Chapel of Kamutef Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Comprehensive Guide to Luxor Historical Sites
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
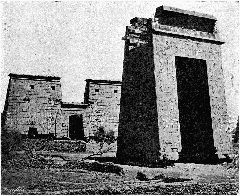
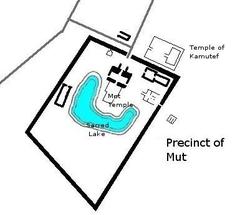
The Chapel of Kamutef, located within the iconic temple complexes of Luxor, Egypt, stands as a vibrant testament to the religious, cultural, and architectural achievements of ancient Thebes. Dedicated to Amun in his form as Kamutef, or “Bull of His Mother,” the chapel encapsulates the concepts of fertility, renewal, and divine kingship that were central to New Kingdom Egypt. Its role in major ceremonial events—most notably the Opet Festival—underscores the chapel’s significance within the religious landscape of Thebes (Global Egyptian Museum; Jakada Tours; History Hit).
In addition to religious importance, the Chapel of Kamutef is celebrated for its remarkable artistry and architectural features. Visitors encounter exquisite reliefs, hieroglyphic inscriptions, and decorative motifs that narrate the relationship between pharaohs and the divine order (Greek Reporter; Holiday and Trips). Ongoing archaeological discoveries, including those from 2024–2025, continue to reveal artifacts and inscriptions linked to Queen Hatshepsut and Thutmose III, further illuminating the chapel’s evolving role in Egyptian spirituality and politics (Xinhua).
For modern visitors, practical details such as opening hours (typically 6:00 AM–10:00 PM at Luxor Temple), ticket pricing (around 160 EGP for foreigners), accessibility, and options for guided tours are crucial for planning (Jakada Tours; escholarship.org). The chapel’s advantageous location enables easy exploration of other renowned sites—including Karnak Temple, the Luxor Museum, and the Valley of the Kings—providing a holistic view of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background and Recent Discoveries
- Theological Role and Symbolism
- Architectural Features and Artistic Program
- Practical Visitor Information
- Restoration and Preservation Efforts
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Visuals and Interactive Media
- Conclusion
- References
Historical Background and Recent Discoveries
Origins and Historical Context
The Chapel of Kamutef is integral to understanding ancient Thebes’ religious and ceremonial traditions. “Kamutef” refers to Amun’s self-generating aspect, emphasizing creation and fertility. The chapel, dating primarily to the New Kingdom and especially the reigns of Amenhotep III, Hatshepsut, and Thutmose III, was crucial in royal rituals—most notably the Opet Festival, which celebrated the pharaoh’s divine renewal (Global Egyptian Museum; Jakada Tours).
Archaeological Discoveries
19th–20th Century Excavations
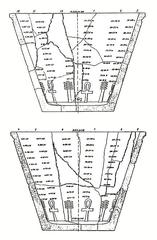
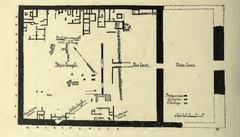
Excavations from the late 19th century revealed the layout of Luxor Temple, subsidiary chapels, and caches of statues, sphinxes, and foundation deposits. The 1989 discovery of a cachette beneath the temple floor yielded 18th Dynasty statues, providing insights into artistic and religious practices (Jakada Tours; Global Egyptian Museum).
Recent Discoveries (2024–2025)
Archaeologists have recently unearthed more than 1,000 decorated blocks and fragments from the reigns of Hatshepsut and Thutmose III, as well as over 100 inscribed tablets, affirming the chapel’s royal patronage and religious significance (Xinhua). Middle Kingdom tombs found nearby, with sealed burials and ritual artifacts, further illustrate the area’s long-standing ceremonial use (The Collector; AP News; The Peninsula Qatar).
Artistic and Epigraphic Insights
The chapel’s reliefs and inscriptions—depicting pharaonic offerings, festival rituals, and divine iconography—are among Luxor Temple’s best preserved. Restoration and analysis have identified reused blocks and traces of evolving religious ideologies (Greek Reporter; Holiday and Trips; Global Egyptian Museum).
Preservation and Modern Archaeology
Cutting-edge technologies, including ground-penetrating radar, 3D scanning, and digital epigraphy, have improved documentation and conservation. These efforts, supported by collaboration between Egyptian and international teams, allow for greater public appreciation and understanding of the chapel’s artistry and significance (Daily Galaxy; Jakada Tours).
Theological Role and Symbolism
Kamutef in Ancient Egyptian Religion
Amun-Kamutef, “Bull of His Mother,” symbolizes self-generation and creative potency. His worship was especially prominent in Thebes, reinforcing the pharaoh’s divine legitimacy and the land’s fertility. Rituals within the chapel affirmed both the king’s right to rule and Egypt’s ongoing prosperity (History Hit).
Ritual Practices and Festival Connections
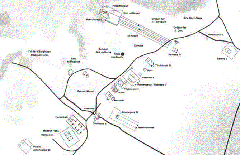
During the Opet Festival, the barques of Amun, Mut, and Khonsu traveled from Karnak to Luxor, pausing at the Chapel of Kamutef for rituals that renewed both the pharaoh’s mandate and cosmic order (Tales from the Two Lands; Britannica).
Iconography and Symbolic Motifs
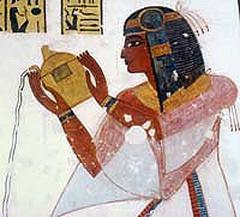
The chapel’s reliefs depict Kamutef in ithyphallic form, surrounded by deities and fertility symbols such as lotus and papyrus. These motifs reinforce themes of creation, renewal, and the perpetuation of the royal line (History Hit).
Cultural Layers and Political Implications
The chapel’s evolving architectural and decorative program reflects changing religious and political priorities across the New Kingdom, Ptolemaic, and Roman eras (Ancient Origins). By centering Amun-Kamutef, the chapel linked pharaonic authority with divine creation, reinforcing the inseparability of religion and governance in ancient Egypt (Britannica).
Architectural Features and Artistic Program
Layout and Construction
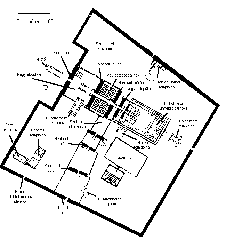
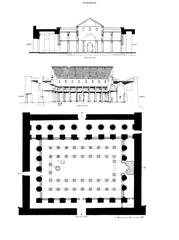
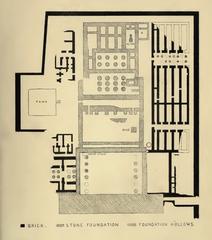
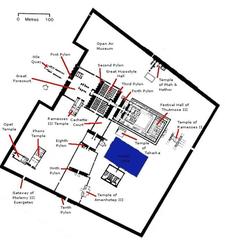
The Chapel of Kamutef, situated within the Karnak Temple complex, features a multi-chambered layout with seven rooms and two large halls. Built primarily of Silsileh sandstone, the structure is decorated with reliefs, columns with papyrus and lotus capitals, and massive roof slabs (Mapcarta; Greek Reporter; Senses Atlas).
Decorative Elements
Wall reliefs depict pharaohs—especially Thutmose III—performing rituals, and are accompanied by hieroglyphic prayers and hymns (Holiday and Trips). Symbolic motifs include the lotus and papyrus, solar discs, ankhs, sphinxes, and baboons.
Artistic Techniques
Artisans used sunk and raised reliefs, enhanced by mineral pigments, to create vibrant narrative scenes. Figures are arranged in registers, emphasizing order and balance (Holiday and Trips).
Cosmological Symbolism
The chapel’s orientation and spatial progression—from outer halls to the innermost sanctuary—mirror Egyptian cosmology and the journey from the earthly to the divine (Holiday and Trips; Senses Atlas).
Practical Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Tickets
- Hours: Luxor Temple (including the Chapel of Kamutef) is open daily from 6:00 AM to 10:00 PM. Karnak Temple is generally open from 6:00 AM to 5:00 PM (Jakada Tours; escholarship.org).
- Tickets: Standard entry is about 160 EGP for foreign visitors, with discounts for students and Egyptian nationals. Combined tickets are available for multiple sites.
- Purchase: Tickets can be bought at the site or online via the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism.
Getting There
The chapel is within walking distance of Luxor’s city center and is easily reached by taxi, horse carriage, or organized tour (Mapcarta).
Accessibility
Recent restoration projects have improved physical accessibility, adding ramps and clear pathways (Greek Reporter; happyegypt.com).
Guided Tours and Special Events
Expert-guided tours, often available in multiple languages, enrich the visitor experience. Special events, such as Opet Festival reenactments, occasionally take place (tourradar.com).
Nearby Attractions
Combine your visit with the Karnak Temple, Luxor Museum, Valley of the Kings, and the avenue of sphinxes for a broader understanding of Theban religious traditions.
Tips for Visitors
- Visit early or late for cooler temperatures and optimal lighting.
- Wear comfortable shoes and bring water and sun protection.
- Book tours in advance during peak seasons.
Restoration and Preservation Efforts
Restoration Initiatives
Ongoing conservation includes structural stabilization, stone cleaning, and artifact reassembly using non-invasive techniques (fionadeal.com). Digital documentation through 3D scanning and photogrammetry supports research and education.
Accessibility Enhancements
Enhanced pathways and signage accommodate wheelchair users and visitors with mobility challenges (happyegypt.com).
Visitor Management
Timed entries and crowd management ensure a respectful and enjoyable experience (saltinourhair.com).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the visiting hours for the Chapel of Kamutef?
A: Typically 6:00 AM–10:00 PM at Luxor Temple; 6:00 AM–5:00 PM at Karnak Temple.
Q: How much do tickets cost?
A: Around 160 EGP for foreign adults; discounts available.
Q: Is the site accessible to those with disabilities?
A: Yes, with ramps and level pathways in place.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, in multiple languages from various operators.
Q: Where can I buy tickets?
A: Onsite or via the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism.
Visuals and Interactive Media
Visitors can access high-quality images and virtual tours via official tourism platforms and mobile apps. Look for alt-tagged images such as “Chapel of Kamutef reliefs, Karnak Temple” for accessibility (Greek Reporter).
Conclusion
The Chapel of Kamutef merges ancient religious significance, architectural innovation, and modern heritage preservation. Its role in the Opet Festival, exquisite artistry, and the ongoing efforts to restore and interpret its legacy make it a cornerstone of Luxor’s historical landscape. Thorough planning, guided tours, and the use of digital resources can greatly enhance your visit to this profound site.
Call to Action
Plan your visit to the Chapel of Kamutef and Luxor’s extraordinary heritage sites today. Download the Audiala app for personalized tours, real-time updates, and exclusive content. For the latest restoration news, travel tips, and event information, follow our channels and consult the resources below.
References
- Global Egyptian Museum
- Jakada Tours
- History Hit
- Xinhua
- The Collector
- AP News
- The Peninsula Qatar
- Daily Galaxy
- Mapcarta
- Greek Reporter
- Holiday and Trips
- Senses Atlas
- escholarship.org
- fionadeal.com
- happyegypt.com
- saltinourhair.com
- tourradar.com
- Ancient Origins
- Britannica
- Britannica on Opet Festival
- Tales from the Two Lands