Temple of Taharqa, Luxor, Egypt: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Travel Guide
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
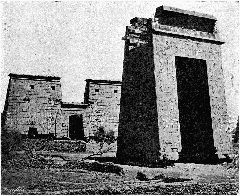
The Temple of Taharqa, also known as the Kiosk of Taharqa, is an iconic monument within the renowned Karnak Temple Complex in Luxor, Egypt. Erected during the reign of Pharaoh Taharqa of the 25th Dynasty (690–664 BCE), the structure is a testament to the profound Nubian influence on Egyptian architecture, religion, and culture. This comprehensive guide explores the temple’s historical significance, architectural features, archaeological discoveries, preservation challenges, and provides essential visitor information including hours, ticketing, accessibility, and travel tips.
Table of Contents
- Historical Background of the Temple of Taharqa
- Archaeological Discoveries and Excavation History
- Preservation Efforts and Challenges
- Visitor Information
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
- References
Historical Background of the Temple of Taharqa
Origins and Historical Context
Pharaoh Taharqa, a distinguished ruler of the 25th Dynasty — also known as the Kushite or Nubian Dynasty — rose to power during a period of political fragmentation in Egypt. Hailing from Nubia (modern-day Sudan), Taharqa sought to unify Egypt and legitimize his reign by embracing and restoring ancient Egyptian religious traditions. His architectural legacy includes monumental projects at Karnak, Jebel Barkal, and Kawa, reflecting both his piety and his strategic efforts to reinforce political authority (worldhistoryedu.com).
Significance in Ancient Egyptian History
The construction of the Kiosk of Taharqa at Karnak reflects the broader objectives of the 25th Dynasty: religious revival, political consolidation, and cultural integration. Situated at Egypt’s most significant religious complex, the kiosk was designed as a ceremonial station for the sacred barque of Amun during the annual Opet Festival, a key event that reinforced the divine status of the pharaoh and the unity of the Egyptian state (egypttourslovers.com). Its continued use and restoration by later rulers, including Ptolemy IV, underscore its enduring ceremonial and religious importance (arabamerica.com).
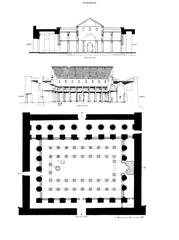
Architectural Features
The Kiosk of Taharqa is a remarkable hypostyle pavilion, originally featuring ten colossal papyrus-bundle columns, each standing approximately 21 meters high. The capitals, shaped like papyrus plants, symbolize rebirth and the fertility of the Nile. The open design allowed for ceremonial processions and public rituals, while the reliefs and inscriptions depicted Taharqa’s offerings to Amun and celebrated his divine favor (historytools.org, egypttourslovers.com).
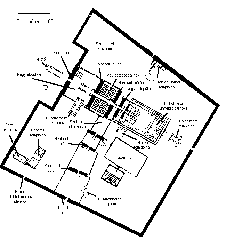
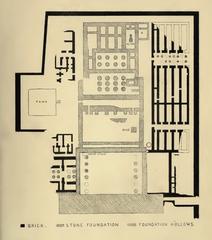
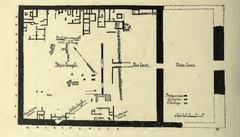
Role within the Karnak Temple Complex
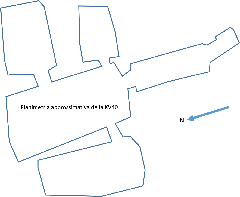
The kiosk occupies a prominent position in the First Court, just beyond the First Pylon of the Karnak Temple Complex. This placement underscores its function in processional rites, serving as the link between the outer public spaces and the inner sanctuaries. Its strategic alignment on the sacred axis connected the temple with the Nile, integrating riverine rituals into the temple’s religious life (historytools.org).
Cultural and Religious Symbolism
The use of papyrus columns and open architecture evokes the mythological marshes of creation, symbolizing renewal and cosmic order. Taharqa’s patronage at Karnak furthered the fusion of Nubian and Egyptian traditions, fostering a renaissance in temple building, religious festivals, and artistic innovation (worldhistoryedu.com).
Legacy and Preservation
Despite centuries of change, the Kiosk of Taharqa endures as a symbol of Nubian-Egyptian integration and religious continuity. Successive rulers restored and preserved the structure, demonstrating the temple’s deep-rooted significance in Egyptian culture (egypttourslovers.com). Today, the kiosk is a focal point for visitors, scholars, and conservationists, reflecting the complex interplay of politics, spirituality, and artistry in ancient Egypt (historytools.org).
Archaeological Discoveries and Excavation History
Rediscovery and Early Excavations
Systematic excavations of the Luxor and Karnak complexes began in the late 19th century. French Egyptologist Gaston Maspero’s work in the 1880s was pivotal, removing centuries of debris and uncovering the grandeur of the Taharqa court (egypt-uncovered.com). These early efforts revealed layers of occupation and construction spanning millennia.
Recent Advances and Notable Finds
Modern archaeological missions, utilizing advanced imaging technologies, have continued to unearth new architectural fragments, inscribed blocks, and ceremonial objects. Notable finds include over 1,500 decorated limestone blocks and more than 100 royal stone tablets, many bearing Taharqa’s cartouche (egyptindependent.com). These discoveries have deepened our understanding of temple life, religious rituals, and the integration of Nubian and Egyptian styles (ancientengineeringmarvels.com).
Artifacts such as ritual vessels and amulets provide insight into daily activity and ceremonial practices, while ongoing conservation ensures the preservation of these finds for future study (eztouregypt.com).
Preservation Efforts and Challenges
Environmental and Human Threats
The temple’s proximity to the Nile exposes it to flooding, while Luxor’s harsh climate accelerates the decay of stone surfaces and pigments. Urban expansion and heavy tourist traffic further threaten the monument’s integrity (ancientengineeringmarvels.com, egyptmythology.com).
Modern Conservation Techniques
Conservation teams employ laser cleaning, digital mapping, and environmental monitoring to address these threats. Restoration prioritizes the use of local materials and traditional methods, with barriers and controlled pathways limiting direct contact and reducing wear (ancientengineeringmarvels.com).
International Collaboration and UNESCO Status
Since its designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979, the site has benefitted from international collaboration and funding. Ongoing educational initiatives foster community engagement and promote a culture of heritage stewardship (myancientegypt.com, ancientengineeringmarvels.com).
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours & Ticketing
- Karnak Temple Complex (including the Kiosk of Taharqa): Open daily from 6:00 AM to 5:00 PM; hours may extend to 10:00 PM during special events or summer.
- Tickets: General admission for foreign tourists is approximately 150–160 EGP. Discounts for students and Egyptian nationals are available. Tickets can be purchased onsite or online via official tourism platforms (eztouregypt.com).
Accessibility
Efforts have been made to improve accessibility, including ramps and designated pathways. Some areas remain uneven, so visitors with mobility challenges may require assistance. Facilities such as restrooms and shaded rest areas are available near the entrance.
Guided Tours & Travel Tips
- Guided Tours: Highly recommended for historical context; available in multiple languages.
- Best Time to Visit: October to April (cooler months). Early morning or late afternoon offers pleasant temperatures and the best light for photography.
- Tips: Bring water, sun protection, and comfortable shoes. Follow conservation etiquette by respecting barriers and avoiding contact with ancient stonework.
Nearby Attractions
Enhance your visit by exploring:
- Luxor Temple
- Valley of the Kings
- Temple of Hatshepsut
- Luxor Museum
- Abu Haggag Mosque (within the Luxor Temple complex)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the visiting hours for the Temple of Taharqa?
A: Open daily from 6:00 AM to 5:00 PM; hours may extend during certain periods.
Q: How much do tickets cost?
A: Approximately 150–160 EGP for foreign tourists, with discounts for students and locals.
Q: Is the Temple of Taharqa accessible for visitors with disabilities?
A: Ramps and designated paths are available, but some uneven terrain may require assistance.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, guided tours are widely available and recommended.
Q: What other historical sites are nearby?
A: Karnak Temple, Luxor Temple, Valley of the Kings, Temple of Hatshepsut, and the Luxor Museum.
Conclusion
The Temple of Taharqa stands as a monumental testament to the fusion of Nubian and Egyptian traditions, offering a window into the religious, political, and artistic life of the 25th Dynasty. Its architectural grandeur, archaeological significance, and ongoing preservation make it an essential destination for travelers in Luxor. By planning your visit around recommended hours, ticketing, and guided tours, you will gain a deeper appreciation for this remarkable site and its role in Egypt’s enduring cultural legacy.
For the latest travel tips, interactive maps, and expert audio guides, download the Audiala app. Follow us on social media to stay updated on Egypt’s historical treasures and visitor experiences.
References
- Pharaoh Taharqa, World History Edu
- Historical Significance of Karnak’s Temple, Arab America
- Karnak Temple Complex Overview, Egypt Tours Lovers
- Karnak Temple Insights, History Tools
- Must-Visit Attractions in Luxor, Food and Travel Utsav
- Karnak Temple Guide, Earth Trekkers
- Luxor Temple Facts and History, The World Travel Guy
- Luxor Temple Visitor Guide, Paliparan
- Luxor Temple Archaeological Discoveries, Egypt Independent
- The Luxor Temple, Ancient Engineering Marvels
- Luxor Temple Visitor Information, EZ Tour Egypt
- Luxor Temple Preservation and Community Engagement, Egypt Uncovered
- Luxor Temple Spiritual Legacy, Spiritual Divine Insight