Kontopigado Site Athens: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Travel Guide
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
Located in the Alimos district, just south of central Athens, Kontopigado is one of the city’s most remarkable—and underappreciated—archaeological sites. As the largest known Mycenaean workshop complex in the Aegean, it offers visitors a unique window into the industrial and technological achievements of Late Bronze Age Athens (ca. 1700–1100 BCE). Characterized by its advanced hydraulic infrastructure, large-scale pottery production, and evidence of both economic and ritual activities, Kontopigado stands as a testament to the ingenuity of Mycenaean civilization.
Modern visitors can enjoy free entry, accessible pathways, and the convenience of nearby public transportation, making Kontopigado an excellent addition to any Athens itinerary. This comprehensive guide covers everything from historical context and site features to practical visiting tips, accessibility, and connections to Athens’ other renowned attractions.
Contents
- Mycenaean Origins and Historical Framework
- Industrial and Economic Importance
- Palatial System Connections
- Ritual and Social Context
- Site Layout and Archaeological Highlights
- Hydraulic Engineering: Wells, Cisterns, and Drains
- Workshop Complex: Kilns, Clay Processing, Storage
- Administrative and Residential Features
- Practical Visitor Information
- Hours and Tickets
- Accessibility and Getting There
- Facilities and Services
- Guided Tours and Photography
- Notable Finds and Display Highlights
- Preservation Efforts and Site Management
- Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Regional Context and Suggested Itineraries
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion and Resources
Mycenaean Origins and Historical Framework
Kontopigado’s archaeological significance lies in its continuous habitation and industrial activity, dating back to the Early Helladic period and peaking during the 14th–13th centuries BCE (archaeology.wiki; oeaw.ac.at). Excavations between 1986 and 2008 revealed extensive workshop complexes, confirming the site’s crucial role in Mycenaean Attica.
Industrial and Economic Importance
Kontopigado stands out for its scale and sophistication in industrial production, particularly ceramics and textiles. The site’s name—meaning “short well”—reflects its defining hydraulic features, including stone-lined wells, cisterns, and clay-lined water channels.
Key Industrial Elements
- Ceramic Production: Multiple kilns and extensive pottery debris indicate mass manufacture.
- Textile Manufacture: Loom weights and spindle whorls point to significant weaving activity.
- Hydraulic Engineering: A 64-meter channel and large cisterns ensured water supply for industrial needs.
This infrastructure underscores Kontopigado’s role as a technological hub and economic engine in the Late Bronze Age (oeaw.ac.at).
Palatial System Connections
Evidence such as Linear B tablets, administrative facilities, and proximity to the Acropolis links Kontopigado to the Mycenaean palace system. The site likely operated as a specialized production unit, supplying goods to the central administration (archaeology.wiki).
Ritual and Social Context
Archaeological findings—including votive deposits and special constructions—reveal that economic and spiritual activities were closely intertwined. These elements highlight the complex social fabric of Mycenaean Athens.
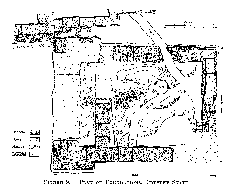
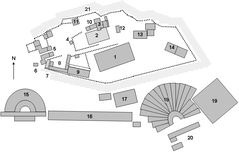
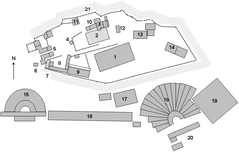
Site Layout and Archaeological Highlights
Hydraulic Engineering
Wells and Cisterns
Kontopigado’s advanced water management system features:
- Large stone-lined wells: Main water sources, up to 10 meters deep.
- Underground cisterns: Each capable of storing over 10,000 liters.
- Clay-lined channels: Efficient water distribution to workshops and kilns (source).
Drainage
A network of drains and overflow channels prevented flooding and ensured a constant supply of clean water.
Workshop Complex
Pottery Kilns
Three large circular kilns, made of fired brick and stone, were used for high-volume ceramic production. Features include:
- Central fireboxes and perforated floors for even heating.
- Chimney flues for smoke ventilation (source).
Clay Processing
Nearby pits and basins were used to clean, soak, and knead clay. Work benches and tables, identified by stone supports and postholes, provided space for shaping pottery.
Storage and Administrative Rooms
Rectangular rooms housed raw materials, finished goods, and administrative tablets, pointing to organized oversight and record-keeping.
Administrative and Residential Features
Small residential units with hearths and storage bins suggest on-site accommodation for workers or overseers. Administrative rooms yielded Linear B tablets and seal impressions.
Practical Visitor Information
Hours and Tickets
- Opening Hours: Typically open Tuesday–Sunday, 8:00/9:00 AM to 3:30/5:00 PM (seasonal variations apply). Closed Mondays and public holidays.
- Tickets: Entry is free. Check official sources for updates or special events (Greek Ministry of Culture).
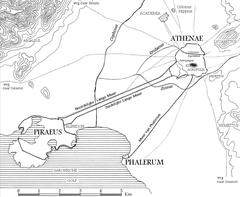
Accessibility and Getting There
- Public Transport: Alimos Metro Station (Line 2) is a 10–15 minute walk away; trams and buses also serve the area.
- On Foot: Expect uneven terrain, compacted earth, and stone features—sturdy footwear recommended.
- Accessibility: Limited for wheelchair users; no paved or ramped pathways. Nearby metro stations offer accessible amenities (Accessible Athens Initiative).
Facilities and Services
- Restrooms: Not available on-site; use facilities at nearby metro stations.
- Visitor Center: Minimal onsite; bring a digital or printed guide.
- Guided Tours: Not officially provided, but private guides can be arranged through tour operators.
- Photography: Allowed throughout the site, with optimal lighting in the morning.
Notable Finds and Display Highlights
- Pottery with Mycenaean potters’ marks
- Clay stamps, spindle whorls, and bronze tools
- Linear B tablets and sealings
- Artifacts displayed at the National Archaeological Museum of Athens and occasionally on-site (source)
Preservation Efforts and Site Management
The Hellenic Ministry of Culture and the local Ephorate oversee preservation, employing protective shelters, masonry stabilization, environmental monitoring, and visitor flow controls.
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Combine your visit with the Acropolis, Ancient Agora, and Athens Riviera.
- Best time to visit: Spring or autumn mornings for pleasant weather and good lighting.
- What to bring: Water, sun protection, and sturdy shoes.
- Local amenities: Alimos Marina, beaches, and taverns nearby (This is Athens).
Regional Context and Suggested Itineraries
Kontopigado can be part of a broader exploration of Athens’ ancient industrial and cultural heritage. Suggested stops include:
- Kerameikos: Ancient potters’ quarter
- National Archaeological Museum: Mycenaean collections (PlanetWare)
- Benaki Museum: Greek material culture (Benaki Museum)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the opening hours?
A: Tuesday to Sunday, generally 8:00/9:00 AM to 3:30/5:00 PM. Closed Mondays. Always check for seasonal changes.
Q: Is there an entry fee?
A: No, entry is free.
Q: Is the site wheelchair accessible?
A: Terrain is uneven and not equipped with ramps; accessible facilities are at nearby metro stations.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: No official tours, but private guides can be arranged.
Q: Are there restrooms or cafes?
A: No; use nearby metro station amenities.
Q: How do I get there from central Athens?
A: Metro Line 2 to Alimos, then a 10–15 minute walk.
Conclusion
Kontopigado is a hidden gem among Athens’ archaeological sites, offering deep insights into Mycenaean industrial organization, technology, and society. Its advanced hydraulic infrastructure, large-scale workshop remains, and ritual features provide a unique perspective on ancient Greek life. While visitor facilities are limited, the site’s proximity to other major attractions and its free entry make it a must-see for archaeology enthusiasts and cultural travelers. For the most up-to-date information on visiting hours, accessibility, and guided tours, consult official resources and consider combining Kontopigado with other highlights of Athens for a comprehensive historical experience.
Discover Kontopigado and unlock a lesser-known chapter of Athens’ extraordinary heritage!