Yerevan Lake Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Guide to Yerevan Historical Sites
Date: 03/07/2025
Introduction to Yerevan Lake and Its Significance
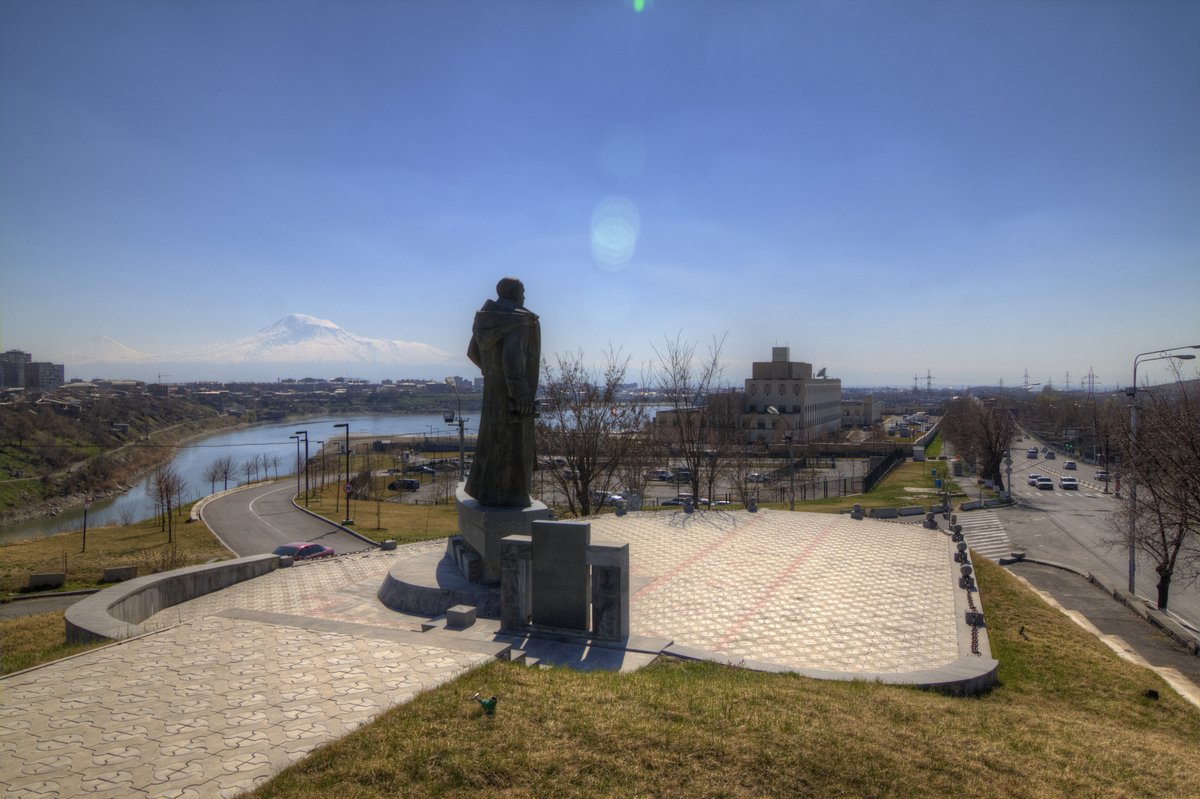
Yerevan Lake, an artificial reservoir at the heart of Armenia’s capital, serves as a dynamic urban oasis that merges history, ecology, and recreation. Built between 1963 and 1970 during the Soviet era, this 0.65-square-kilometer lake was designed for water storage, irrigation, and flood management along the Hrazdan River. Over the decades, it has become a beloved landmark symbolizing Armenia’s transformation from Soviet industrialization to modern urban renewal, ecological stewardship, and community engagement (Oneway Tour; armenpress.am).
Yerevan Lake not only enhances the city’s landscape with its parks and accessible pathways but also supports biodiversity, plays a vital role in water supply, and contributes to climate adaptation strategies through international collaborations (geographypin.com; futurehubs.eu). Whether you’re interested in tranquil strolls, cultural festivals, or learning about urban sustainability, Yerevan Lake epitomizes the convergence of nature, history, and modern city life.
Table of Contents
- Discover Yerevan Lake: Urban Oasis in Armenia’s Capital
- Origins and Construction
- Historical Significance and Notable Events
- Urban and Environmental Impact
- Cultural and Social Role
- Visiting Yerevan Lake: Hours, Tickets, and Accessibility
- Environmental Management and Challenges
- Recreation and Visitor Information
- Economic Impact and Urban Renewal
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Plan Your Visit
- References
Discover Yerevan Lake: Urban Oasis in Armenia’s Capital
Yerevan Lake, also called Yerevani Tzov, is a distinctive artificial reservoir embedded in the city’s landscape. It offers visitors a blend of historical intrigue, scenic beauty, and recreational amenities, making it a must-visit site for anyone wishing to explore Yerevan’s culture and natural environment.
Origins and Construction
Yerevan Lake was established as part of a Soviet-era initiative to modernize Yerevan’s infrastructure, with construction spanning from 1963 to 1970. The project required the relocation of the Nor Koghb village and involved damming the Hrazdan River. The lake covers 0.65 km², reaches depths of up to 18 meters, and holds approximately 6.9 million cubic meters of water (Hike Armenia). Its primary purposes include irrigation, urban water supply, and flood control—functions vital to the city’s semi-arid climate.
Historical Significance and Notable Events
Yerevan Lake has witnessed both engineering feats and remarkable human stories. In 1976, champion finswimmer Shavarsh Karapetyan became a national hero by rescuing 20 passengers from a submerged trolleybus, an event that has become legendary in Armenian culture (Hike Armenia). When water levels drop, remnants of an ancient bridge from the old Nor Koghb village emerge, physically linking the site’s present and past (Oneway Tour).
Urban and Environmental Impact
The lake influences Yerevan’s microclimate by providing cooling during hot months and improving air quality. Its creation significantly shaped urban planning, integrating green and blue spaces into the city’s design. Recent revitalization efforts have improved ecological health and recreational infrastructure, with the introduction of modern parks, walking and cycling paths, and pollution control measures (Oneway Tour).
Cultural and Social Role
Yerevan Lake is a thriving community hub. Landscaped gardens, playgrounds, and open-air seating attract families, joggers, and nature enthusiasts. The area is a popular venue for festivals and environmental education programs. Its proximity to major sites like Erebuni Fortress and the Ararat Brandy Factory enriches the cultural experience for visitors (Oneway Tour).
Visiting Yerevan Lake: Hours, Tickets, and Accessibility
- Visiting Hours: Open daily from 6:00 AM to 10:00 PM, offering ample time for morning walks or evening strolls.
- Entry: Access to the lake and surrounding parks is free of charge. Some special events or festivals may require tickets (yerevan.am).
- Accessibility: The park features wheelchair-accessible paths, ramps, and visitor support upon request.
- Transportation: Easily reached by public buses, taxis, cycling paths, and pedestrian walkways. Parking is available near main entrances.
Best Time to Visit: March through early autumn is ideal, with mild weather and seasonal festivals (Oneway Tour).
Tip: Bring comfortable shoes, sun protection, and a camera—swimming is prohibited for safety and water quality reasons.
Environmental Management and Challenges
Hydrology and Water Management
Yerevan Lake covers 0.65 km², reaches a depth of up to 18 meters, and stores up to 4.8 million m³ of water. It is fed by the Hrazdan River and four feeder canals, supplying about 30% of the city’s potable water and irrigating the Ararat Plain (geographypin.com).
Pollution Control and Ecology
The lake faces challenges from urban runoff, siltation, and pollutants. Ongoing restoration—such as improved wastewater management and educational initiatives—aims to preserve ecosystem health (geographypin.com). Hydroelectric turbines installed at the dam provide clean energy, supporting both the municipal grid and local industries.
Biodiversity and Sustainability
Thermal stratification supports diverse aquatic life, and citizen science projects foster community stewardship. The lake is internationally recognized for its integrated watershed management and climate adaptation strategies (rec-caucasus.am, sczhe.sci.am).
Ongoing Challenges
- Pollution from runoff and illegal dumping
- Climate change impacts on water security
- Infrastructure maintenance in a seismic zone
- Balancing water supply, irrigation, recreation, and energy needs (geographypin.com)
Recreation and Visitor Information
- Parks & Activities: Over 15 hectares of landscaped parks, jogging and cycling promenades, playgrounds, picnic areas, and boat rentals.
- Events: Annual festivals such as Yerevan LakeFest, live music, and artisan bazaars.
- Guided Tours: Offered seasonally; book in advance, especially for ecological or historical tours.
- Family-Friendly: Safe, accessible, and offering amenities for all ages.
- Nearby Attractions: Erebuni Fortress, Armenian Genocide Memorial, and Matenadaran Manuscript Library within 10 km.
Environmental Education: Informative signage and volunteer events promote environmental awareness.
Economic Impact and Urban Renewal
Tourism and Local Economy
The revitalization of Yerevan Lake enhances the city’s tourism appeal and supports local businesses, including cafes, restaurants, and tour operators. Tourism around the lake contributes to the broader city economy (futurehubs.eu).
Infrastructure and Community Benefits
Urban renewal projects have improved transport, utilities, and public spaces. Collaborations with international organizations ensure sustainable development and boost employment in maintenance and hospitality services (armenpress.am; thetourism.institute).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are Yerevan Lake’s visiting hours?
A: Open daily from 6:00 AM to 10:00 PM.
Q: Is there an entry fee?
A: No, access is free; some events may require tickets.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, especially in summer—book ahead for specialized tours.
Q: Is the lake area accessible for people with disabilities?
A: Yes, with ramps and paved paths.
Q: How do I get there using public transport?
A: Multiple bus and minibus routes stop near the lake; taxis and walking from the city center are also convenient.
Q: Are pets allowed?
A: Yes, but pets must be leashed and owners should clean up after them.
Plan Your Visit
Yerevan Lake is an essential destination for locals and visitors—offering relaxation, recreation, and cultural enrichment. For up-to-date visitor information, events, and interactive maps, download the Audiala app and follow official tourism channels.
Visitor Tips:
- Respect posted guidelines and participate in stewardship events.
- Support local businesses and enjoy the diverse culinary offerings.
- Check weather and event updates before your visit.
References
- Oneway Tour
- ADB Project Documentation
- armenpress.am
- futurehubs.eu
- geographypin.com
- rec-caucasus.am
- sczhe.sci.am
- thetourism.institute
- yerevan.am
- Hike Armenia
Yerevan Lake stands as a symbol of resilience and renewal, blending natural beauty with urban vibrancy. Plan your visit to experience this unique fusion of history, community, and sustainability in the heart of Armenia’s capital.