stands are located near the Forum.
- What to Bring: Comfortable shoes, water, sun protection, and a hat.
Guided Tours and Visitor Experience
Guided tours are available through the park and private operators, often led by archaeologists or local experts. These provide deeper insight into the Eumachia Building and its context within Pompeii (timetravelturtle.com). Audio guides and mobile apps such as Audiala can also enhance your self-guided experience.
Visuals and Media
High-quality images and virtual tours are available on official websites and through the Audiala app. Descriptive alt text such as “Eumachia Building Pompeii marble façade” and “Colonnaded courtyard of Eumachia Building” improve accessibility and search engine optimization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the opening hours for the Eumachia Building?
A: The building follows Pompeii Archaeological Park hours, typically 9:00 AM to 7:00 PM (last admission 5:30–6:00 PM).
Q: Do I need a separate ticket for the Eumachia Building?
A: No, entrance is included with your Pompeii site ticket.
Q: Is the Eumachia Building accessible for wheelchair users?
A: The area has some uneven terrain; consult official maps and request assistance if needed.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, both group and private tours are offered. Audio guides and mobile apps are also available.
Q: Can I take photos inside the Eumachia Building?
A: Photography is allowed, but flash and tripods may be restricted.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The Eumachia Building stands as a powerful symbol of Pompeii’s economic strength, architectural sophistication, and the civic engagement of its elite women. Its history and preservation provide a unique lens into the complexities of Roman urban life and the interplay of commerce, religion, and politics.
We encourage you to plan your visit by consulting official information, booking tickets in advance, and enhancing your exploration with the Audiala app for in-depth guides and audio tours. Follow us on social media for updates on Pompeii and other fascinating historical destinations.
References
- Eumachia Building Pompeii: Visiting Hours, Tickets & Historical Insights (ItalyGuides)
- Building of Eumachia in Pompeii: Architecture, History, and Visitor Information (planetpompeii.com; madainproject.com)
- A Priestess and Benefactress from Pompeii (Wisdom Words)
- Pompeii Archaeological Park Official Website (Pompeii Archaeological Park)
- Visiting the Eumachia Building in Pompeii: History, Tickets, and Visitor Tips (thegeographicalcure.com)
- Visit Pompeii (timetravelturtle.com)
- Edificio di Eumachia, Pompeii (trek.zone)
- Building of Eumachia Attraction (Evendo)