Polcevera Viaduct Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Guide to Genoa Historical Sites
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction to the Polcevera Viaduct and Its Significance in Genoa
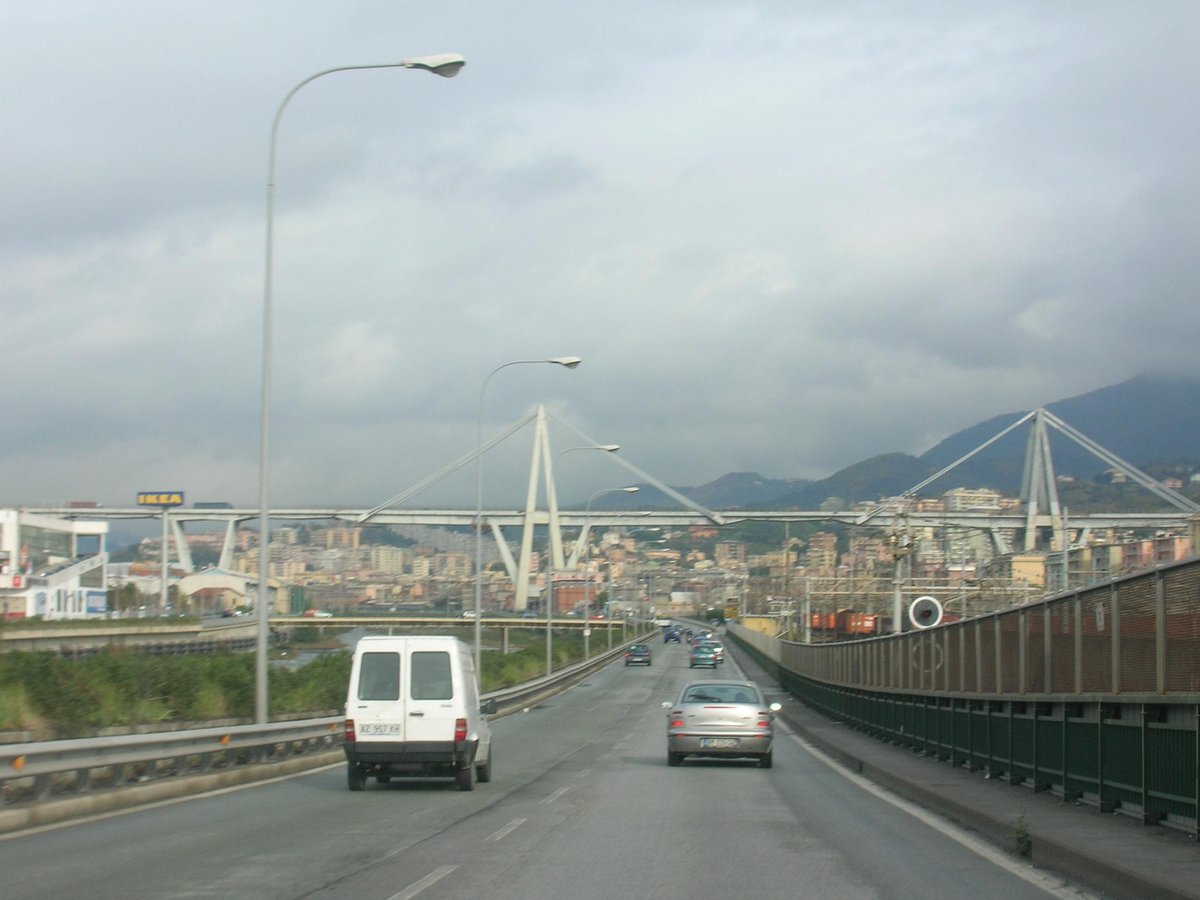
The Polcevera Viaduct—historically known as the Morandi Bridge—has long represented engineering prowess and urban connectivity for Genoa, Italy. Conceived in the 1960s by the distinguished engineer Riccardo Morandi, the original bridge was an emblem of Genoa’s industrial optimism, linking the A10 and A7 motorways across the Polcevera Valley. Its use of prestressed concrete and its striking design made it a landmark of modern infrastructure.
However, on August 14, 2018, a catastrophic collapse resulted in 43 fatalities, prompting national reflection on infrastructure safety. In the wake of this tragedy, Genoa embarked on an ambitious project to rebuild, culminating with the Genoa San Giorgio Bridge, designed by renowned architect Renzo Piano. The new structure not only restored a vital transport artery but also set new standards in sustainability, technological innovation, and civic renewal.
This comprehensive guide offers an in-depth look at the history and legacy of the Polcevera Viaduct, its reconstruction, and its ongoing significance. You’ll also find practical visitor information, including visiting hours, ticketing, accessibility, and highlights of nearby Genoa historical sites.
For a deeper dive into the bridge’s design and reconstruction, refer to these resources:
- [Polcevera Viaduct history and visitor information](#polcevera-viaduct-history-and-visitor-information)
- [Genoa San Giorgio Bridge engineering and sustainability](#genoa-san-giorgio-bridge-engineering-and-sustainability)
- [Social and economic impact of the reconstruction](#social-and-economic-impact-of-the-reconstruction)
Contents Overview
- Introduction
- Origins and Design of the Polcevera Viaduct
- Engineering Innovations and Challenges
- Role in Genoa’s Urban and Economic Development
- Maintenance, Warnings, and Structural Concerns
- The 2018 Collapse and Its Aftermath
- Legacy and Replacement
- Visiting the Polcevera Viaduct Site and Genoa Historical Sites
- Architectural Vision and Symbolism of the Genoa San Giorgio Bridge
- Technological Innovation and Sustainability
- Practical Visitor Information (Hours, Tickets, Accessibility)
- Nearby Attractions
- Social, Economic, and Cultural Impact
- Sustainability and Future Developments
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Summary and Visitor Recommendations
- Sources
Origins and Design of the Polcevera Viaduct
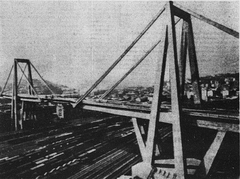
The Polcevera Viaduct was designed in the early 1960s to address Genoa’s growing transportation needs. Riccardo Morandi’s innovative cable-stayed structure, completed in 1967, connected two crucial motorways and enhanced the movement of goods and people throughout the city. Its 1,182-meter span and 90-meter-high concrete pylons made it a defining feature of Genoa’s skyline.
Morandi’s use of prestressed concrete encasing steel cables was considered revolutionary for the era, combining structural strength with aesthetic appeal. The bridge quickly became an icon of postwar Italian engineering.
Engineering Challenges and Maintenance
Constructed in a dense urban setting, the bridge spanned rivers, railways, and industrial districts. Over time, design limitations—such as limited prestressing and a single-cable system per span—made the structure vulnerable to environmental stresses. Despite ongoing maintenance, expert warnings about potential weaknesses were not fully addressed, in part to preserve its iconic silhouette.
The 2018 Collapse and Its Aftermath
On August 14, 2018, during a heavy rainstorm, a portion of the bridge collapsed, causing tragic loss of life and disrupting the city’s transport and economy (italiaguida.it). The disaster underscored the critical importance of infrastructure maintenance and prompted a national call to action.
Legacy and the Genoa San Giorgio Bridge
In response, Genoa rapidly initiated the construction of a replacement: the Genoa San Giorgio Bridge, designed by Renzo Piano. Opened in August 2020, the new bridge incorporates advanced engineering solutions for durability, safety, and sustainability. Its swift construction—less than two years—demonstrated Italian resilience and ingenuity (italiaguida.it; webuildgroup.com).
Visiting the Polcevera Viaduct Site and Genoa Historical Sites
Visiting Hours and Tickets
- Bridge Access: The Genoa San Giorgio Bridge is a motorway bridge; pedestrian access is restricted for safety. No tickets are required for vehicular passage.
- Polcevera Park and Red Circle: The surrounding Polcevera Park and Red Circle walkway are open to the public daily, typically from 7:00 AM to 10:00 PM. Entrance is free.
Guided Tours and Special Events
Seasonal guided tours of Polcevera Park and memorial spaces are available through local operators. Special events, especially around the August 14 anniversary, offer opportunities for deeper engagement with the site’s history and redevelopment efforts.
Accessibility
The park and walkway are fully accessible for all visitors, with ramps, elevators, and multilingual signage. Public transport options (bus and train) serve the area well, and parking is available nearby.
Photography Tips
The park and walkway offer excellent vantage points for panoramic shots of the bridge and city skyline. Early morning or late afternoon provides the best light. Please be respectful in memorial areas.
Architectural Vision and Symbolism
Renzo Piano’s design for the San Giorgio Bridge pays tribute to Genoa’s maritime heritage. The bridge’s sleek, ship-like profile and reflective white steel cladding evoke a sense of harmony with the surrounding landscape (RPBW). Eighteen slender piers support a 1,067-meter span, creating an impression of lightness and transparency.
Technological Innovation and Sustainability
The bridge incorporates cutting-edge technology, including:
- Intelligent Monitoring: Sensors and robotic systems continuously monitor structural health (Engineering.com). Specialized robots inspect and maintain the bridge, ensuring safety and longevity.
- Sustainable Features: Solar panels power lighting and monitoring systems, making the bridge energy-efficient (RPBW). The surrounding park is 100% carbon neutral, powered by renewable sources, and features permeable surfaces for rainwater management (investingenova.com).
What to See and Do
The Genoa San Giorgio Bridge
Admire the bridge’s architecture from Polcevera Park, the Red Circle walkway, and nearby hills. While you cannot walk across the bridge, several overlooks provide excellent photo opportunities.
Polcevera Park and the Red Circle
Covering 23 hectares, Polcevera Park offers gardens, sports and wellness areas, and the innovative Red Circle walkway—a 1,570-meter elevated path for pedestrians and cyclists. The park also features the Conservatory of Mediterranean Biodiversity and memorials commemorating the 43 victims of the 2018 collapse (investingenova.com).
Memorials and Art Installations
Memorial gardens with 43 tree species—one for each victim—offer spaces for reflection. Art installations and the “Clearing of Memory” further honor those lost and promote community healing.
Sustainable Urban Design
The park’s design by Stefano Boeri and the Inside Outside studio emphasizes ecological renewal and urban connectivity, featuring renewable energy sources, green infrastructure, and inclusive public spaces (investingenova.com).
Practical Visitor Information
- Getting There: Easily accessible via bus, train, and car. Public transportation is recommended due to limited parking.
- Facilities: Park amenities include information points, rest areas, playgrounds, sports facilities, bike-sharing, and EV charging stations.
- Safety: The park is well-lit and regularly patrolled. Visitors are encouraged to respect memorial areas and follow local health guidelines.
Nearby Genoa Historical Sites
While in the area, consider visiting:
- Porto Antico (Old Port): Genoa’s lively harbor area with museums, restaurants, and the aquarium.
- Via Garibaldi: Lined with Renaissance palaces.
- San Lorenzo Cathedral: The city’s historic cathedral.
- Other Sites: The Polcevera Valley’s regeneration projects and various museums and gardens (visitgenoa.it).
Social, Economic, and Cultural Impact
Social Impact
The collapse and reconstruction of the bridge deeply affected Genoa and Italy, triggering national mourning and debate about infrastructure safety. The transparent, rapid rebuilding process fostered community involvement, public pride, and educational opportunities (Geco Expo).
Economic Impact
Restoring this critical transport artery quickly was essential for Genoa’s port, regional logistics, and the broader economy. The project supported over 1,000 jobs and involved more than 300 companies, demonstrating the economic multiplier effect of major infrastructure (webuildgroup.com).
Cultural and Architectural Renewal
The new bridge honors Genoa’s engineering heritage while setting benchmarks in sustainability. The area’s redevelopment is transforming a site of tragedy into a vibrant, inclusive urban space that celebrates the city’s resilience (Domus).
Sustainability and Future Developments
Polcevera Park and the Red Circle are ongoing projects, with more amenities and green spaces opening in phases. The initiative is recognized by UNESCO as one of the world’s leading urban renewal projects started in 2020, blending remembrance, recreation, and innovation (investingenova.com).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I walk across the Genoa San Giorgio Bridge?
A: No. Pedestrian access is not permitted on the bridge itself.
Q: When is Polcevera Park open, and is there an entry fee?
A: The park and Red Circle walkway are open daily from 7:00 AM to 10:00 PM. Access is free.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, guided tours are available seasonally and can be booked in advance through local operators.
Q: Is the area accessible for disabled visitors?
A: Yes, all public areas are fully accessible.
Q: What are the best spots for photography?
A: The Red Circle walkway, Polcevera Park, and surrounding hills offer excellent views—visit early or late in the day for optimal lighting.
Summary and Visitor Recommendations
The story of the Polcevera Viaduct and its successor, the Genoa San Giorgio Bridge, illustrates Genoa’s journey from tragedy to renewal. The original Morandi Bridge’s innovative engineering, the devastating collapse, and the rapid, transparent reconstruction under Renzo Piano’s guidance represent a model of civic resilience and sustainable urban development.
Today, the bridge and its environs offer not only a vital transportation link but also a living memorial and a hub for community, recreation, and learning. Visitors can engage with Genoa’s layered history through accessible parks, thoughtful memorials, and guided experiences that highlight the city’s enduring spirit.
For up-to-date visitor information, guided tour schedules, and local events:
Enhance your visit with interactive guides in the Audiala app, and share your experience to celebrate Genoa’s heritage and innovation.
Sources and Further Reading
- Polcevera Viaduct (Morandi Bridge) History, Visitor Info, and Genoa Historical Sites Guide, 2025
- Genoa San Giorgio Bridge: Visitor Guide, History, and Architectural Marvel, 2025
- Genoa San Giorgio Bridge: History, Visitor Information, and Cultural Significance, 2025
- Polcevera Viaduct Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Guide to Genoa’s Historical Sites, 2025
- Official Genoa Tourism Website, 2025