The Column of Taharqa: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Significance in Luxor, Egypt
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
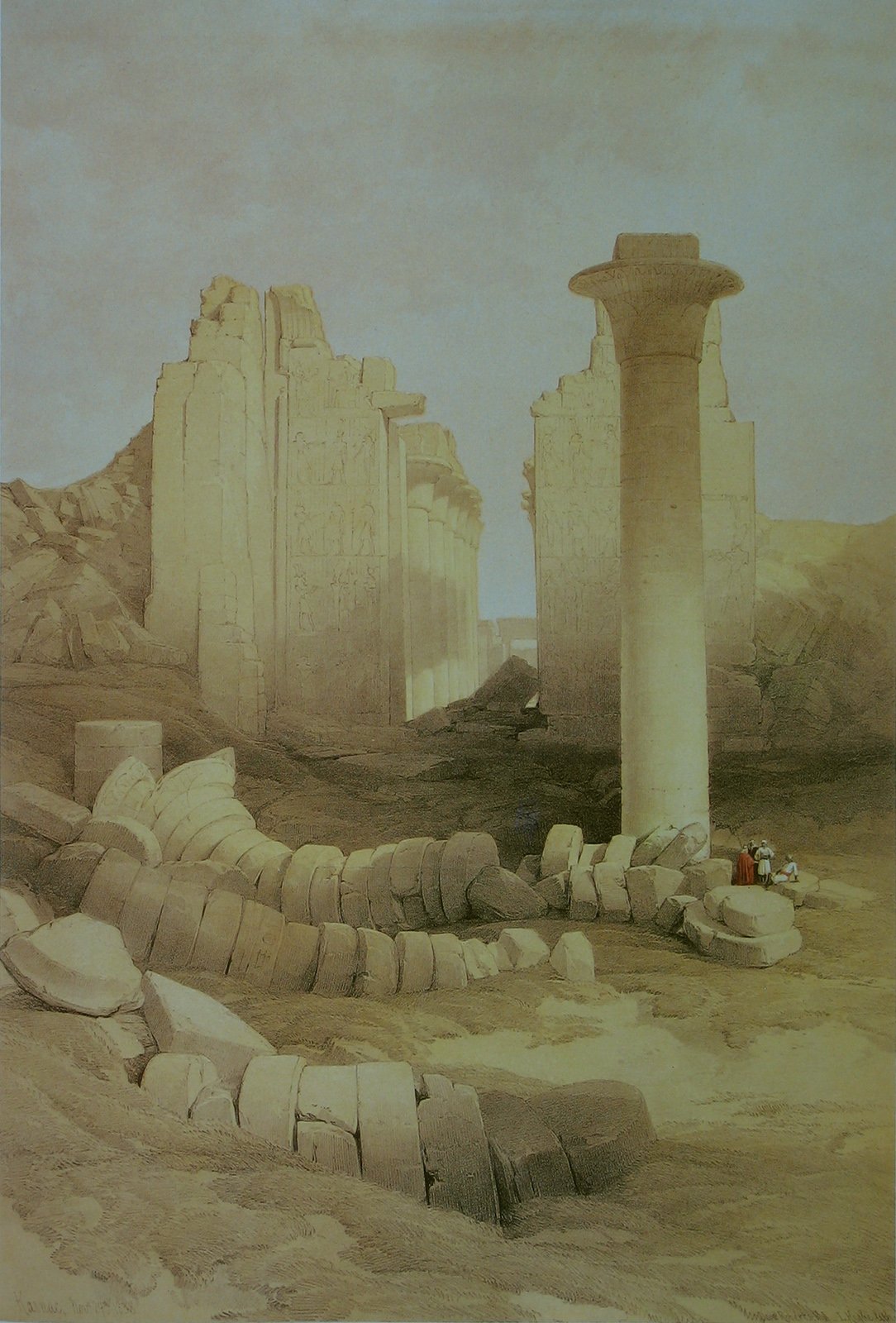
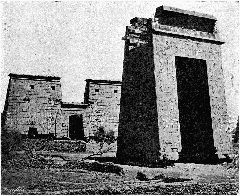
Rising in the heart of Karnak Temple in Luxor, the Column of Taharqa is a compelling symbol of Egypt’s Nubian legacy and architectural ingenuity. Erected by Pharaoh Taharqa during the 25th Dynasty (the so-called Nubian or Kushite Dynasty), this monumental sandstone column, with its elegant papyrus-bundle capital, stands nearly 20 meters high and is the last surviving pillar of a once grand ceremonial kiosk. For history enthusiasts, cultural travelers, and photographers, the Column of Taharqa is not only an architectural marvel but also a window into the religious and cultural revival that swept ancient Thebes under Nubian rule.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the column’s historical context, architectural features, religious symbolism, and practical visitor information—including opening hours, ticketing, accessibility, and tips for integrating this monument into a broader Luxor itinerary. Whether you’re planning your first visit or seeking to learn more about Luxor’s rich past, the Column of Taharqa is an essential stop.
Authoritative resources for further reading include World History Edu, HAL Open Science Archive, and History Hit.
Table of Contents
- Historical Context
- Architectural Features
- Visiting Information
- Enhancing Your Visit
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Summary and Recommendations
- References and Further Reading
Historical Context
The 25th Dynasty and Nubian Rule
The Column of Taharqa dates to the reign of Pharaoh Taharqa (690–664 BCE), one of the most influential rulers of Egypt’s 25th Dynasty. This era, known as the Kushite or Nubian Dynasty, saw the rise of pharaohs from Kush (in present-day Sudan) who revitalized Egypt’s traditions. Taharqa distinguished himself through military skill, immense building projects, and a religious revival that left a lasting imprint on Thebes and the Karnak Temple (World History Edu).
Cultural and Religious Impact
Taharqa and his fellow Nubian rulers embraced Egyptian customs, blending their own traditions with those of Thebes. The column’s inscriptions and reliefs—depicting Taharqa with deities like Amun-Ra—reflect this cultural fusion, as well as the king’s assertion of divine legitimacy over both Egypt and Nubia. The dual uraei on his crown symbolize this authority, and his monuments reinforce his role as a restorer of Egypt’s ancient grandeur (divinenarratives.org).
Architectural Innovations at Karnak
Taharqa’s kiosk—of which this column is the last survivor—originally featured ten towering columns supporting a ceremonial roof. Situated within Karnak’s First Courtyard, it served as a focal point for religious processions and festivals, especially the annual Opet Festival. The structure marked a key transition between sacred and public spaces and remains one of the tallest surviving columns at Karnak (HAL Open Science Archive).
Architectural Features
Design, Symbolism, and Construction
The Column of Taharqa is notable for its papyrus-bundle capital—a motif symbolizing creation and rebirth, evoking the primordial marshes of the Nile. Standing nearly 20 meters tall, the column is carved from sandstone and inscribed with hieroglyphs celebrating Taharqa’s divine kingship (archarticulate.com). The column’s surface reliefs reinforce the pharaoh’s relationship with Amun-Ra and his dedication to restoring Egypt’s religious traditions (egyptmythology.com).
Construction required sophisticated engineering, likely involving ramps and levers to maneuver the massive stones. The column’s precision and durability are a testament to the craftsmanship achieved during the Nubian Dynasty (archarticulate.com).
Integration with Temple Ceremonies
Karnak Temple’s ceremonial processions once passed through the kiosk, pausing at the columned porch for offerings and prayers before proceeding into the temple’s most sacred areas. During festivals, the columned porch was adorned with banners and offerings, serving both religious and political functions—proclaiming Taharqa’s piety and royal legitimacy (HAL Open Science Archive).
Visiting Information
Location and Access
The Column of Taharqa stands in the First Courtyard of Karnak Temple, on Luxor’s East Bank—about 2.5 kilometers north of the city center. The temple is accessible by taxi, ride-share, on foot, or as part of organized tours (Wandering Wagars). The main entrance features ticketing facilities, security checks, and visitor amenities.
Opening Hours and Ticket Prices
- Opening Hours: Karnak Temple is open daily from 6:00 AM to 5:30 PM (hours may vary seasonally and for special events) (Eagle Travel Egypt).
- Ticket Prices: As of 2025, adult admission is about 200–220 EGP (approx. $6.50–$7 USD), with discounts for students and children. Tickets are available onsite or online via official tourism portals.
Accessibility
The First Courtyard and the area surrounding the column are largely flat but feature some uneven paving. Wheelchair access is possible throughout much of the complex; assistance may be needed in certain areas. Restrooms and refreshments are available near the main entrance.
Guided Tours and Best Times to Visit
Hiring a licensed Egyptologist guide is highly recommended for insights into the column’s history, symbolism, and its place within Karnak (Odynovo Tours). Tours can be arranged onsite or in advance. The best times to visit are in the early morning or late afternoon for cooler temperatures, softer lighting, and fewer crowds (TravelTriangle).
Photography and Visitor Etiquette
Photography is allowed throughout Karnak Temple, including the Column of Taharqa. Flash is permitted, but tripods may require special permission. Please do not touch or climb on the monuments to help preserve their ancient surfaces.
Enhancing Your Visit
Nearby Attractions and Suggested Itineraries
- Luxor Museum: Between Karnak and Luxor Temples, displaying artifacts contextualizing the 25th Dynasty (Egypt Planners).
- Luxor Temple: South of Karnak, open late and beautifully illuminated at night (Salt in Our Hair).
- West Bank Sites: Valley of the Kings, Temple of Hatshepsut, and Colossi of Memnon, easily reached by taxi or ferry.
Sample Itinerary
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 6:00–7:00 AM | Explore Column of Taharqa in Karnak’s quietest hour |
| 7:00–9:00 AM | Continue through Karnak Temple complex |
| 10:00–11:30 AM | Visit Luxor Museum |
| 12:00–1:00 PM | Lunch along Nile Corniche |
| 2:00–4:00 PM | Visit Luxor Temple |
| 7:00–8:00 PM | Sound & Light Show at Karnak (optional) |
Cultural Insights and Sustainability
- Greet locals with “salaam alaikum” and practice tipping.
- Respect local customs and opening hour changes during festivals.
- Support conservation by following site guidelines and minimizing waste.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the visiting hours for the Column of Taharqa?
A: Karnak Temple, including the column, is open daily from 6:00 AM to 5:30 PM.
Q: How much does it cost to visit?
A: Tickets are about 200–220 EGP ($6.50–$7 USD); discounts for students/children apply.
Q: Is the site wheelchair accessible?
A: Major paths are accessible, but some uneven surfaces may require assistance.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, and they are highly recommended for a richer experience.
Q: When is the best time to visit?
A: October to April for pleasant weather; early morning or late afternoon for best lighting and fewer visitors.
Q: Can I take photos?
A: Yes, but tripods require special permission and professional equipment may incur additional fees.
Summary and Recommendations
The Column of Taharqa is a unique monument that embodies the cultural convergence and architectural innovation of ancient Egypt’s 25th Dynasty. As the last remnant of a once-magnificent kiosk, it stands as a powerful symbol of Nubian influence and the revival of Thebes. By visiting the Column of Taharqa within the broader context of Karnak Temple and Luxor’s other historical sites, travelers gain a deeper appreciation for Egypt’s diverse heritage.
For the best experience, arrive early or visit late in the day, purchase tickets in advance when possible, and consider hiring a guide. Enhance your trip by exploring nearby attractions and using digital resources like the Audiala app for up-to-date information.
References and Further Reading
- Pharaoh Taharqa, 2024, World History Edu
- HOURDIN, Ancient Egypt 2017, HAL Open Science Archive
- Karnak Temple: The Secrets of an Ancient Egyptian Sanctuary, 2024, History Hit
- The Symbolism of Columns in Egyptian Sacred Architecture, 2024, Egypt Mythology
- Importance of Columns in Ancient Egyptian Architecture, 2024, Archarticulate
- Karnak Temple Visitor Guide, 2024, Odynovo Tours
- Things to Do in Luxor, 2024, Wandering Wagars
- The Fascinating History of Luxor’s Karnak Temple, 2024, Eagle Travel Egypt
- Luxor Egypt Travel Tips, 2024, TravelTriangle
- Luxor Temple: History and Visiting Tips, 2024, Salt in Our Hair
- Luxor Sightseeing and Things to Do, 2024, Holidify
- Official Karnak Temple website, Luxor Government Tourism
- Luxor Tourism Board, Egypt Tourism Authority