Fortress of Mainz: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Sites Guide
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction to the Fortress of Mainz and Its Cultural Significance
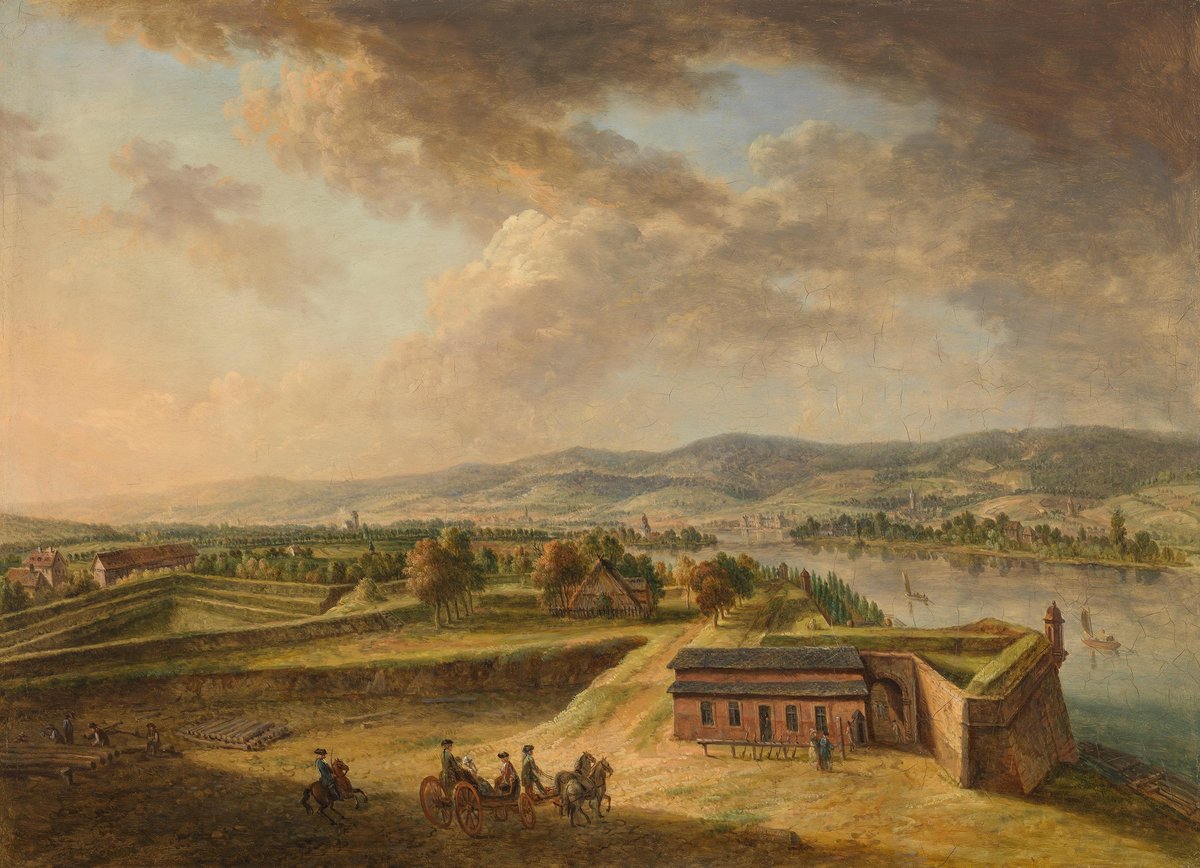
Perched at the strategic juncture where the Rhine and Main rivers meet, the Fortress of Mainz stands as a monumental testament to over two millennia of European military history, urban resilience, and architectural innovation. From its beginnings as the Roman legionary camp Mogontiacum in the 1st century BCE, the site evolved through the Middle Ages, the Renaissance, and the Baroque era, culminating in its role as one of Central Europe’s most formidable fortifications. The fortress—crowned by the star-shaped citadel atop Jakobsberg hill—embodies the cutting-edge military engineering of its time, shaped by renowned architects and influenced by shifting regimes, from the Holy Roman Empire to Napoleonic France and the German Confederation. Today, the Fortress of Mainz is not only a window into the city’s tactical and political significance but also a vibrant cultural venue hosting exhibitions, concerts, and educational events (GermanSights.com; Mainz Citadel - Wikipedia; FORTE CULTURA).
Table of Contents
- Roman Origins and Early Fortifications
- Medieval and Renaissance Expansion
- Baroque Transformation and Star-Shaped Design
- Role in Major Conflicts
- 19th Century Modernization
- 20th Century: World Wars and Decline
- Preservation and Contemporary Use
- Architectural Features and Legacy
- Notable Events and Historical Figures
- Visitor Information: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion and Call to Action
- References
Roman Origins and Early Fortifications
Mainz’s strategic importance was established during the Roman era. Founded as Mogontiacum in the 1st century BCE, it served as a military stronghold on the empire’s northern frontier. Roman engineers constructed a network of defensive walls, towers, and gates to safeguard the settlement and control vital river traffic. Remnants of these Roman defenses remain visible in modern Mainz, affirming the city’s long-standing military heritage (GermanSights.com; Map of Thrones).
Medieval and Renaissance Expansion
After the decline of Roman power, Mainz emerged as a critical urban and ecclesiastical center. Throughout the Middle Ages, the city’s fortifications were expanded to defend against invasions. By the Renaissance, Mainz was among the most fortified cities in the Holy Roman Empire. The establishment of the citadel (Zitadelle) during this period provided a strategic stronghold on Jakobsberg hill, offering panoramic views and effective defense (Tourist Guide Map).
Baroque Transformation and Star-Shaped Design
The 17th and 18th centuries ushered in a dramatic Baroque transformation for Mainz. The fortress adopted the star-shaped bastion system—a hallmark of Baroque military architecture—designed to counter the power of contemporary siege artillery. Architects such as Johann Caspar Bagnato contributed to a layout featuring angular bastions, ravelins, and interconnected defensive structures, including the arsenal and underground casemates (Map of Thrones).
Role in Major Conflicts
Mainz’s fortress played pivotal roles in European conflicts, notably the Thirty Years’ War and the French Revolutionary Wars. The city was besieged, occupied, and reconstructed multiple times, most dramatically under French control during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. The fortress was further strengthened and modernized to adapt to evolving military needs (Map of Thrones).
19th Century Modernization
As advances in artillery made older defenses less effective, Mainz underwent further modernization. The fortress’s defenses expanded to include additional outworks and longer defensive lines, making it one of Central Europe’s largest fortress systems. Its importance grew within the German Confederation, serving as a key military garrison (Map of Thrones).
20th Century: World Wars and Decline
The fortress retained military significance during World War I and World War II, serving variously as a defensive stronghold, barracks, and air-raid shelter. However, modern warfare rendered its defenses obsolete, and heavy wartime destruction led to the partial demolition and repurposing of many fortress structures (Map of Thrones).
Preservation and Contemporary Use
Despite wartime losses, significant elements of the fortress have survived. The citadel is now a protected historical monument and a hub for cultural and educational activities. It houses event spaces, museums, and research facilities, maintaining its relevance in Mainz’s contemporary life (Map of Thrones).
Architectural Features and Legacy
The Fortress of Mainz showcases a blend of architectural styles. Key features include:
- Star-shaped bastions: Maximizing defensive capabilities and minimizing blind spots.
- Casemates and tunnels: Subterranean passages for troop and supply movement.
- Arsenal and barracks: Storage for weapons and provisions.
- Command centers and observation towers: Strategic oversight during military operations.
The fortress’s enduring legacy lies in its layered history—linking Roman origins, medieval expansion, and Baroque grandeur (Tourist Guide Map; GermanSights.com).
Notable Events and Historical Figures
The fortress has witnessed significant historical moments, including the founding of the short-lived Republic of Mainz during the French Revolutionary era. Architects such as Johann Caspar Bagnato and leaders like Prince-Elector Johann Philipp von Schönborn left a lasting mark on its development. The site echoes the turbulent shifts of European history, from the rise and fall of empires to the birth of nation-states.
Visitor Information: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Tips
Visiting Hours:
- Citadel and grounds: 9:00 AM – 6:00 PM (April–October); 9:00 AM – 4:00 PM (November–March).
- Museum and exhibitions: Vary; check the official website.
Tickets:
- Fortress grounds: Free entry.
- Museums and guided tours: €5–€10 per person; discounts available for students, seniors, and groups.
Guided Tours:
- Offered regularly in multiple languages; advance booking recommended.
- Tours access underground casemates and restricted areas.
Accessibility:
- Most outdoor areas accessible; some historic and underground sections may not be.
Tips:
- Wear comfortable shoes; expect cobbled and uneven surfaces.
- Check event calendars for festivals and exhibitions.
- Combine your visit with nearby attractions like Mainz Cathedral, Gutenberg Museum, and the old town.
Travel:
- Easily reached by public transport; limited parking nearby.
- Ideal visit: Spring to early autumn for best weather and event schedules.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the Fortress of Mainz visiting hours?
A: 9:00 AM–6:00 PM (Apr–Oct), 9:00 AM–4:00 PM (Nov–Mar); museum hours may differ.
Q: How much do tickets cost?
A: Grounds are free; guided tours and museums €5–€10.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, in multiple languages; check with the tourism office for schedules.
Q: Is the fortress accessible for people with disabilities?
A: Outdoor areas are largely accessible; some underground areas are not.
Q: What other attractions are nearby?
A: Mainz Cathedral, Gutenberg Museum, Rhine riverfront, and the historic old town.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The Fortress of Mainz is a living monument to European history, blending military innovation, architectural splendor, and cultural vitality. With free access to the grounds, engaging guided tours, and a full calendar of events, it is an essential destination for anyone visiting Mainz. For up-to-date information on Fortress of Mainz visiting hours, tickets, and events, consult the official tourism websites or download the Audiala app for interactive tours and insider tips.
Plan your journey through Mainz’s layered history—explore the imposing bastions, wander the citadel’s ramparts, and immerse yourself in centuries of heritage. For more travel inspiration, follow our related articles and stay connected on social media.
Visuals and Media
- Include high-quality images of the star-shaped bastions, citadel hilltop views, underground casemates, and event spaces (with descriptive alt tags).
- Utilize official tourism websites and heritage portals for virtual tours and interactive maps.
References to Official Sources and Further Reading
- GermanSights.com: Fortress of Mainz Guide
- Mainz Citadel - Wikipedia
- SpottingHistory.com: Mainz Citadel
- FORTE CULTURA: Mainz Fortress
- Fortresses of the German Confederation - Wikipedia
- PlanetWare: Fortress of Mainz
- City of Mainz Official Site: Citadel