Visiting Eppendorfer Moor: History, Tips, and Visitor Information
Date: 24/07/2024
Introduction
Eppendorfer Moor, located in the bustling city of Hamburg, Germany, is a treasure trove of natural beauty and historical significance. As the largest inner-city moor in Europe, it offers visitors a unique opportunity to immerse themselves in a landscape that has evolved over centuries. The moorland’s formation dates back to the last Ice Age, and it has since become a vital part of Hamburg’s ecological fabric (Wikipedia). Over the years, Eppendorfer Moor has witnessed significant transformations, from medieval urbanization to 19th-century developments, and has survived the impacts of World War II to emerge as a protected nature reserve in 1982 (Wikipedia). Today, it stands as a testament to the importance of urban nature conservation, offering a haven for a diverse array of flora and fauna, including irises, kingfishers, frogs, dragonflies, and bats (Hamburg Travel). Whether you are a nature enthusiast, a history buff, or simply looking for a peaceful retreat from city life, Eppendorfer Moor promises a memorable experience.
Table of Contents
- [History of Eppendorfer Moor](#history-of-eppendorfer-moorhistory-of-eppendorfer-moor)
- [Early History and Formation](#early-history-and-formationearly-history-and-formation)
- [Medieval Period and Urbanization](#medieval-period-and-urbanizationmedieval-period-and-urbanization)
- [19th Century Developments](#19th-century-developments19th-century-developments)
- [Impact of World War II](#impact-of-world-war-iiimpact-of-world-war-ii)
- [Conservation Efforts](#conservation-effortsconservation-efforts)
- [Ecological Significance](#ecological-significanceecological-significance)
- [Visitor Information](#visitor-informationvisitor-information)
- [Visiting Hours](#visiting-hoursvisiting-hours)
- [Tickets and Guided Tours](#tickets-and-guided-tourstickets-and-guided-tours)
- [Travel Tips](#travel-tipstravel-tips)
- [Modern-Day Eppendorfer Moor](#modern-day-eppendorfer-moormodern-day-eppendorfer-moor)
- [FAQ](#faqfaq)
- [Conclusion](#conclusionconclusion)
- [References](#referencesreferences)
History of Eppendorfer Moor
Early History and Formation
Eppendorfer Moor, located in the Hamburg district of Eppendorf, is a significant natural reserve with a rich history dating back to the Middle Ages. The moorland, which is the largest inner-city moor in Europe, was formed after the last Ice Age on a river terrace. This flat moorland, with remnants of raised bogs, is a vestige of the once extensive wet lowlands in the Alster valley (Wikipedia).
Medieval Period and Urbanization
During the medieval period, the increasing urbanization led to the drainage and peat extraction of biologically valuable areas for construction and agricultural use. By 1862, parts of the Eppendorfer Moor were drained to accommodate a shooting range for the Infantry Regiment No. 76. This intervention led to the introduction of trees in the previously treeless moor (Wikipedia).
19th Century Developments
The 19th century marked significant changes for Eppendorfer Moor. As Eppendorf gained popularity among Hamburg’s affluent residents, the low-lying, moist land was banked up and built upon. Despite these developments, the last area of moorland, Eppendorfer Moor, was placed under nature protection in 1982 to preserve its unique ecosystem (Wikipedia).
Impact of World War II
The aftermath of World War II had a profound impact on Eppendorfer Moor. Due to fuel shortages, the birch forest interspersed with willows and alders that had developed by 1945 was almost entirely felled. This deforestation allowed many moor plants to re-establish themselves. However, between 1948 and 1950, reforestation efforts were undertaken to prevent the area from being filled with rubble. The construction of the Alsterkrugchaussee further lowered the groundwater level, causing many light and moisture-loving plants to disappear again (Wikipedia).
Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the ecological significance of Eppendorfer Moor, conservation efforts were intensified in the late 20th century. In 1982, the moor was officially designated as a nature reserve, highlighting its importance as a habitat for various species of flora and fauna. The reserve was expanded from 15 to 26 hectares in January 2015, reinforcing Hamburg’s commitment to urban nature conservation (Wikipedia).
Ecological Significance
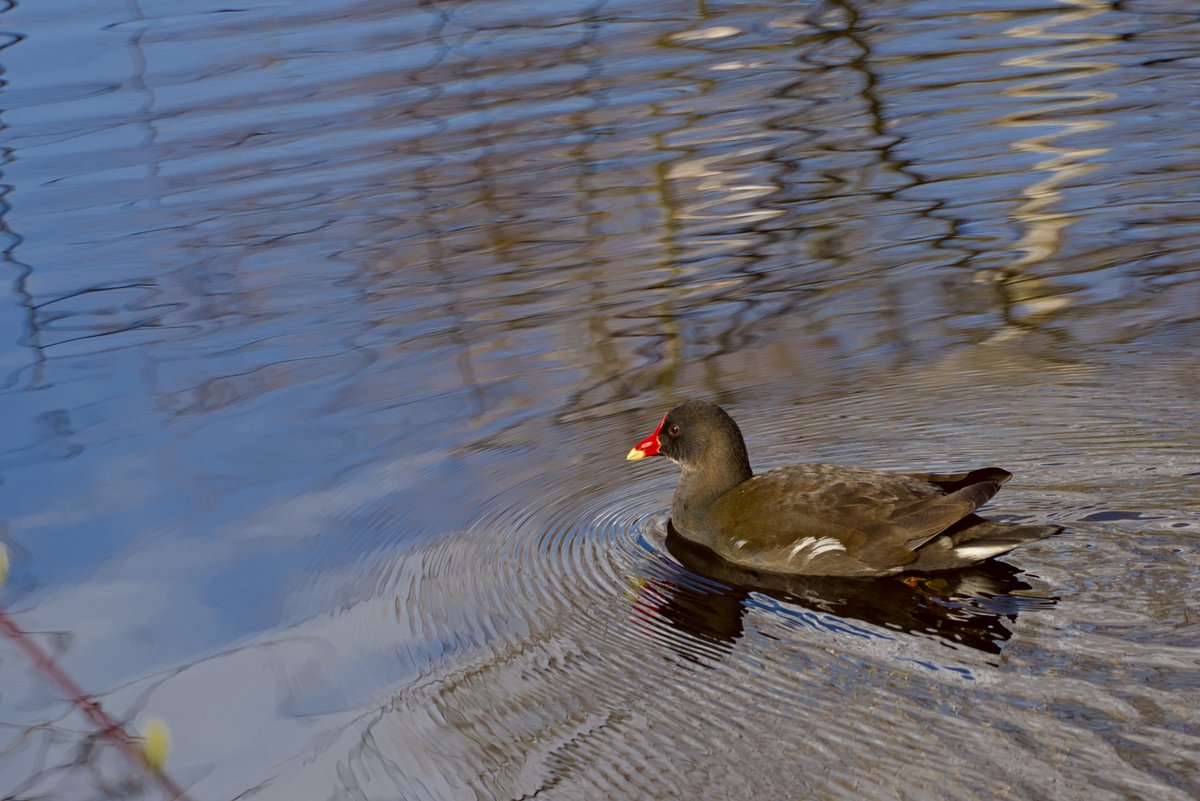
Eppendorfer Moor is a haven for biodiversity, hosting a variety of species including irises, kingfishers, frogs, dragonflies, and bats. The moor’s unique ecosystem supports a range of plant species such as pipe grass and reed beds. Visitors can often spot kingfishers gliding by or observe little grebes in the water, while buzzards or hawks circle overhead (Hamburg Travel).
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours
Eppendorfer Moor is open to visitors year-round. Specific visiting hours may vary depending on the season, so it is recommended to check the official website or local information centers for the most up-to-date hours.
Tickets and Guided Tours
There is no admission fee to visit Eppendorfer Moor, making it an accessible attraction for all. Guided tours are available and offer educational insights into the moor’s ecosystem. It is advisable to book these tours in advance through the official website or local tour operators.
Travel Tips
- Nearby Attractions: While visiting Eppendorfer Moor, consider exploring other nearby attractions such as the Alster River, Hamburg Zoo, and the historic Eppendorf district.
- Accessibility: The moor is accessible by public transport, with several bus and train routes available. The Hamburg CARD provides free travel by bus, train, and harbor ferries, along with up to 50% discounts on over 150 tourist offers, making it convenient for tourists to explore this natural gem (Hamburg Travel).
- What to Bring: Wear comfortable walking shoes and bring a camera to capture the scenic beauty. Binoculars can enhance wildlife viewing experiences.
Modern-Day Eppendorfer Moor
Today, Eppendorfer Moor stands as a testament to the importance of preserving urban green spaces. It offers a peaceful retreat for nature enthusiasts and hikers, providing a green refuge in the midst of the bustling city of Hamburg. The moor is interlaced with walking trails and natural water bodies, each element contributing to the narrative of Hamburg’s dedication to environmental protection (Explorial).
FAQ
- What are the visiting hours for Eppendorfer Moor?
- Visiting hours vary by season. Check the official website for current hours.
- Are there guided tours available at Eppendorfer Moor?
- Yes, guided tours are available and can be booked in advance.
- Is there an admission fee to enter Eppendorfer Moor?
- No, entry is free.
Conclusion
Eppendorfer Moor’s history is a rich tapestry of natural beauty, urban development, and dedicated conservation efforts. Its transformation from a medieval wetland to a protected nature reserve underscores the importance of preserving urban green spaces for future generations. As Hamburg’s oldest nature reserve, Eppendorfer Moor continues to be a vital ecological and recreational asset, inviting visitors to connect with nature and appreciate the city’s commitment to environmental stewardship (Explorial).
References
- Wikipedia (n.d.). Naturschutzgebiet Eppendorfer Moor. Retrieved from https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naturschutzgebiet_Eppendorfer_Moor
- Wikipedia (n.d.). Eppendorf, Hamburg. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eppendorf,_Hamburg
- Hamburg Travel (n.d.). Eppendorfer Moor. Retrieved from https://www.hamburg-travel.com/see-explore/green-hamburg/parks-green-spaces/eppendorfer-moor/
- Explorial (n.d.). Discovering 5 Hidden Gems of Hamburg. Retrieved from https://explorial.com/discovering-5-hidden-gems-of-hamburg/