Castellum Aquae Pompeii: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Guide to Pompeii’s Ancient Water Marvel
Date: 04/07/2025
Introduction
Nestled near Naples, the archaeological ruins of Pompeii offer a vivid and enduring glimpse into Roman urban life, where advanced engineering met daily necessity. Among the city’s most significant structures stands the Castellum Aquae—the heart of Pompeii’s water distribution system and a testament to Roman hydraulic mastery. This guide delves into the Castellum Aquae’s historical context, architectural features, engineering innovations, and practical visitor information, including up-to-date visiting hours, ticketing, accessibility advice, and travel tips. Whether you are a history enthusiast, traveler, or student of engineering, this article will ensure you experience one of Pompeii’s most fascinating and essential monuments to the fullest (Pompeii Sites, Leisure Italy, roemer-tour.de).
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background and Urban Development
- Roman Water System: Castellum Aquae and Infrastructure
- Social and Urban Significance
- Visiting the Castellum Aquae: Practical Information
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Visuals and Resources
- Conclusion and Planning Your Visit
- References and Further Reading
Historical Background and Urban Development
Pompeii, founded in the 7th century BCE, flourished due to its strategic location near the Sarno River and the Bay of Naples. Initially a trading hub for Greek, Phoenician, and Etruscan merchants, it underwent significant expansion under Samnite and later Roman rule. By the time Pompeii became a Roman colony in 80 BCE, advanced urban planning and public works—including roads, marketplaces, and a sophisticated water supply—transformed the city into a vibrant commercial and social center (source).
With a growing population and thriving economy, the need for reliable water drove the construction of extensive infrastructure, culminating in the arrival of the Aqua Augusta aqueduct and the erection of the Castellum Aquae.
Roman Water System: Castellum Aquae and Infrastructure
Aqueducts and Water Supply
The lifeblood of Pompeii’s water system was the Aqua Augusta, a monumental aqueduct stretching over 100 kilometers from the Apennines. Entering the city at its highest point near Porta Vesuvio, the aqueduct used gravity to efficiently feed the urban network, supplying fresh water for both public and private use (source).
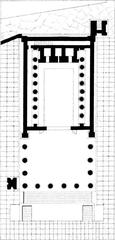
Architectural Features of the Castellum Aquae
Located at Pompeii’s northernmost and highest reach, the Castellum Aquae is a circular masonry structure measuring approximately 7 meters in diameter and 1.4 meters deep. Built using opus incertum (irregular stonework set in mortar), its basin was lined with waterproof opus signinum, ensuring durability and resistance to leaks (Pompeii Sites, Leisure Italy).
Key Features:
- Three Internal Compartments: Stone partitions divided the basin, each connected to a specific outlet (specus) serving public fountains, baths, and private residences.
- Bronze Sluice Gates: Controlled water flow and prioritized supply, especially during shortages.
- Roofed Design: Originally covered, likely with a vaulted stone or brick roof, to protect against contamination and evaporation.
- Lead and Terracotta Pipes: Channeled water beneath the streets, visible at multiple excavation sites (Ancient Engineering Technologies; lucris.lub.lu.se).
Water Towers and Pressure Regulation
To manage varying elevations and ensure balanced pressure, at least fourteen water towers (castella secundaria) were distributed throughout Pompeii. These towers, built from local materials and ingeniously designed, maintained consistent pressure, enabling the system to serve everything from street fountains to private homes (source).
Notable Water Towers
- Tower No. 1: Nocera tuff masonry, single-phase construction.
- Tower No. 2: Brickwork with evidence of multiple phases.
- Tower No. 4: Tuff masonry, features a fountain basin—evidence of continuous adaptation.
These towers, strategically located and periodically reconstructed after earthquakes, demonstrate the resilience and adaptability of Roman engineering (source).
Maintenance, Adaptation, and Seismic Challenges
The 62 CE earthquake caused significant damage to Pompeii’s water infrastructure. The Castellum Aquae and many towers were repaired or reinforced, with stratigraphic studies revealing multiple restoration phases. While the original structures were not designed for seismic events, the Romans’ willingness to adapt and maintain their public works is evident in the archaeological record (source).
Social and Urban Significance
The Castellum Aquae was more than a technical achievement; it was central to Pompeii’s public and private life:
- Public Fountains and Baths: Supported hygiene, social interaction, and daily routines.
- Social Stratification: Access to private water connections reflected wealth and status.
- Civic Identity: The system symbolized the benefits of Roman citizenship and urban belonging.
Aediles (magistrates) supervised water management, enforcing strict regulations and maintaining the system’s integrity, as shown by inscriptions and fines recorded near the castellum (Pompeii Sites).
Visiting the Castellum Aquae: Practical Information
Location and Access
The Castellum Aquae is located near the Porta Vesuvio entrance, at Pompeii’s northern edge in Regio VI. Detailed maps are available at entrances and online (touristplaces.guide). Signage and guided paths lead visitors directly to the site.
Visiting Hours and Tickets
- Summer (April–October): 9:00 AM – 7:00 PM (last entry: 5:30 PM)
- Winter (November–March): 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM (last entry: 3:30 PM)
- Closed: January 1st, December 25th
- Tickets: General admission covers the Castellum Aquae and all main attractions. Prices are approximately €18 for adults, with discounts for EU citizens aged 18–25, and free entry for children under 18. Purchase online in advance for convenience (Official Pompeii Site).
Accessibility
While Pompeii has improved main pathways, uneven ancient paving and some steps near the Castellum Aquae present challenges for those with limited mobility. Consult the official accessibility map or ask at the visitor center for the best routes.
Guided Tours and Amenities
- Guided Tours: Engineering-focused and general tours often include the Castellum Aquae. Audio guides (available in multiple languages) and on-site panels provide historical context (touristplaces.guide).
- Nearby Facilities: Restrooms and refreshment stands are near the Porta Vesuvio entrance. Drinking fountains and shaded rest areas are located throughout the park.
Tips for Your Visit
- Best Times: Visit early or late in the day to avoid crowds and summer heat.
- Footwear: Wear sturdy shoes for uneven surfaces.
- Sun Protection: Bring sunblock and water; shade is limited.
- Photography: Capture exterior and interior views through the observation window—ideal for those interested in ancient technology.
- Combine with Other Sites: Pair your visit with walks along the city walls or explorations of Regio VI’s preserved houses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the Castellum Aquae visiting hours?
A: The site is open during regular Pompeii Archaeological Park hours: 9:00 AM – 7:00 PM in summer (April–October), with shorter hours in winter. Always check the official site before your visit.
Q: How do I get tickets for Pompeii and the Castellum Aquae?
A: Tickets are available online and at park entrances. Advance purchase is recommended, especially in peak seasons.
Q: Is the Castellum Aquae wheelchair accessible?
A: Accessibility is limited due to ancient paving. Consult park resources for accessible routes.
Q: Can I take photographs at the Castellum Aquae?
A: Yes, photography is permitted. The observation window offers unique views of the interior basin and pipework.
Q: Are there guided tours that include the Castellum Aquae?
A: Yes, specialized engineering and thematic tours often feature the site; audio guides and information panels are also available.
Visuals and Resources
For a richer experience, explore official and reputable travel sites for images, aerial views, and videos of the Castellum Aquae. Use descriptive alt tags such as “Castellum Aquae Pompeii water distribution system” for your photos. Interactive maps and virtual tours are available via the official Pompeii website.
Conclusion and Planning Your Visit
The Castellum Aquae stands as a remarkable monument to Roman ingenuity, resilience, and civic pride. Its gravity-fed design, compartmentalized basins, and advanced pressure regulation enabled Pompeii to thrive and grow. Today, visitors can witness this legacy firsthand—experiencing the tangible remains of a system that once sustained a vibrant ancient city.
To ensure a memorable and enriching visit:
- Book tickets online in advance.
- Use official maps for orientation.
- Consider guided tours or audio guides for deeper insight.
- Plan your day with accessibility and weather in mind.
For an immersive experience and expert commentary, download the Audiala app, and follow us on social media for the latest updates and inspiration.
References and Further Reading
- Seismic Assessment of Ancient Water Towers in Roman Pompeii
- Official Pompeii Archaeological Park website
- Castellum Aquae in Pompeii – Curiosities
- Castellum Aquae – Site Details and Technical Information
- Leisure Italy: 13 Things You Need to Know Before a Visit to Pompeii
- Ancient Engineering Technologies: Water Collection in Pompeii
- Lund University Research Paper on Pompeii’s Water System
- Tourist Places Guide: Pompeii Maps and Attractions
Ready to step into the world of ancient Roman engineering? Start planning your journey to the Castellum Aquae today and experience one of Pompeii’s most extraordinary historical sites.