Complete Guide to Visiting the Ashmolean Museum, Oxford, UK
Publication Date: 18/07/2024
Introduction to the Ashmolean Museum
The Ashmolean Museum in Oxford, United Kingdom, is a cornerstone of historical and cultural significance. As the world’s first university museum, its establishment in 1683 marked a pivotal moment in the history of museums. Founded by Elias Ashmole, who donated his extensive collection to the University of Oxford, the museum has grown exponentially over the centuries. Its collections now span a diverse range of artifacts, from ancient Egyptian relics to contemporary art, making it a must-visit for history buffs, art enthusiasts, and casual visitors alike (Ashmolean Museum History).
The architectural evolution of the Ashmolean Museum is equally noteworthy. Initially housed in a building designed by Thomas Wood, the museum moved to its current neoclassical structure on Beaumont Street in the 19th century, designed by Charles Cockerell. This architectural journey culminated in a significant redevelopment in 2009, led by Rick Mather Architects, which modernized the museum’s facilities and doubled its display space (Ashmolean Museum Architecture).
The Ashmolean Museum is not just a repository of artifacts but a dynamic institution committed to education, research, and public engagement. It offers a variety of educational programs, guided tours, and special events that enrich the visitor experience. Additionally, the museum’s commitment to accessibility ensures that it remains an inclusive space for all visitors (Ashmolean Museum Education; Ashmolean Museum Accessibility).
As you delve into this comprehensive guide, you’ll find detailed information about the museum’s history, architectural evolution, significant collections, visiting hours, and much more. Whether you’re planning a visit or simply curious about this iconic institution, this guide will provide you with all the essential information you need to appreciate the Ashmolean Museum fully.
Contents Overview
- Introduction
- Origins and Foundation
- Architectural Evolution
- Significant Expansions
- Collections and Exhibitions
- Visiting Information
- Visiting Hours
- Tickets
- Special Events and Guided Tours
- Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Accessibility
- Educational and Research Contributions
- Technological Advancements
- Cultural Impact and Legacy
- Notable Directors and Curators
- Community Engagement and Outreach
- Future Prospects
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Origins and Foundation
The Ashmolean Museum, located in Oxford, United Kingdom, is renowned as the world’s first university museum. Its origins date back to 1677 when Elias Ashmole, an antiquary and collector, donated his collection to the University of Oxford. Ashmole’s collection included artifacts, books, manuscripts, and natural specimens, which he had inherited from the Tradescant family, notable collectors of the time. The museum officially opened its doors to the public in 1683, housed in a building designed by Thomas Wood. This establishment marked a significant milestone in the history of museums, setting a precedent for future institutions (Ashmolean Museum History).
Architectural Evolution
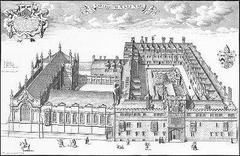
The original building, known as the Old Ashmolean, was a three-story structure featuring a lecture hall, a chemical laboratory, and display rooms. Over the centuries, the museum underwent several expansions and renovations to accommodate its growing collection. In the 19th century, the museum moved to its current location on Beaumont Street, designed by Charles Cockerell in a neoclassical style. This new building, completed in 1845, provided a more spacious and grand setting for the museum’s extensive collections (Ashmolean Museum Architecture).
Significant Expansions
The Ashmolean Museum has seen numerous significant expansions throughout its history. One of the most notable was the addition of the Randolph Galleries in 1894, funded by a bequest from Dr. Henry William Acland. These galleries were designed to house the museum’s growing collection of art and antiquities. Another major expansion occurred in 2009, with the opening of the new Ashmolean building designed by Rick Mather Architects. This £61 million redevelopment project doubled the museum’s display space and introduced modern facilities, including a rooftop restaurant and state-of-the-art conservation studios (Ashmolean Museum Expansion).
Collections and Exhibitions
The Ashmolean Museum’s collections have grown exponentially since its inception, encompassing a wide range of artifacts from different cultures and time periods. The museum’s holdings include ancient Egyptian mummies, classical sculptures, Renaissance paintings, and contemporary art. Notable pieces include the Alfred Jewel, a 9th-century Anglo-Saxon artifact, and the Parian Marble, an ancient Greek chronicle. The museum also hosts temporary exhibitions, showcasing works from renowned artists and exploring various historical themes (Ashmolean Museum Collections).
Visiting Information
Visiting Hours
The Ashmolean Museum is open Tuesday to Sunday from 10:00 AM to 5:00 PM, and it is closed on Mondays. Special holiday hours may apply, so it is advisable to check the museum’s website for up-to-date information (Ashmolean Museum Visiting Hours).
Tickets
Admission to the Ashmolean Museum is free, but donations are welcomed to support the museum’s activities and preservation efforts. Some special exhibitions may require a ticket, which can be purchased online or at the museum’s entrance (Ashmolean Museum Tickets).
Special Events and Guided Tours
The Ashmolean Museum offers a variety of special events and guided tours throughout the year. These include lectures, workshops, and themed tours that provide deeper insights into the museum’s collections and exhibitions. Visitors can check the museum’s event calendar for upcoming activities (Ashmolean Museum Events).
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
When visiting the Ashmolean Museum, consider exploring other historical sites in Oxford, such as the Bodleian Library, the Radcliffe Camera, and the Oxford University Museum of Natural History. The museum is conveniently located near public transportation and various dining options, making it easy to plan a full day of cultural exploration (Oxford Historical Sites).
Accessibility
The Ashmolean Museum is committed to accessibility and provides various services to ensure all visitors have a positive experience. The museum offers wheelchair access, accessible restrooms, and assistance for visitors with visual and hearing impairments. For more detailed information, visitors can consult the museum’s accessibility guide (Ashmolean Museum Accessibility).
Educational and Research Contributions
The Ashmolean Museum has played a pivotal role in education and research since its foundation. It serves as a vital resource for students and scholars, offering access to its extensive collections and archives. The museum’s education department provides a range of programs and workshops for schools, families, and adult learners. Additionally, the Ashmolean collaborates with academic institutions and researchers worldwide, contributing to the advancement of knowledge in fields such as archaeology, art history, and conservation (Ashmolean Museum Education).
Technological Advancements
In recent years, the Ashmolean Museum has embraced technological advancements to enhance the visitor experience and improve access to its collections. The museum’s website features a comprehensive online database, allowing users to explore its collections from anywhere in the world. Interactive displays and multimedia guides within the museum provide visitors with in-depth information about the exhibits. The Ashmolean also utilizes social media platforms to engage with a global audience and promote its exhibitions and events (Ashmolean Museum Technology).
Cultural Impact and Legacy
The Ashmolean Museum has had a profound cultural impact, both locally and internationally. It has inspired generations of visitors, artists, and scholars, fostering a greater appreciation for art and history. The museum’s commitment to accessibility and public engagement has made it a beloved institution in Oxford and beyond. Its legacy continues to evolve, as it adapts to the changing needs of its audience and embraces new opportunities for growth and innovation (Ashmolean Museum Legacy).
Notable Directors and Curators
The Ashmolean Museum has been shaped by the vision and leadership of numerous notable directors and curators. One of the most influential figures in the museum’s history was Sir Arthur Evans, who served as Keeper of the Ashmolean from 1884 to 1908. Evans is best known for his archaeological work at Knossos in Crete, where he uncovered the remains of the Minoan civilization. Other prominent directors include Sir David Piper, who oversaw the museum’s expansion in the 1970s, and Dr. Christopher Brown, who led the 2009 redevelopment project (Ashmolean Museum Directors).
Community Engagement and Outreach
The Ashmolean Museum is dedicated to engaging with the local community and fostering a sense of inclusivity. The museum offers a variety of outreach programs, including workshops, lectures, and community events. These initiatives aim to make the museum’s collections and resources accessible to diverse audiences, including underrepresented groups. The Ashmolean also collaborates with local schools, community organizations, and cultural institutions to promote lifelong learning and cultural enrichment (Ashmolean Museum Community).
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the Ashmolean Museum continues to pursue its mission of preserving and sharing its collections with the world. Future plans include further expansions, new exhibitions, and innovative educational programs. The museum remains committed to sustainability and environmental responsibility, implementing green practices in its operations and facilities. As it approaches its 350th anniversary, the Ashmolean Museum stands as a testament to the enduring value of art, history, and culture (Ashmolean Museum Future).
FAQs
What are the Ashmolean Museum’s visiting hours?
The museum is open Tuesday to Sunday from 10:00 AM to 5:00 PM, and it is closed on Mondays.
Is there an admission fee?
Admission to the museum is free, but donations are welcomed. Some special exhibitions may require a ticket.
Are guided tours available?
Yes, the museum offers a variety of guided tours and special events throughout the year.
How can I get to the Ashmolean Museum?
The museum is located on Beaumont Street in Oxford, near public transportation options and other historical sites.
Is the museum accessible?
Yes, the museum provides various accessibility services, including wheelchair access and assistance for visitors with visual and hearing impairments.
Stay Updated
To stay up to date with the latest news and events at the Ashmolean Museum, follow the museum on social media and download the mobile app Audiala. Check out other related posts on our website for more information on Oxford’s historical sites and cultural offerings.
Summary and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the Ashmolean Museum stands as a testament to the enduring value of art, history, and culture. From its origins as the world’s first university museum to its current status as a leading cultural institution, the Ashmolean has continually evolved to meet the needs of its visitors and the academic community. Its extensive collections, ranging from ancient Egyptian artifacts to contemporary art, offer something for everyone, making it a must-visit destination in Oxford (Ashmolean Museum Collections).
The museum’s architectural evolution, marked by significant expansions and modernizations, reflects its ongoing commitment to accessibility and innovation. The 2009 redevelopment project, in particular, has enhanced the visitor experience by providing state-of-the-art facilities and expanded exhibition spaces (Ashmolean Museum Expansion).
The Ashmolean’s dedication to education and research is evident in its numerous programs, workshops, and collaborations with academic institutions worldwide. Its role as a center for research and conservation underscores its importance as a steward of cultural heritage (Ashmolean Museum Research).
As the Ashmolean approaches its 350th anniversary, it continues to adapt and innovate, ensuring that it remains a relevant and dynamic institution for future generations. Whether you’re a local resident or a tourist, a visit to the Ashmolean Museum promises a rich and rewarding experience. For more information, visit the Ashmolean Museum’s official website.
Cited Sources and Further Reading
- Ashmolean Museum History. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ashmolean.org/history
- Ashmolean Museum Architecture. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ashmolean.org/architecture
- Ashmolean Museum Expansion. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ashmolean.org/expansion
- Ashmolean Museum Collections. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ashmolean.org/collections
- Ashmolean Museum Education. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ashmolean.org/education
- Ashmolean Museum Accessibility. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ashmolean.org/accessibility
- Ashmolean Museum Research. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ashmolean.org/research