Comprehensive Guide to Visiting the Monument of Lysicrates, Athens, Greece
Date: 19/07/2024
Introduction
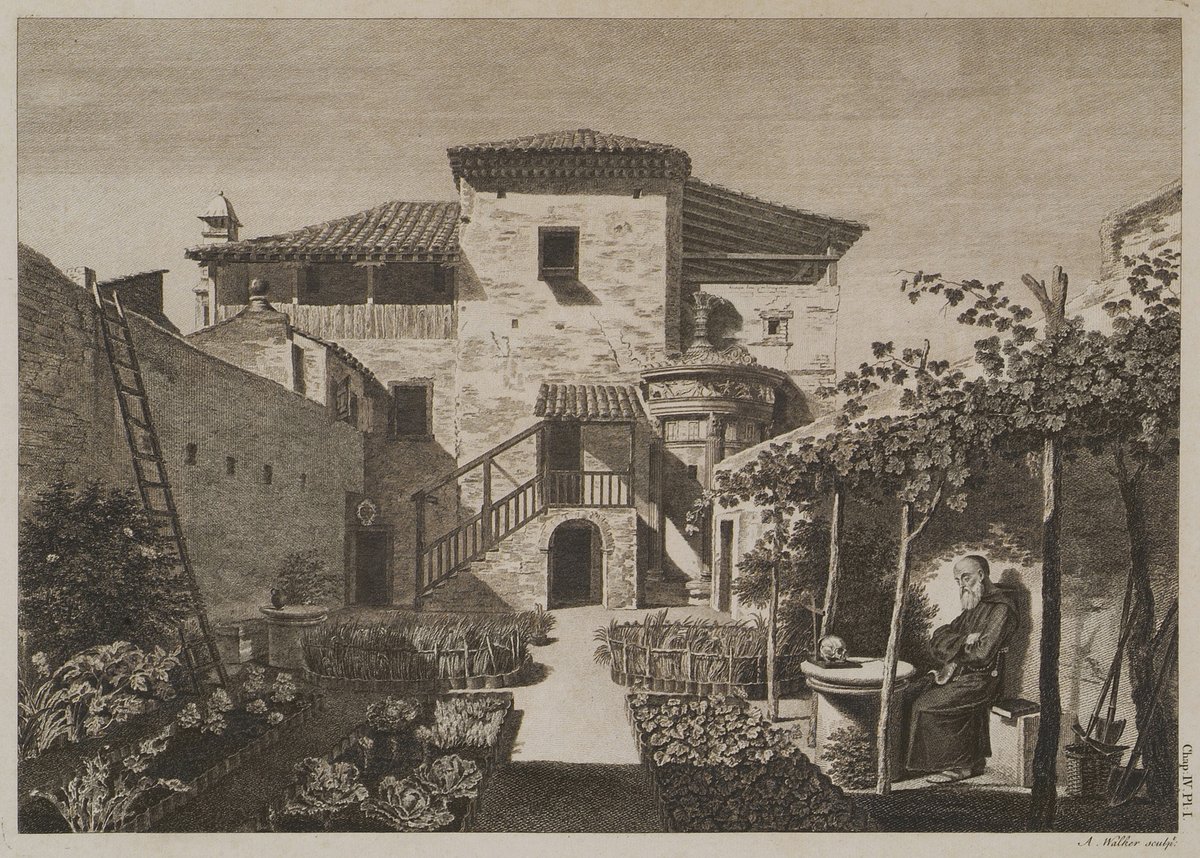
Nestled in the heart of Athens’ historic Plaka district, the Lysicrates Monument, or Μνημείο Λυσικράτους, stands as a timeless testament to the rich cultural and artistic heritage of ancient Greece. Erected in 334 BCE by Lysicrates, a notable patron of the arts, this captivating structure commemorates a victory in a choral competition held during the Dionysia festival, dedicated to the god Dionysus (Ancient Greece). The monument is a prime example of a choragic monument, reflecting the city’s deep connection to theatrical arts and public performances. As one of the earliest uses of the Corinthian order in Greek architecture, the Lysicrates Monument is not only significant for its historical context but also for its architectural innovation (Britannica). This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the monument’s history, cultural significance, visitor information, and nearby attractions, offering a valuable resource for anyone planning to explore this historical gem.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- History of the Lysicrates Monument
- Visiting the Lysicrates Monument
- Preservation and Restoration
- Influence on Later Architecture
- Modern-Day Relevance
- FAQ
- Conclusion
History of the Lysicrates Monument
Origins and Construction
The Lysicrates Monument was built to commemorate a victory in a choral competition held during the Dionysia, a festival dedicated to the god Dionysus. This structure is a prime example of a choragic monument, which celebrated the sponsorship of theatrical performances (Ancient Greece).
Architectural Design
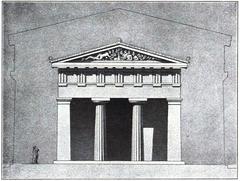
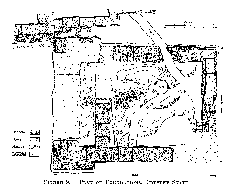
Standing at approximately 9 meters (30 feet) tall, the monument is constructed from Pentelic marble, renowned for its pure white appearance and fine grain. It features a cylindrical tholos supported by six Corinthian columns, marking one of the earliest uses of the Corinthian order in Greek architecture (Britannica).
The tholos is adorned with a frieze depicting scenes from the myth of Dionysus, showcasing the transformation of pirates into dolphins. This intricate carving demonstrates the high level of craftsmanship of the period. Originally, the monument supported a bronze tripod, a prize awarded to the winning choregos (sponsor) of the choral competition (Athens Info Guide).
Historical Significance
The Lysicrates Monument offers valuable insights into the cultural and artistic practices of ancient Athens. The Dionysia festival, during which the monument was erected, was a major cultural event featuring theatrical performances, processions, and sacrifices, highlighting the importance of theater and the arts in Athenian society (Theatre History).
Additionally, the monument is an early example of the Corinthian order, which later became a prominent feature in Roman and Renaissance architecture. Its preservation and study provide valuable information about the evolution of architectural styles and techniques in ancient Greece (Greek Architecture).
Visiting the Lysicrates Monument
Visiting Hours and Tickets
The Lysicrates Monument is accessible to the public year-round. There are no entry fees, making it an excellent addition to any itinerary for those exploring Athens’ historical sites. However, it is recommended to check with local tourist information centers for any changes in visiting hours or special events that might affect access.
Travel Tips
- Location: The monument is located in the Plaka district, near other notable ancient sites such as the Acropolis and the Theatre of Dionysus.
- Accessibility: The area is pedestrian-friendly, but visitors should wear comfortable shoes as the terrain can be uneven.
- Photography: The monument offers excellent photographic opportunities, especially during early morning or late afternoon when the lighting is ideal.
- Nearby Attractions: After visiting the Lysicrates Monument, explore the surrounding Plaka district, known for its charming streets, shops, and restaurants.
Preservation and Restoration
Over the centuries, the Lysicrates Monument has undergone various preservation and restoration efforts. During the Ottoman occupation of Greece, the monument was incorporated into a Capuchin monastery, which helped protect it from potential damage. In the 19th century, following Greece’s independence, the Greek Archaeological Society restored the monument to preserve its historical and cultural significance (Greek Archaeological Society).
Recent conservation efforts have addressed issues related to environmental damage and pollution, including cleaning the marble, stabilizing the structure, and implementing measures to prevent future deterioration. The monument is now a protected site and continues to attract scholars and tourists interested in ancient Greek history and architecture (UNESCO).
Influence on Later Architecture
The Lysicrates Monument has had a lasting influence on architectural design, particularly during the Renaissance and Neoclassical periods. Its use of the Corinthian order and the tholos form inspired numerous architects and designers. Elements of the monument’s design can be seen in the Choragic Monument of Thrasyllus, the Tower of the Winds in Athens, and various structures across Europe and North America (Neoclassical Architecture).
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the monument’s design was replicated in public buildings, memorials, and garden follies. Notable examples include the Choragic Monument of Lysicrates in Sydney, Australia, and the Dugald Stewart Monument in Edinburgh, Scotland. These structures highlight the enduring legacy of ancient Greek architectural principles and their adaptation in different cultural contexts (Sydney Lysicrates Monument).
Modern-Day Relevance
Today, the Lysicrates Monument remains a significant cultural and historical landmark in Athens. Situated in the Plaka district, it is a popular spot for tourists due to its proximity to other ancient sites. The monument is accessible to the public and serves as an educational resource, providing visitors with a tangible connection to ancient Greek history and culture (Visit Greece).
The monument also plays a role in contemporary cultural events. The Lysicrates Foundation, established in 2014, promotes the arts and cultural heritage by organizing events and competitions inspired by the ancient Dionysia festival. This modern initiative underscores the enduring impact of the Lysicrates Monument and its relevance in today’s cultural landscape (Lysicrates Foundation).
FAQ
What are the visiting hours for the Lysicrates Monument? The Lysicrates Monument is accessible to the public year-round. It is recommended to check with local tourist information centers for any changes in visiting hours or special events.
Are there any entry fees to visit the Lysicrates Monument? No, there are no entry fees to visit the Lysicrates Monument.
What are some nearby attractions to the Lysicrates Monument? The monument is located in the Plaka district, near the Acropolis, the Theatre of Dionysus, and other historical sites.
Is the Lysicrates Monument accessible to people with disabilities? The area is pedestrian-friendly, but the terrain can be uneven. Visitors with mobility issues should exercise caution.
Can I take photographs at the Lysicrates Monument? Yes, the monument offers excellent photographic opportunities, especially during early morning or late afternoon.
Conclusion
The Lysicrates Monument is more than just an ancient structure; it is a symbol of Athens’ enduring legacy as a center of classical civilization. From its origins as a commemorative choragic monument to its role in influencing later architectural styles, the monument embodies the rich cultural and artistic achievements of ancient Athens. Today, it remains a must-visit landmark in the Plaka district, offering visitors a tangible connection to the past. Thanks to ongoing preservation efforts and the work of organizations like the Lysicrates Foundation, the monument continues to inspire and educate future generations about the importance of cultural heritage (Lysicrates Foundation). Whether you are a history enthusiast, an architecture aficionado, or simply a curious traveler, the Lysicrates Monument provides an enriching and unforgettable experience. Plan your visit, explore the surrounding historical sites, and immerse yourself in the vibrant history of Athens.
References
- Ancient Greece, 2006, Mark Cartwright source url
- Britannica, 2023, Editors of Encyclopaedia source url
- Athens Info Guide, 2023, Editors source url
- Theatre History, 2023, Editors source url
- Greek Archaeological Society, 2023, Editors source url
- UNESCO, 2023, Editors source url
- Neoclassical Architecture, 2023, Editors of Encyclopaedia source url
- Sydney Lysicrates Monument, 2023, Editors source url
- Visit Greece, 2023, Editors source url
- Lysicrates Foundation, 2023, Editors source url
- Athens Walking Tours, 2023, Editors source url
- Context Travel, 2023, Editors source url
- Rick Steves Audio Europe, 2023, Editors source url