BT Tower Birmingham: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Significance Guide
Date: 03/07/2025
Introduction
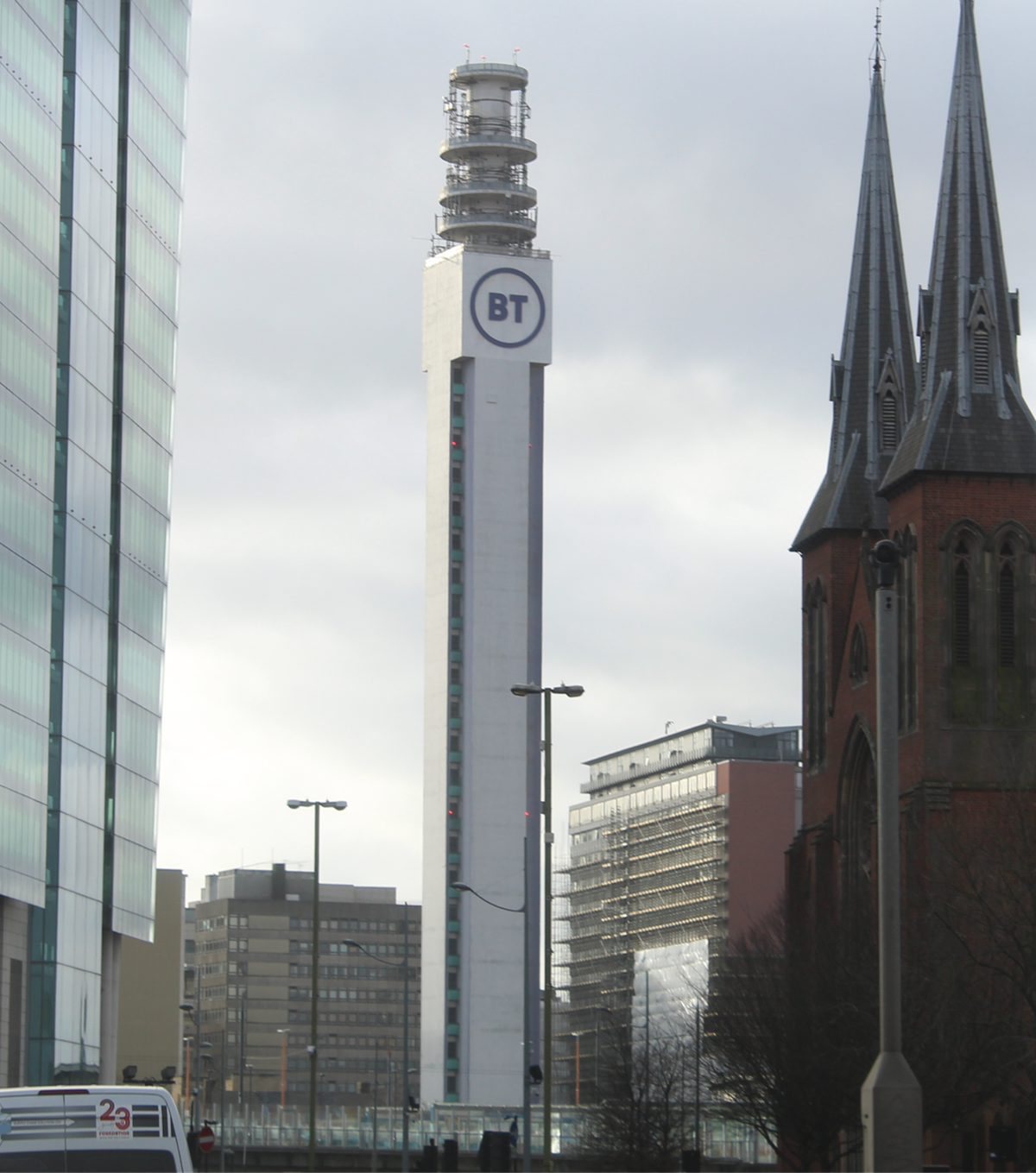
The BT Tower in Birmingham stands as a symbol of the city’s post-war modernization and telecommunications heritage. Constructed in the 1960s and opened in 1967, this 152-meter Grade II listed landmark not only transformed the Birmingham skyline but also played a pivotal role in the UK’s communications network. While public access is generally restricted, the tower continues to captivate locals and visitors with its architectural presence and historical importance. This comprehensive guide covers the BT Tower’s history, architectural features, visiting information, and its enduring significance within Birmingham’s urban landscape. (Historic England; Birmingham Mail; Triphobo)
Table of Contents
- Historical Background
- Architectural Features
- Visiting Information
- Community and Cultural Significance
- Maintenance, Upgrades & the Changing Skyline
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion and Visitor Tips
- Sources
Historical Background
Origins and Purpose
Commissioned in the early 1960s, the BT Tower was built by the General Post Office (GPO) to serve as a central node in the UK’s microwave telecommunications network. Its primary function was to relay telephone and television signals, connecting Birmingham to the national grid during a period of rapid technological advancement. The choice of a tall, unobstructed site in Birmingham’s city center was essential for effective line-of-sight microwave transmission.
Construction and Timeline
Construction began in 1963 and was completed in 1965, with the tower officially opening in 1967. Upon completion, it was the tallest structure in Birmingham, quickly becoming an emblem of the city’s ambitions and technological progress (Skyscraper News).
Development Role
The BT Tower’s emergence paralleled Birmingham’s urban renewal in the mid-20th century. As a hub for telecommunications, it played a crucial role in supporting the city’s commercial growth and connected Birmingham to the broader UK and international networks.
Historical Significance
The tower has adapted through the decades, shifting from analog microwave relays to digital communications. Its Grade II listed status ensures the preservation of its architectural and historic value (Historic England).
Architectural Features
Design and Structure
Designed in a modernist style, the BT Tower’s slender cylindrical form rises to 152 meters (499 feet). Constructed primarily from reinforced concrete, the tower’s shape and materials were chosen for durability, stability, and wind resistance. The design includes a series of platforms for microwave dishes and telecommunications equipment.
Engineering Highlights
The tower’s slip-form construction allowed for efficient, continuous concrete pouring, creating a robust, seamless structure. Foundations are deeply anchored for stability. The internal core houses elevators and stairwells, ensuring efficient vertical access for authorized personnel.
Adaptations and Upgrades
Over time, the original microwave dishes have been replaced or removed, as fiber optic and satellite technology became dominant. Upgrades have kept the tower operationally relevant, with modernized internal systems and lighting schemes that illuminate the structure at night.
Preservation and Heritage Status
As a Grade II listed building, any alterations to the BT Tower are strictly regulated. Its preservation reflects recognition of its architectural and technological contributions to Birmingham.
Place Within the City Skyline
The BT Tower was Birmingham’s tallest structure for decades and remains one of its most recognizable landmarks, even as new skyscrapers redefine the city’s silhouette (Express & Star).
Visiting Information
Visiting Hours & Tickets
Public Access:
The BT Tower Birmingham is not open for regular public tours due to its operational status and security restrictions. There are no standard visiting hours or tickets.
Special Events:
Occasionally, the tower may participate in special events such as Birmingham Heritage Week, when limited guided tours are offered. These are rare and require advance booking via event organizers (Birmingham Heritage Week).
Accessibility & Transport
- Location: 1 St. Chad’s Queensway, Birmingham B4 6AU, United Kingdom.
- Nearest stations: Birmingham Snow Hill and Birmingham New Street (both within walking distance) (National Rail).
- Buses: Multiple routes stop nearby (Colmore Row, Corporation Street).
- Parking: Nearby options include Snow Hill Car Park and NCP Birmingham High Street (NCP Birmingham). Public transport is recommended.
Viewing Locations & Photography
While interior access is restricted, the BT Tower can be admired and photographed from various vantage points:
- St. Paul’s Square (sunset views)
- Snow Hill Station Forecourt (full tower perspective)
- Colmore Row & Livery Street (urban backdrops)
- Jewellery Quarter (contrasts with historic architecture)
The tower is especially photogenic at dusk when illuminated in blue and white. Use a tripod for night photography (Birmingham Mail).
Nearby Attractions
- Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery
- Library of Birmingham
- Jewellery Quarter
- National Sea Life Centre
- Symphony Hall
- Bullring Shopping Centre
All are accessible on foot or by public transport (Triphobo).
Community and Cultural Significance
The BT Tower remains a beloved symbol of Birmingham’s resilience and modernity. It serves as a navigational landmark, features in local branding, and has hosted peregrine falcons with a live webcam for public viewing (ICE; Wikipedia). Community events and illuminations further embed the tower into Birmingham’s cultural life.
Maintenance, Upgrades & the Changing Skyline
Recent refurbishment (2020–2022) ensured operational reliability and removed obsolete equipment (Wikipedia). While new skyscrapers have surpassed its height, the BT Tower remains a defining feature of the city (Birmingham World; Westside BID; BBC News).
BT has confirmed there are no plans to decommission or repurpose the tower, maintaining its strategic importance for regional connectivity (Birmingham Mail).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I visit the BT Tower Birmingham?
No, public access is not available except during infrequent special events.
Are tickets required for the BT Tower?
Not for general visits. Tickets may be needed for special guided tours during events.
Where are the best places to view the BT Tower?
Recommended spots include St. Paul’s Square, Snow Hill Station, Colmore Row, and the Jewellery Quarter.
Is the BT Tower accessible for people with disabilities?
The surrounding area is accessible, but the tower itself has limited accessibility and is closed to the public.
What is the tower’s role today?
It continues as an active telecommunications hub, supporting regional network connectivity.
Conclusion and Visitor Tips
Though not open for regular tours, the BT Tower remains an essential part of Birmingham’s cityscape and technological heritage. Admire its architecture from public spaces and include nearby attractions in your visit. Stay updated on potential special events through official channels and local heritage organizations.
Download the Audiala app for the latest on Birmingham’s landmarks, visiting hours, and exclusive event announcements. Follow us on social media for updates, photo contests, and more.
Sources
- Historic England
- Birmingham Mail
- Triphobo
- ICE
- Express & Star
- Klook
- Wikipedia
- Birmingham World
- Westside BID
- BBC News