Visiting فناء الخبيئة in Luxor: Hours, Tickets, and Tips
Published Date: 31/07/2024
Introduction to فناء الخبيئة
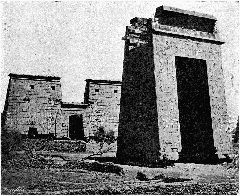
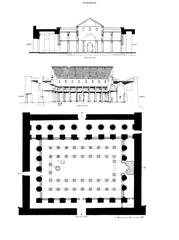
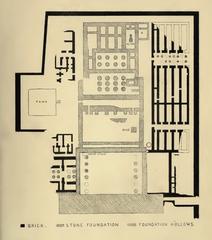
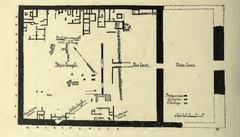
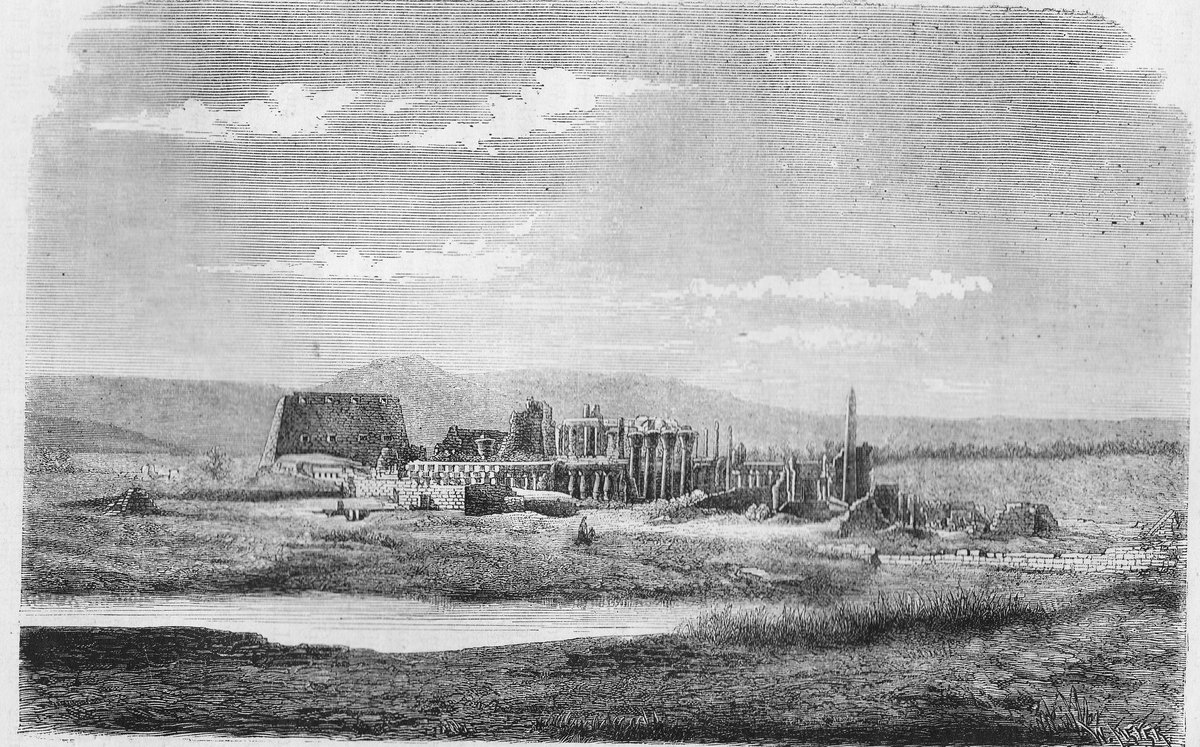
Luxor, Egypt, is a city that stands as a testament to the grandeur of ancient civilizations. Among its many historical treasures, none captivate the imagination quite like فناء الخبيئة (Cache Court), located within the Karnak Temple Complex. Discovered in 1903 by French Egyptologist Georges Legrain, the Cache Court is one of the most significant archaeological finds in Egypt, revealing a hidden cache of over 700 statues and stelae (Exploratory Glory). These artifacts offer invaluable insights into the art, religion, and political landscape of ancient Egypt, dating back to the New Kingdom period, specifically the 18th Dynasty (1550 to 1292 BCE) (BBC). This guide delves into the rich history of the Cache Court, its archaeological significance, and provides practical tips for visitors, ensuring an enriching and memorable experience.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- History of Cache Court
- Significance of the Artifacts
- Preservation and Display
- Archaeological Techniques and Challenges
- Impact on Egyptology
- Ongoing Research and Discoveries
- Visitor Experience
- Practical Tips for Visitors
- FAQ
- Conclusion
History of Cache Court
Discovery and Initial Excavations
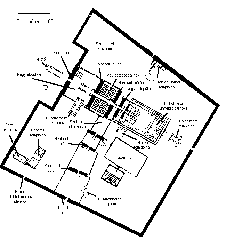
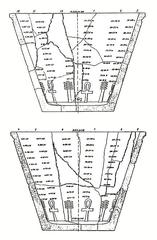
The Cache Court, also known as فناء الخبيئة, is a significant archaeological site discovered in 1903 by French Egyptologist Georges Legrain. During his excavations, Legrain uncovered a hidden cache of over 700 statues and stelae buried in a pit within the court. This monumental discovery provided invaluable insights into the art, religion, and politics of ancient Egypt.
Historical Context
Dating back to the New Kingdom period, specifically the 18th Dynasty (1550 to 1292 BCE), the Cache Court is situated within the Karnak Temple Complex, a focal point of religious activity dedicated to Amun-Ra. The statues and artifacts found here were likely buried around 1000 BCE during the 21st Dynasty to protect them from looting or during periods of political instability.
Significance of the Artifacts
Statues and Stelae
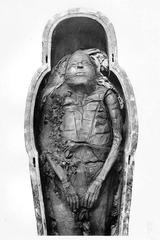
The artifacts unearthed in the Cache Court are diverse, ranging from statues of pharaohs and deities to stelae inscribed with hieroglyphs. Notable is a statue of Pharaoh Amenhotep III, showcasing the high level of craftsmanship of ancient Egyptian artisans. The stelae provide a wealth of information through their inscriptions, recounting religious hymns, decrees, and dedications to the gods.
Preservation and Display
Following their discovery, the artifacts were meticulously cataloged and preserved. Many are now housed in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo and the Luxor Museum, where they continue to be studied and admired.
Archaeological Techniques and Challenges
Georges Legrain and his team employed a combination of traditional and innovative archaeological techniques to uncover the artifacts. The excavation was complex due to the fragile condition of some items, requiring delicate handling and immediate conservation measures.
Impact on Egyptology
The discovery of the Cache Court has had a profound impact on Egyptology, providing a wealth of primary source material for researchers. It has underscored the importance of Karnak as a religious and cultural hub in ancient Egypt.
Ongoing Research and Discoveries
Modern technologies like 3D scanning and digital imaging are being used to study the artifacts in greater detail. Recent studies focus on translating and interpreting the stelae inscriptions, shedding new light on the religious practices and political dynamics of the New Kingdom period.
Visitor Experience
Guided Tours
For visitors to Luxor, the Cache Court offers a unique opportunity to connect with the ancient past. The site is accessible as part of the larger Karnak Temple Complex, with guided tours available to provide detailed explanations of its history and significance.
Where to See Artifacts
Some of the artifacts from the Cache Court can be viewed at the nearby Luxor Museum, which houses a collection of items from the Karnak excavations.
Practical Tips for Visitors
Best Time to Visit
When planning a visit to the Cache Court, it is advisable to go early in the morning or late in the afternoon to avoid the midday heat. The Karnak Temple Complex is open daily from 6:00 AM to 5:30 PM.
Entry Fees and Tickets
Tickets can be purchased at the entrance. The entrance fee to the Karnak Temple Complex, which includes access to Cache Court, is approximately 200 EGP for adults and 100 EGP for students (Totally Egypt).
Guided Tours
Hiring a local guide is recommended for a more informative experience. Guides can provide valuable context and historical background before you enter.
What to Wear
Wear comfortable clothing and shoes, and bring sunscreen, hats, and plenty of water. Egypt is a conservative country, so it is important to dress respectfully, especially when visiting historical and religious sites (Wandering Wagars).
Photography
Photography is allowed, but check for any restrictions, such as the use of flash photography. Always be respectful of the site and avoid touching the statues and inscriptions (Wandering Wheatleys).
Hydration and Snacks
The dry, hot climate of Luxor can quickly lead to dehydration, so it is crucial to carry plenty of water. Light snacks such as fruits, nuts, and energy bars can help maintain your energy levels during your visit (Wandering Wagars).
Safety and Security
Luxor is generally safe for tourists, but it is always wise to take standard precautions. Keep your belongings secure and be aware of your surroundings. Avoid isolated areas, especially after dark (Wandering Wheatleys).
Tipping and Baksheesh
Tipping, or ‘baksheesh,’ is a common practice in Egypt and is expected for various services. It is advisable to carry small denominations of Egyptian pounds for tipping guides, drivers, and site guards (Wandering Wheatleys).
Accessibility
Fane al-Khabiya, like many ancient sites in Luxor, may present challenges for visitors with mobility issues. Uneven terrain, narrow passageways, and steps can make navigation difficult. It is advisable to check with tour operators about the accessibility of specific sites and to plan accordingly (Wandering Wagars).
Nearby Attractions
Consider exploring other nearby attractions such as the Valley of the Kings, Karnak Temple, and Luxor Temple to make the most of your trip (Exploratory Glory).
Local Etiquette
Respecting local customs and traditions is important when visiting any cultural site. Always ask for permission before taking photos of people, and be mindful of your behavior in sacred spaces (Wandering Wagars).
FAQ
What are the visiting hours for Cache Court?
- The Cache Court is part of the Karnak Temple Complex, open daily from 6:00 AM to 5:30 PM.
How much are tickets to the Karnak Temple Complex?
- The entrance fee is approximately 200 EGP for adults and 100 EGP for students.
Can I take photographs?
- Yes, photography is allowed, but check for any restrictions on flash photography.
Conclusion
Visiting فناء الخبيئة offers a unique opportunity to delve into the rich history and culture of ancient Egypt. The site, with its remarkable artifacts and historical significance, provides a fascinating glimpse into the religious and artistic achievements of the ancient Egyptians. By following the visitor tips and exploring the nearby attractions, tourists can ensure a memorable and enriching experience in Luxor.
Summary and Key Points
Visiting فناء الخبيئة (Cache Court) in Luxor is more than just a journey through time; it is an immersion into the rich tapestry of ancient Egyptian culture and history. The discovery of this hidden cache of statues and artifacts has provided profound insights into the religious practices, artistic achievements, and political dynamics of ancient Egypt (DW). By following the practical tips and recommendations provided, tourists can ensure a safe, respectful, and enriching visit. Whether you are a history enthusiast or a casual traveler, فناء الخبيئة promises a fascinating glimpse into the ancient world, making it a must-visit destination in Luxor.