Ponte dell’Accademia: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Significance
Date: 17/07/2024
Introduction
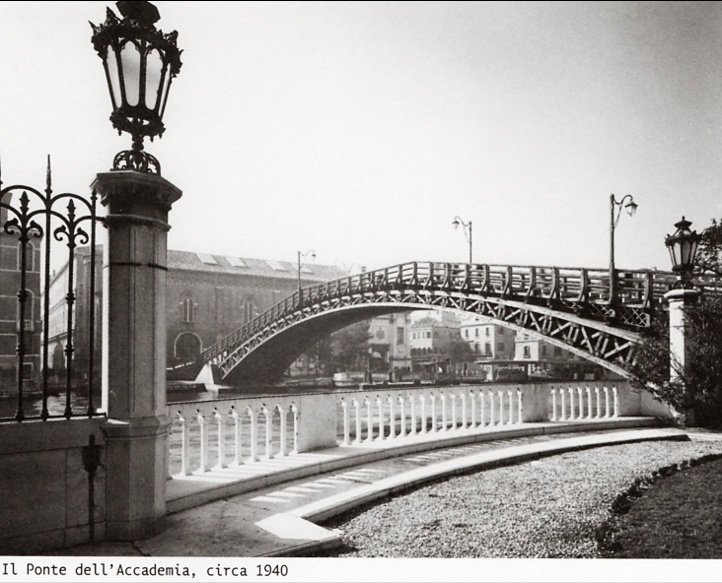
The Ponte dell’Accademia, an iconic bridge in Venice, Italy, is renowned not just for its practical function but also for its rich historical and cultural significance. Spanning the Grand Canal, it connects the districts of Dorsoduro and San Marco, standing as a testament to Venice’s architectural ingenuity and historical evolution. Originally constructed in 1854 by the Austrian engineer Alfred Neville, its iron structure was replaced in 1933 by a wooden bridge designed by Eugenio Miozzi. This temporary solution became a beloved landmark, harmonizing with Venice’s aesthetic (Venice Tourism). The bridge’s subsequent renovations in the 1980s and its hybrid construction in 1986, combining wood and steel, underscore the city’s commitment to preserving its cultural heritage while adapting to modern needs (Structurae). The Ponte dell’Accademia is not merely an architectural marvel but also a cultural icon, symbolizing the city’s enduring artistic legacy and vibrant contemporary life, facilitated by its proximity to the Accademia di Belle Arti di Venezia (Accademia Gallery).
Table of Contents
- [History of Ponte dell’Accademia](#history-of-ponte-dellaccademiahistory-of-ponte-dellaccademia)
- [Early Conception and Construction](#early-conception-and-constructionearly-conception-and-construction)
- [The Wooden Bridge of 1933](#the-wooden-bridge-of-1933the-wooden-bridge-of-1933)
- [Structural Challenges and Renovations](#structural-challenges-and-renovationsstructural-challenges-and-renovations)
- [The Modern Bridge](#the-modern-bridgethe-modern-bridge)
- [Visiting Information](#visiting-informationvisiting-information)
- [Visiting Hours](#visiting-hoursvisiting-hours)
- [Tickets](#ticketstickets)
- [Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions](#travel-tips-and-nearby-attractionstravel-tips-and-nearby-attractions)
- [Nearby Attractions](#nearby-attractionsnearby-attractions)
- [Accessibility](#accessibilityaccessibility)
- [Unique Features](#unique-featuresunique-features)
- [Preservation Efforts](#preservation-effortspreservation-efforts)
- [Historical Events and Anecdotes](#historical-events-and-anecdoteshistorical-events-and-anecdotes)
- [Architectural Details](#architectural-detailsarchitectural-details)
- [Future Prospects](#future-prospectsfuture-prospects)
- [FAQ](#faqfaq)
- [Conclusion](#conclusionconclusion)
History of Ponte dell’Accademia
Early Conception and Construction
The need for a bridge at this location was first proposed in the early 19th century to connect the districts of Dorsoduro and San Marco, facilitating easier access to the Gallerie dell’Accademia, from which the bridge derives its name. The first bridge was constructed in 1854, designed by the Austrian engineer Alfred Neville. This initial structure was an iron bridge, reflecting the industrial advancements of the time. However, the iron bridge was not well-received by the Venetians, who felt it clashed with the city’s historic and aesthetic character.
The Wooden Bridge of 1933
By the early 20th century, the iron bridge had deteriorated significantly, necessitating a replacement. In 1933, a new wooden bridge was constructed, designed by the Italian engineer Eugenio Miozzi. This bridge was intended as a temporary solution, but its elegant design and the use of wood, which harmonized better with Venice’s architectural heritage, made it a beloved landmark. The wooden bridge was notable for its arched design and the use of Istrian stone for the abutments, which provided both strength and aesthetic appeal.
Structural Challenges and Renovations
Despite its popularity, the wooden bridge faced numerous structural challenges over the decades. The humid Venetian climate and the constant flow of traffic caused significant wear and tear. In the 1980s, the bridge underwent extensive renovations to address these issues. The restoration efforts aimed to preserve the bridge’s original design while reinforcing its structural integrity. This included replacing decayed wooden elements and strengthening the overall framework.
The Modern Bridge
In 1986, the wooden bridge was replaced with a more durable structure, designed to maintain the aesthetic qualities of Miozzi’s design while incorporating modern engineering techniques. The new bridge, completed in 1985, utilized a combination of wood and steel, ensuring greater longevity and stability. This hybrid construction allowed the bridge to withstand the demands of modern usage while preserving its historical appearance.
Visiting Information
Visiting Hours
The Ponte dell’Accademia is open 24 hours a day, allowing visitors to explore it at their convenience. However, the best times to visit are early in the morning or late in the afternoon to avoid the crowds.
Tickets
There is no fee to cross the Ponte dell’Accademia. Visitors can enjoy this historical site without the need for tickets.
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
Nearby Attractions
- Gallerie dell’Accademia - Located adjacent to the bridge, this gallery houses an extensive collection of Venetian art, making it a must-visit for art lovers (Gallerie dell’Accademia).
- Peggy Guggenheim Collection - A short walk from the bridge, this museum offers modern art and stunning views of the Grand Canal (Peggy Guggenheim Collection).
- Santa Maria della Salute - This iconic basilica, located at the entrance of the Grand Canal, is renowned for its stunning Baroque architecture and offers a serene escape from the bustling city (Santa Maria della Salute).
Accessibility
The Ponte dell’Accademia is accessible to pedestrians, but its steep steps can be challenging for those with mobility issues. There are no ramps available, so visitors with wheelchairs or strollers may find it difficult to cross.
Unique Features
- Romantic Gestures - The bridge has become a popular site for romantic gestures, with couples attaching padlocks to the railings as a symbol of their love. However, this practice is discouraged due to concerns about the structural impact on the bridge.
- Special Events - Occasionally, the bridge is used as a vantage point for special events like the Regata Storica and other Venetian festivals.
Preservation Efforts
Preserving the Ponte dell’Accademia has been a priority for the city of Venice. Regular maintenance and monitoring are conducted to ensure the bridge remains safe and functional. In recent years, there have been discussions about further renovations to address ongoing wear and tear, with a focus on using materials and techniques that respect the bridge’s historical integrity.
Historical Events and Anecdotes
The Ponte dell’Accademia has witnessed numerous historical events and anecdotes over the years. During World War II, the bridge was a strategic point for both the Axis and Allied forces, given its crucial location over the Grand Canal. In more recent times, the bridge has become a popular site for romantic gestures, with couples attaching padlocks to the railings as a symbol of their love. This practice, however, has raised concerns about the structural impact on the bridge, leading to efforts to discourage it.
Architectural Details
The architectural details of the Ponte dell’Accademia reflect a blend of functionality and aesthetics. The bridge’s arch design allows for the smooth passage of boats underneath, while the use of wood and stone creates a visually pleasing structure that complements the surrounding historic buildings. The bridge’s balustrades and railings are designed to provide safety for pedestrians while offering unobstructed views of the Grand Canal.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the future of the Ponte dell’Accademia involves balancing preservation with modernization. As Venice continues to face challenges related to climate change and rising sea levels, there is an ongoing need to ensure that the bridge can withstand these environmental pressures. Innovative engineering solutions and sustainable materials will play a crucial role in the bridge’s future maintenance and preservation efforts.
FAQ
- What are the visiting hours for Ponte dell’Accademia? The bridge is open 24 hours a day.
- How much do tickets cost for Ponte dell’Accademia? There is no fee to cross the bridge.
- Are guided tours available for Ponte dell’Accademia? While there are no specific guided tours for the bridge, many walking tours of Venice include a stop at the Ponte dell’Accademia.
Conclusion
The history of the Ponte dell’Accademia is a testament to Venice’s enduring commitment to preserving its cultural heritage while adapting to modern needs. From its early conception as an iron bridge to its current incarnation as a hybrid wooden and steel structure, the bridge has evolved to meet the demands of time and usage. Its significance as a cultural landmark and a vital pedestrian link underscores its importance in the fabric of Venetian life. As efforts continue to preserve and maintain the bridge, the Ponte dell’Accademia will undoubtedly remain a cherished symbol of Venice’s architectural and cultural legacy.
References
- Venice Tourism. (n.d.). Ponte dell’Accademia. https://www.veneziaunica.it/en/content/ponte-dellaccademia
- Structurae. (n.d.). Ponte dell’Accademia. https://structurae.net/en/structures/ponte-dell-accademia
- Accademia Gallery. (n.d.). Gallerie dell’Accademia. https://www.gallerieaccademia.it/en
- Peggy Guggenheim Collection. (n.d.). https://www.guggenheim-venice.it/en/