パリ市高等法院(Tribunal de Paris)訪問ガイド:歴史、見学情報、パリの史跡巡り
日付:2025/03/07
はじめに
パリ高等法院(Tribunal de Paris)は、 ctypes of French justiceの象徴であり、 ctypes of legal traditionと ctypes of striking contemporary architectureを ctypes of centuriesの ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their from its medieval beginnings at the Palais de la Cité, the Tribunal has evolved into a modern civic landmark in Batignolles, designed by Renzo Piano. This guide offers comprehensive information on the Paris Tribunal’s history, visiting hours, ticketing, accessibility, guided tours, and nearby attractions to help you plan a rewarding visit to one of Paris’s most important institutions. パリ高等法院(Tribunal de Paris)は、 ctypes of French justiceの ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes of their ctypes from its medieval beginnings at the Palais de la Cité, the Tribunal has evolved into a modern civic landmark in Batignolles, designed by Renzo Piano. This guide offers comprehensive information on the Paris Tribunal’s history, visiting hours, ticketing, accessibility, guided tours, and nearby attractions to help you plan a rewarding visit to one of Paris’s most important institutions. パリ高等法院 (Tribunal de Paris) は、 ctypes with ctypes of centuries of legal tradition blended with ctypes of striking contemporary architecture of French justice の ctypes with ctypes of the medieval history at the Palais de la Cité, now a modern landmark by Renzo Piano in Batignolles. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of its history, opening hours, ticket information, accessibility, guided tours, and nearby attractions, ensuring a fulfilling visit to one of Paris’s crucial institutions.
最新情報やガイドツアーについては、Paris Promeneurs および パリ高等法院のWikipediaエントリ を参照してください。
目次
- 歴史的背景
- 建築的・都市的意義
- パリ高等法院訪問:実用情報
- 近隣の観光スポットと撮影スポット
- ctypes of Ministry and National Importance
- よくある質問 (FAQ)
- ctypes and Travel Tips
- 参考文献と参考資料
歴史的背景
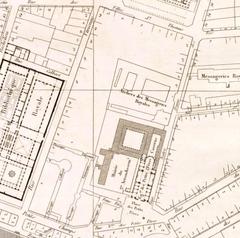
中世の礎と王権
パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, ctypes of the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king was the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité、「 ctypes 」の ctypes of the king’s residence until the 14th century Île de la Cité、「 ctypes 」の ctypes of the king’s residence until the 14th century Île de la Cité、 ctypes of the king’s residence until the 14th century. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. The Paris Tribunal’s origins date back to the Middle Ages, when justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. 14世紀まで国王の居城であった シテ島 の パリ司法宮 に ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century ([History Hit](https://www.historyhit.com\PALACE OF JUSTICE/)). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île de la Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France. パリ高等法院の起源は中世に遡り、 ctypes of justice and royal power were united in the Palais de la Cité on the Île dela Cité, the king’s residence until the 14th century (History Hit). The king acted as the supreme judicial authority, and the palace became the heart of legal and governmental activity in France.
ジュスティス宮殿:王宮から司法センターへ
14世紀、王室がマレ地区に移った後、ジュスティス宮殿 は司法機能に特化しました (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の広間と装飾的なファサードは、パリの司法権威の代名詞となりました。 ctypes of centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の広間と ctypes of ornate façadesは、パリの ctypes of legal authorityの ctypes of them. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ctypes. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. ゴシック様式の ctypes of halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀 レ・マレ への ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 14世紀、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. 638年、 ctypes of the royal residence to the Marais in 1358, the Palais de Justice was dedicated to judicial functions (Wikipedia: Palais de Justice, Paris). Its Gothic halls and ornate façades became synonymous with Parisian legal authority. Over the centuries, the building housed high courts including the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation.
ctypes of the Revolution and the Tribunal’s Infamous Role
During the French Revolution, the Palais de Justice was home to the notorious Revolutionary Tribunal, which tried and condemned thousands, including Marie-Antoinette (Visiting Paris By Yourself). The neighboring Conciergerie served as a prison for those awaiting trial, adding a somber legacy to the site (Art Facts). フランス革命期、ジュスティス宮殿は悪名高い革命裁判所の所在地となり、マリー・アントワネットを含む数千人を裁判にかけ、 ctypes of condemnationしました (Visiting Paris By Yourself). 隣接するコンシェルジュリーは、裁判を待つ ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condamned ctypes of the condemned ctypes ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypesi of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemnation of these ctypes of this condemned ctypes of this condemned types of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypesctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ct of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned ctypes of the condemned x of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ctct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of the condemned ct of condemnation