Imperial Cult Chapel Luxor Egypt: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Sites Guide
Date: 03/07/2025
Introduction
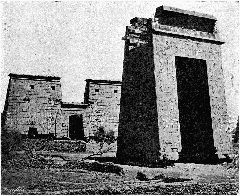
Nestled on the east bank of the Nile in Luxor, the Imperial Cult Chapel within the Luxor Temple complex stands as a vivid intersection of ancient Egyptian tradition and Roman imperial authority. Originally dedicated to the goddess Mut, this chapel was transformed in the late 3rd and early 4th centuries CE by Roman architects into a center for the Imperial Cult—venerating Roman emperors as divine figures. Today, the chapel is celebrated for its rare fusion of Egyptian and Roman architectural features, as well as for its frescoes depicting emperors in pharaonic guise. The story of the Imperial Cult Chapel is one of religious, political, and artistic transformation, reflecting Egypt’s layered spiritual and administrative history across pharaonic, Roman, Christian, and Islamic eras.
This guide provides detailed visitor information—including visiting hours, ticketing, accessibility, and travel tips—alongside historical context and practical recommendations to help you explore one of Luxor’s most compelling archaeological treasures (Wikipedia, Academia.edu, madainproject.com).
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Origins and Transformation of Luxor Temple and the Imperial Cult Chapel
- Roman Adaptation: Architecture and Function
- Religious Shifts: From Egyptian Deities to Imperial Cult and Beyond
- Artistic and Ritual Highlights
- Preservation and Archaeological Legacy
- Visiting Guide: Hours, Tickets, Accessibility, and Travel Tips
- Navigating Luxor Temple and the Imperial Cult Chapel
- Guided Tours and Visitor Experience
- Practical Tips and Facilities
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
- References
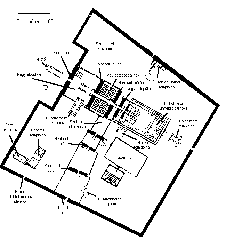
Origins and Transformation of Luxor Temple and the Imperial Cult Chapel
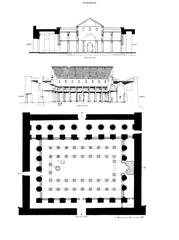
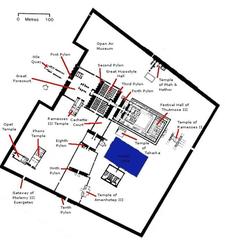
Luxor Temple, known in ancient times as ipet resyt (“the southern sanctuary”), was constructed primarily under Amenhotep III around 1400 BCE. Unlike other temples focused solely on divine worship or mortuary rites, Luxor Temple was dedicated to the rejuvenation of kingship and the celebration of royal power. Over the centuries, additional contributions came from rulers such as Tutankhamun, Ramesses II, and Alexander the Great (Wikipedia).
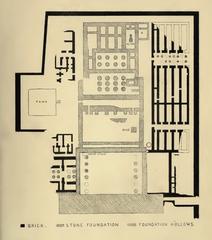
During the Roman era, the temple’s southern sector—originally a chapel for Mut—was repurposed as the Imperial Cult Chapel. This transformation reflected the new rulers’ strategy of integrating local religious traditions to legitimize their authority (Academia.edu).
Roman Adaptation: Architecture and Function
Under Roman rule, the temple complex was fortified and reorganized. Roman architects introduced a grid of streets and monumental tetrastyla (four-columned structures) to honor the emperors, in line with the Tetrarchy system of Diocletian. The Imperial Cult Chapel was adapted to serve both ceremonial and administrative purposes, blending Roman arches and vaults with traditional Egyptian columned halls (Academia.edu).
The site also served as a military fortress, housing up to 1,500 soldiers and acting as the region’s administrative center (ancient-origins.net).
Religious Shifts: From Egyptian Deities to Imperial Cult and Beyond
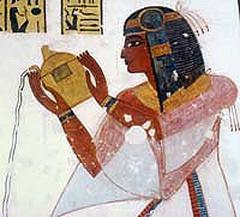
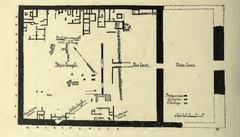
Luxor Temple was integral to the annual Opet Festival, during which statues of Amun, Mut, and Khonsu were paraded from Karnak to Luxor. With Roman conquest, the focus shifted to the imperial cult. Emperors were depicted as pharaohs in temple frescoes, participating in Egyptian rituals to reinforce their divine legitimacy. Shrines to syncretic deities like Serapis were also introduced, blending Egyptian, Greek, and Roman traditions (madainproject.com).
Later, as Christianity spread, the Imperial Cult Chapel was converted into a church in the 4th century CE, with frescoes modified to reflect the new faith. By the 7th century CE, part of the temple became the Abu Haggag Mosque, which remains active today (Wikipedia).
Artistic and Ritual Highlights
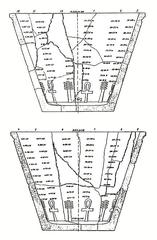
The Imperial Cult Chapel is renowned for its vivid Roman frescoes—rare in Egyptian temple art—depicting emperors such as Diocletian, Maximian, Galerius, and Constantius Chlorus as both Roman and Egyptian rulers. These frescoes were painted using the “secco” technique, ensuring vibrant colors. Ritual scenes blend Roman imperial iconography with Egyptian religious symbolism, underscoring the syncretic nature of Roman Egypt (NMEC, madainproject.com).
Preservation and Archaeological Legacy
Modern restoration and archaeological work, notably by the American Research Center in Egypt, have stabilized the fragile frescoes and architectural elements. Excavations have unearthed statues, inscriptions, and decorative fragments that expand our understanding of the site’s Roman period (Academia.edu, ancient-origins.net).
Visiting Guide: Hours, Tickets, Accessibility, and Travel Tips
Hours and Tickets
- Opening Hours: Luxor Temple (including the Imperial Cult Chapel) is open daily from 6:00 AM to 9:00 or 10:00 PM (confirm locally).
- Tickets: Standard entry is around 150–160 EGP for foreign visitors, with discounts for students and children. Tickets can be purchased onsite or via official platforms (Tripoto).
- Combined Tickets: Consider combined tickets that include Karnak Temple and Luxor Museum.
Accessibility
- The temple complex offers partial accessibility; major pathways are suitable for wheelchairs, but uneven surfaces and steps may limit access in certain areas (Tripoto).
Travel Tips
- Best Time to Visit: October–April for cooler weather and fewer crowds. Early morning or sunset visits offer optimal lighting and quieter experiences (Paliparan).
- Dress Code: Modest attire is recommended—cover shoulders and knees (Tripoto).
- Onsite Facilities: Restrooms are near the entrance; bring water and sun protection, as shaded areas are limited (Against the Compass).
Navigating Luxor Temple and the Imperial Cult Chapel
Enter through the temple’s monumental pylon, pass the colossal statues of Ramesses II, and proceed south to the Imperial Cult Chapel. Signage is minimal, so a guide or audio tour is helpful (Paliparan).
Guided Tours and Visitor Experience
- Guides: Available for hire at the entrance or via pre-booking. Guides provide in-depth context on the Roman period and the chapel’s significance (Tripoto).
- Audio Guides: Offered in multiple languages for self-paced exploration.
- Special Events: Look out for temple light shows and cultural festivals.
Practical Tips and Facilities
- Photography: Allowed, but flash and tripods are restricted to protect the frescoes.
- Safety: Expect security checks; keep valuables secure.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respect the functioning Abu Haggag Mosque—do not enter without invitation (World History Edu).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the Imperial Cult Chapel visiting hours?
A: Open daily from 6:00 AM to 9:00/10:00 PM.
Q: Do I need a separate ticket?
A: No, the main Luxor Temple ticket includes access to the Imperial Cult Chapel.
Q: Is the site wheelchair accessible?
A: Partially; assistance may be needed in some areas.
Q: Can I take photos inside?
A: Yes, but without flash.
Q: When is the best time to visit?
A: October–April, early morning or sunset.
Conclusion
The Imperial Cult Chapel at Luxor Temple is a living chronicle of Egypt’s religious and cultural evolution—from an Egyptian sanctuary to a Roman imperial chapel, later a Christian church, and an Islamic mosque. Its rare frescoes, unique architecture, and layered history make it a must-visit for anyone interested in Egypt’s ancient past and the interplay of global civilizations. To ensure a rewarding visit, plan ahead for tickets and accessibility, respect preservation efforts, and consider guided tours for deeper understanding. Stay connected for the latest updates by downloading the Audiala app and following official tourism channels.
For more insight, see:
References
- Luxor Temple, Wikipedia, 2025
- The 3D reconstruction of the Roman imperial cult temple at Luxor, Academia.edu, 2025
- Luxor Temple and the Imperial Cult Chapel, Madain Project, 2025
- Chapel of Serapis, Madain Project, 2025
- Luxor Temple: History and Visitor Guide, Ancient Origins, 2025
- Luxor Temple Visitor Guide, Paliparan, 2023
- Visiting Luxor Temple, Tripoto, 2025
- Luxor Temple Historical Overview, World History Edu, 2025
- Art of Empire: The Roman Frescoes and Imperial Cult Chamber in Luxor Temple, NMEC
- Against the Compass – Visit Luxor
Experience the convergence of Egyptian tradition and Roman grandeur at the Imperial Cult Chapel—an essential stop on any Luxor journey.