Bab El Amara Gate: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Significance in Luxor, Egypt
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
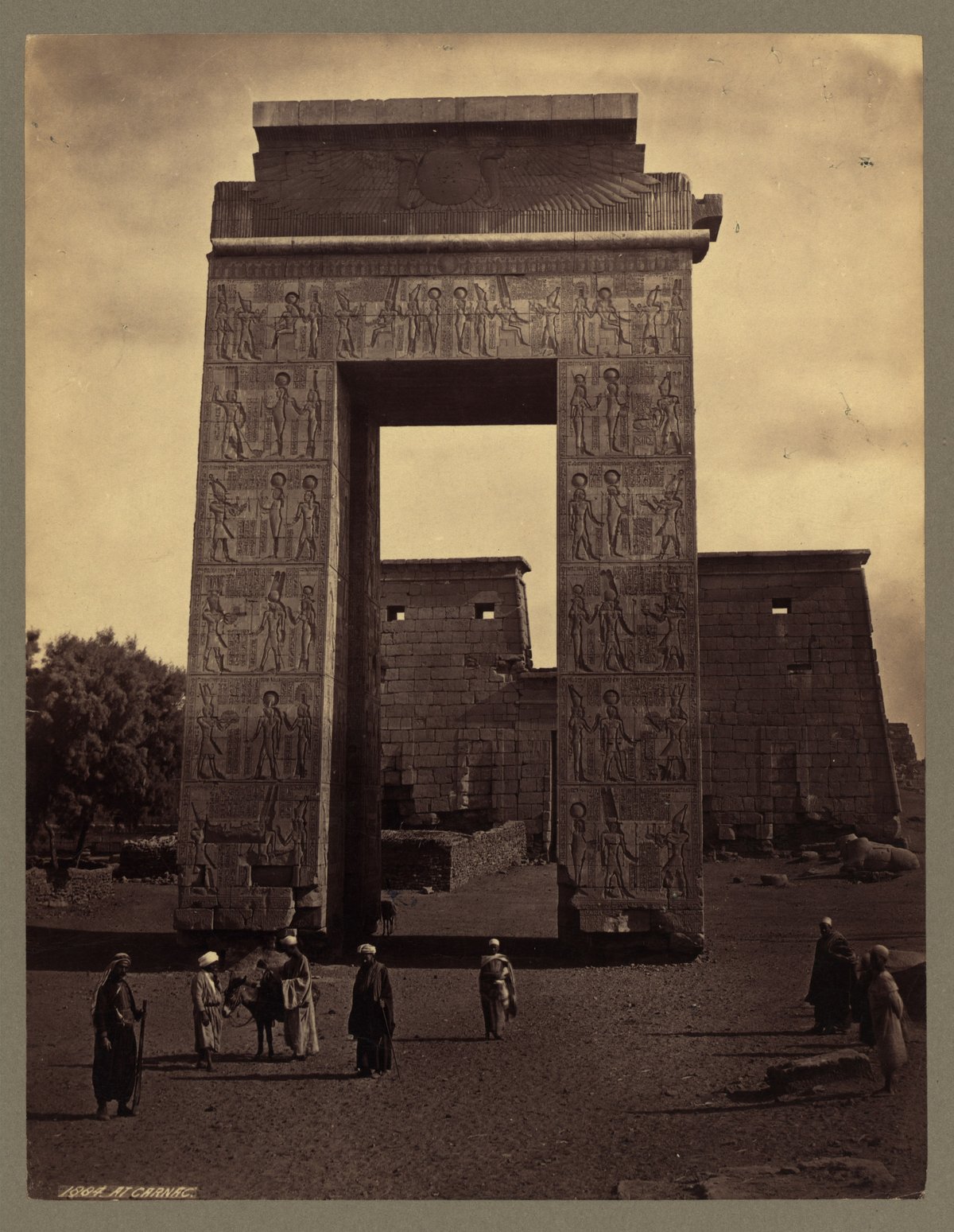
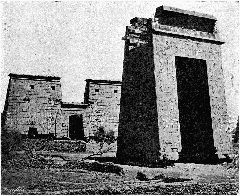
Bab El Amara Gate is a monumental architectural treasure within the Karnak Temple Complex in Luxor, Egypt. Serving as a ceremonial threshold between the sacred and the secular, this gate stands as a testament to the religious, cultural, and political history of ancient Thebes. Built under Pharaoh Nectanebo I in the 30th Dynasty and embellished during the Ptolemaic era, Bab El Amara reflects the syncretism of Egyptian and Hellenistic traditions and remains a vital touchstone for understanding Egypt’s illustrious past. This guide provides a thorough exploration of Bab El Amara Gate’s history, architectural features, cultural context, and essential visitor information, ensuring travelers experience this site to its fullest. (Wikimedia Commons, Antiquities on Postcards, SunPyramids Tours, Egyptopia, Local Guide to Egypt)
Historical Overview
Origins and Construction
Bab El Amara Gate was initiated by Pharaoh Nectanebo I (reigned 380–362 BCE) during a period of renewed Egyptian sovereignty. His ambitious project included constructing new pylons, sphinx-lined avenues, and ceremonial gateways that would affirm the sanctity of Karnak and its precincts (Wikimedia Commons). The gate was later completed and enhanced under Ptolemy III Euergetes (reigned 246–222 BCE), who added Hellenistic artistic elements and inscriptions, further integrating Greek and Egyptian religious iconography (Antiquities on Postcards).
Context within Ancient Thebes
Karnak was the spiritual heart of Thebes (modern Luxor), dedicated to the Theban Triad: Amun, Mut, and Khonsu. The Bab El Amara Gate formed part of the temple’s processional routes, particularly significant during the Opet Festival, when effigies of the gods were carried between Karnak and Luxor Temple via the Avenue of Sphinxes (SunPyramids Tours). As a monumental entrance, the gate symbolized the transition from the profane city into the divine realm of the gods.
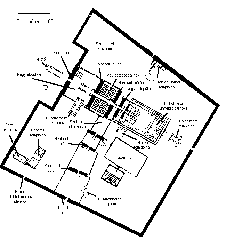
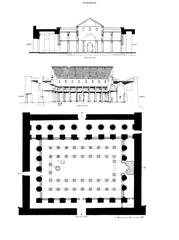
Architectural Features
Standing approximately 21 meters (69 feet) high, Bab El Amara Gate is constructed from massive sandstone blocks typical of the Late Period and Ptolemaic era. Key features include:
- Reliefs and Inscriptions: Depictions of Nectanebo I and Ptolemy III making offerings to the gods, with hieroglyphic texts emphasizing divine legitimacy (Antiquities on Postcards).
- Symbolic Motifs: Flying vultures on the ceiling (protection), a winged sun-disk on the lintel (divine guardianship), and ritualistic hieroglyphs.
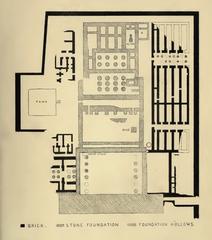
- Structural Elements: The gate was part of a larger complex featuring unfinished pylons and a sphinx-lined alley, illustrating the ongoing evolution of temple architecture.
Religious and Cultural Importance
The Bab El Amara Gate was integral to ritual processions and religious festivals, serving both as a practical and symbolic passage. It marked the boundary between the city and sanctified temple grounds, reinforcing ancient Egyptian beliefs about space, purity, and the sacred. The Ptolemaic enhancements underscore the adaptability of Egyptian religious traditions under foreign rule, blending Greek and Egyptian deities and customs (Egyptopia).
Visiting Bab El Amara Gate
Location
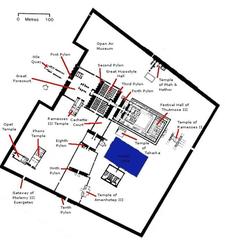
Bab El Amara Gate is located within the Karnak Temple Complex on the East Bank of Luxor, just south of the Khonsu Temple (Antiquities on Postcards, Mapcarta).
Opening Hours
- Daily: 6:00 AM – 5:30 PM (subject to seasonal changes and special events).
- Note: Always check official resources or the Luxor Tourist Information Center for the latest updates.
Ticket Information
- Entry to Gate: Included in the general admission ticket to Karnak Temple Complex.
- 2025 Prices: General admission 200 EGP (foreigners), 10 EGP (Egyptians), Light and Sound Show 250 EGP.
- Where to Buy: Tickets available at the Karnak entrance or through authorized vendors (Official Karnak Ticketing Information).
Accessibility
- Mobility: Paved pathways lead to Bab El Amara Gate, but some uneven terrain may challenge wheelchair users; assistance is recommended.
- Facilities: Restrooms, shaded areas, and cafés are located nearby (egiptoexclusivo.com).
Guided Tours
- Guided Experiences: Licensed guides and audio guides are available at the entrance and through tour operators. Guided tours provide deeper historical and religious context (Quick Whit Travel).
- Special Events: During festivals like the Opet Festival, the gate becomes a focal point for processions and cultural reenactments.
Photography Tips
- Lighting: Early mornings and late afternoons offer the best light for capturing reliefs and architectural details.
- Regulations: Photography is generally permitted, but flash and tripods may be restricted. Always follow site guidelines.
Nearby Attractions
- Temple of Khonsu: Directly connected to Bab El Amara Gate, featuring notable reliefs and sanctuaries (audiala.com).
- Avenue of Sphinxes: The grand processional route linking Karnak and Luxor Temples.
- Great Hypostyle Hall, Sacred Lake, Opet Temple, and Temple of Akhmenu: All within the Karnak complex (foodandtravelutsav.com).
Extend your visit to:
- Luxor Temple: About 3 km south, accessible via the Avenue of Sphinxes.
- Luxor Museum: For artifacts and context about ancient Thebes.
- Luxor’s urban center: With cafés, markets, and additional historical sites.
Travel Tips and Responsible Tourism
- Best Time to Visit: Arrive early or late afternoon to avoid crowds and heat (againstthecompass.com).
- Dress Code: Modest, lightweight clothing is recommended.
- Hydration: Bring water and sun protection.
- Support Locals: Hire local guides and purchase from authorized vendors to sustain the community.
- Respect the Site: Do not touch or climb on ancient structures; follow all conservation guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the opening hours of Bab El Amara Gate?
6:00 AM to 5:30 PM daily; check for seasonal or special event variations.
How do I get tickets?
Tickets are included in Karnak Temple Complex admission, available at the main entrance or through authorized sellers.
Are guided tours available?
Yes—both group and private guides, as well as audio guides, are available.
Is Bab El Amara Gate wheelchair accessible?
Partially; paved paths exist, but uneven terrain may require assistance.
Are photography and videography allowed?
Yes, except during special events or where otherwise posted.
What are other nearby attractions?
Karnak complex highlights, Luxor Temple, Avenue of Sphinxes, and Luxor Museum.
Summary and Call to Action
Bab El Amara Gate is a remarkable emblem of Luxor’s dynamic history, standing at the crossroads of ancient Egyptian and Ptolemaic traditions. Its imposing sandstone structure, detailed reliefs, and ceremonial role within Karnak Temple make it an essential stop for anyone exploring Egypt’s ancient wonders. With accessible visiting hours, straightforward ticketing, and enriching guided tours, travelers can immerse themselves in the spiritual and architectural legacy of Thebes. Preservation efforts continue to safeguard this monument, and responsible tourism plays a crucial part. For an enhanced visit, download the Audiala app and stay connected for updates, guides, and exclusive content on Luxor’s historical sites. (Egyptian Ministry of Tourism - Karnak Temple, Official Karnak Ticketing Information, Audiala)
Official Resources and Further Reading
- Bab El Amara Gate in Karnak - Wikimedia Commons
- Bab El Amara Gate - Antiquities on Postcards
- The Ancient City of Luxor - SunPyramids Tours
- The Temple of Khonsu - Egyptopia
- 10 Best Things to Do in Luxor Egypt - Local Guide to Egypt
- What to Know Before You Visit Luxor - Quick Whit Travel
- Must Visit Attractions in Luxor - Food and Travel Utsav
- Temple of Khonsu at Karnak - Historical Eve
- Best Things to Do in Luxor Egypt - Earth Trekkers
- Travel Guide Luxor - CN Traveller
- Karnak Temple Complex - Egyptian Ministry of Tourism
- Official Karnak Ticketing Information - Egypt Travel
- Bab El Amara Gate - Mapcarta
- Visit Luxor - Against the Compass
- Egypt Exclusive Travel Information - Egipto Exclusivo