Visiting Guide for Hermitage Bridge in Saint Petersburg, Russia
Date: 24/07/2024
Introduction
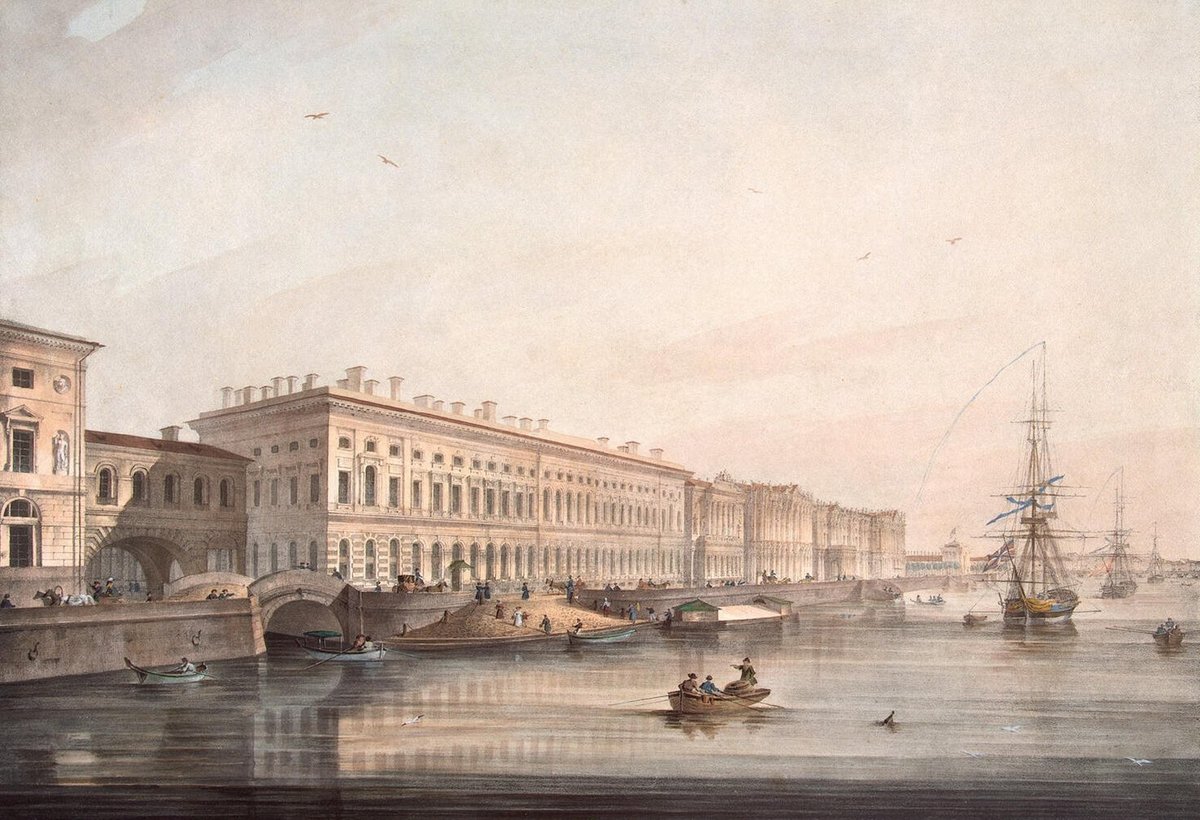
The Hermitage Bridge, or Эрмита́жный мост, stands as a testament to the rich architectural and cultural heritage of Saint Petersburg, Russia. This iconic bridge, originally constructed as a wooden drawbridge between 1718 and 1720 by Dutch engineer Harmen van Bol’es, has undergone significant transformations over the centuries. From its early days as a wooden structure to its current status as a preserved stone bridge, the Hermitage Bridge is a remarkable example of 18th-century engineering and design (Wikipedia).
Located near the Winter Palace and the State Hermitage Museum, the bridge forms an integral part of Saint Petersburg’s historical landscape. It connects the Hermitage Theatre on the First Admiralty Island to the Old Hermitage on the Second Admiralty Island, facilitating movement and commerce between these important cultural and administrative centers (st-petersburg.guide). The bridge’s granite facade and the restoration of its original decor reflect ongoing efforts to maintain its historical integrity while adapting it to contemporary needs.
Visitors to the Hermitage Bridge can appreciate its architectural and cultural significance, as well as its role in the urban development of Saint Petersburg. The bridge is accessible 24/7, and its proximity to major attractions such as the Winter Palace and the Hermitage Theatre makes it a must-visit landmark for tourists. This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on the history, cultural significance, visiting hours, and nearby attractions, ensuring that visitors can make the most of their experience at the Hermitage Bridge.
Table of Contents
- [Exploring the Hermitage Bridge - History, Visiting Hours, and Cultural Significance in Saint Petersburg](#exploring-the-hermitage-bridge---history-visiting-hours-and-cultural-significance-in-saint-petersburgexploring-the-hermitage-bridge-history-visiting-hours-and-cultural-significance-in-saint-petersburg)
- [History of the Hermitage Bridge](#history-of-the-hermitage-bridgehistory-of-the-hermitage-bridge)
- [Early Constructions and Origins](#early-constructions-and-originsearly-constructions-and-origins)
- [Transition to Stone](#transition-to-stonetransition-to-stone)
- [Architectural Evolution](#architectural-evolutionarchitectural-evolution)
- [Restoration Efforts](#restoration-effortsrestoration-efforts)
- [Naming History](#naming-historynaming-history)
- [Visitor Information](#visitor-informationvisitor-information)
- [Visiting Hours and Tickets](#visiting-hours-and-ticketsvisiting-hours-and-tickets)
- [Accessibility](#accessibilityaccessibility)
- [Nearby Attractions](#nearby-attractionsnearby-attractions)
- [The Role of the Hermitage Bridge in Urban Development](#the-role-of-the-hermitage-bridge-in-urban-developmentthe-role-of-the-hermitage-bridge-in-urban-development)
- [Cultural Significance](#cultural-significancecultural-significance)
- [Preservation and Modern Use](#preservation-and-modern-usepreservation-and-modern-use)
- [FAQ](#faqfaq)
- [Conclusion](#conclusionconclusion)
- [History of the Hermitage Bridge](#history-of-the-hermitage-bridgehistory-of-the-hermitage-bridge)
Exploring the Hermitage Bridge - History, Visiting Hours, and Cultural Significance in Saint Petersburg
History of the Hermitage Bridge
Early Constructions and Origins
The original Hermitage Bridge was a three-span wooden drawbridge constructed between 1718 and 1720 by Dutch engineer Harmen van Bol’es. This construction followed the completion of the Winter Canal near the Winter Palace, part of Peter the Great’s grand vision for Saint Petersburg as a ‘window to Europe’ (Wikipedia).
Transition to Stone
In the mid-18th century, the wooden drawbridge was replaced with a permanent stone bridge between 1763 and 1766. This change coincided with the construction of granite embankments along the Neva River, part of a broader effort to modernize the city’s waterways and prevent flooding. The new stone bridge featured an arch made from brick and limestone, covered with a granite exterior, reflecting the architectural style and engineering advancements of the period.
Architectural Evolution
In 1934, the original brick and limestone arch was replaced with a monolithic hinge-free ferroconcrete arch. Despite this structural change, the bridge’s granite facade was meticulously preserved. This renovation was overseen by engineer A. D. Sapestein and architect K. M. Dmitriev, with Professor G. P. Peredery serving as an advisor.
Restoration Efforts
In 1950, efforts were made to restore the original decor of the bridge’s ramps, ensuring the historical aesthetic of the bridge was maintained. These restorations were part of a broader initiative to preserve Saint Petersburg’s architectural heritage.
Naming History
The Hermitage Bridge has had several names throughout its history. Initially named the Upper Embankment Bridge in 1738, it was later referred to as the Winter Palace Bridge and the Palace Bridge before adopting its current name in 1929, derived from the nearby Hermitage Theatre.
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Tickets
The Hermitage Bridge is accessible to the public 24/7. There is no entrance fee as it is a public structure. However, guided tours that include the bridge and nearby attractions may have associated costs.
Accessibility
The bridge is accessible for pedestrians and vehicles. However, visitors with mobility challenges should note that there are no special accommodations like ramps or elevators.
Nearby Attractions
- Winter Palace - A short walk from the bridge, explore this iconic building that houses the Hermitage Museum.
- Hermitage Theatre - Located nearby, this theatre hosts various cultural performances.
- Palace Embankment - A scenic walkway along the Neva River, perfect for a leisurely stroll.
The Role of the Hermitage Bridge in Urban Development
The Hermitage Bridge played a crucial role in the development of Saint Petersburg’s urban landscape. It connected the Hermitage Theatre on First Admiralty Island to the Old Hermitage on Second Admiralty Island, facilitating movement and commerce between these important cultural and administrative centers.
Cultural Significance
The Hermitage Bridge is not only functional but also a symbol of Saint Petersburg’s rich cultural and architectural heritage. It is part of the larger Hermitage and Winter Palace ensemble, which includes some of the most iconic buildings in the city. Its historical and architectural significance makes it a popular attraction for tourists and a subject of study for historians and architects alike.
Preservation and Modern Use
Today, the Hermitage Bridge remains the oldest stone bridge in Saint Petersburg. It continues to serve both practical and aesthetic purposes, accommodating automobile traffic and enhancing the city’s historical ambiance. The preservation of its granite facade and the restoration of its original decor reflect ongoing efforts to maintain the bridge’s historical integrity while adapting it to contemporary needs.
FAQ
What are the visiting hours for Hermitage Bridge?
The Hermitage Bridge is accessible 24/7.
Is Hermitage Bridge accessible for people with disabilities?
There are no special accommodations like ramps or elevators for people with disabilities.
Are there any nearby attractions to visit?
Yes, the Winter Palace, Hermitage Theatre, and Palace Embankment are all nearby.
Conclusion
The Hermitage Bridge stands as a testament to Saint Petersburg’s historical evolution and architectural ingenuity. From its early days as a wooden drawbridge to its current status as a preserved stone structure, the bridge encapsulates the city’s journey through time. Its significance extends beyond mere functionality, embodying the cultural and historical essence of Saint Petersburg. Visitors can appreciate the bridge not only for its beauty but also for its role in the grand narrative of one of Russia’s most important cities.
Call to Action
Plan your visit to Saint Petersburg and explore the rich history and architectural marvels, including the Hermitage Bridge. Follow us on social media for more updates and travel tips!
References
- Hermitage Bridge, Wikipedia source url
- Hermitage Bridge, st-petersburg.guide source url
- Hermitage Bridge, saint-petersburg.com source url
- Hermitage Museum, Britannica source url