Templum Castoris: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Significance in Rome
Date: 01/08/2024
Introduction
The Templum Castoris, also known as the Temple of Castor and Pollux, stands as a monumental testament to Rome’s rich historical and cultural heritage. Situated in the heart of the Roman Forum, this ancient temple was originally constructed in 484 BC to commemorate the Roman victory at the Battle of Lake Regillus. According to legend, the twin gods Castor and Pollux, sons of Zeus and Leda, appeared on the battlefield, aiding the Romans in their triumph. This divine intervention not only cemented their place in Roman mythology but also led to the establishment of their cult in Rome, heavily influenced by Greek traditions brought over from Magna Graecia (Wikipedia).
Over the centuries, the Templum Castoris underwent numerous reconstructions, reflecting the evolving architectural styles and political aspirations of the Roman elites. Significant reconstructions occurred in 117 BC under Lucius Caecilius Metellus Dalmaticus and later in 6 AD by Emperor Tiberius, who dedicated the temple to his deceased brother Drusus. These reconstructions enhanced the temple’s grandeur and reinforced the political legitimacy of those who commissioned them (CoopCulture).
Beyond its architectural beauty, the Templum Castoris played a crucial role in the social and political life of ancient Rome. It served as a venue for public meetings, judicial proceedings, and religious ceremonies, making it a focal point for various civic activities. The temple’s prominence in Roman society is further underscored by events like the annual ‘Transvectio Equitum,’ a grand parade of knights that celebrated the Dioscuri’s association with the Roman cavalry (Sygic Travel).
Table of Contents
The Fascinating History of Templum Castoris in Rome
Origins and Construction
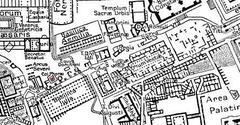
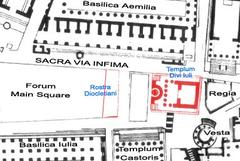
The Templum Castoris, or the Temple of Castor and Pollux, is an ancient Roman temple located in the Roman Forum in Rome, Italy. The temple was originally constructed in 484 BC to commemorate the Roman victory at the Battle of Lake Regillus. According to legend, the Dioscuri, Castor and Pollux, appeared on the battlefield and aided the Romans in their victory. The Dioscuri were the twin sons of Zeus and Leda, and their cult was brought to Rome from Greece via Magna Graecia and the Greek culture of Southern Italy (Wikipedia).
Architectural Evolution
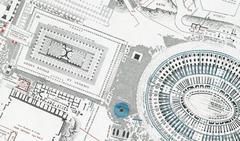
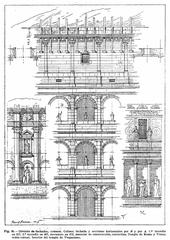
The initial structure of the temple was relatively modest, but it underwent several reconstructions and renovations over the centuries. The most significant reconstruction occurred in 117 BC under the consulship of Lucius Caecilius Metellus Dalmaticus. This renovation transformed the temple into a grander and more elaborate structure, reflecting the increasing importance of the Dioscuri cult in Roman society.
In 6 AD, the temple was once again rebuilt by Emperor Tiberius, who dedicated it to his deceased brother Drusus. This reconstruction was part of a broader effort by Tiberius to associate his family with the divine twins, thereby enhancing their political legitimacy. The temple’s final form featured a high podium, a deep pronaos (porch), and a cella (inner chamber) with a richly decorated interior (CoopCulture).
Role in Roman Society
The Templum Castoris played a significant role in the social and political life of ancient Rome. It served not only as a religious site but also as a venue for public meetings and judicial proceedings. The temple’s prominent location in the Roman Forum made it a focal point for various civic activities.
The Dioscuri were revered as protectors of the Roman state and military, and their temple was a symbol of Roman martial prowess. The annual festival of the Dioscuri, known as the ‘Transvectio Equitum,’ featured a grand parade of knights (equites) who rode through the streets of Rome in full military regalia, culminating at the temple. This event underscored the close association between the Dioscuri and the Roman cavalry (Sygic Travel).
Decline and Rediscovery
With the decline of the Roman Empire, the Templum Castoris fell into disrepair. By the 4th century AD, the temple had been largely abandoned, and its materials were repurposed for other construction projects. The once-grand structure was reduced to ruins, and its significance faded from public memory.
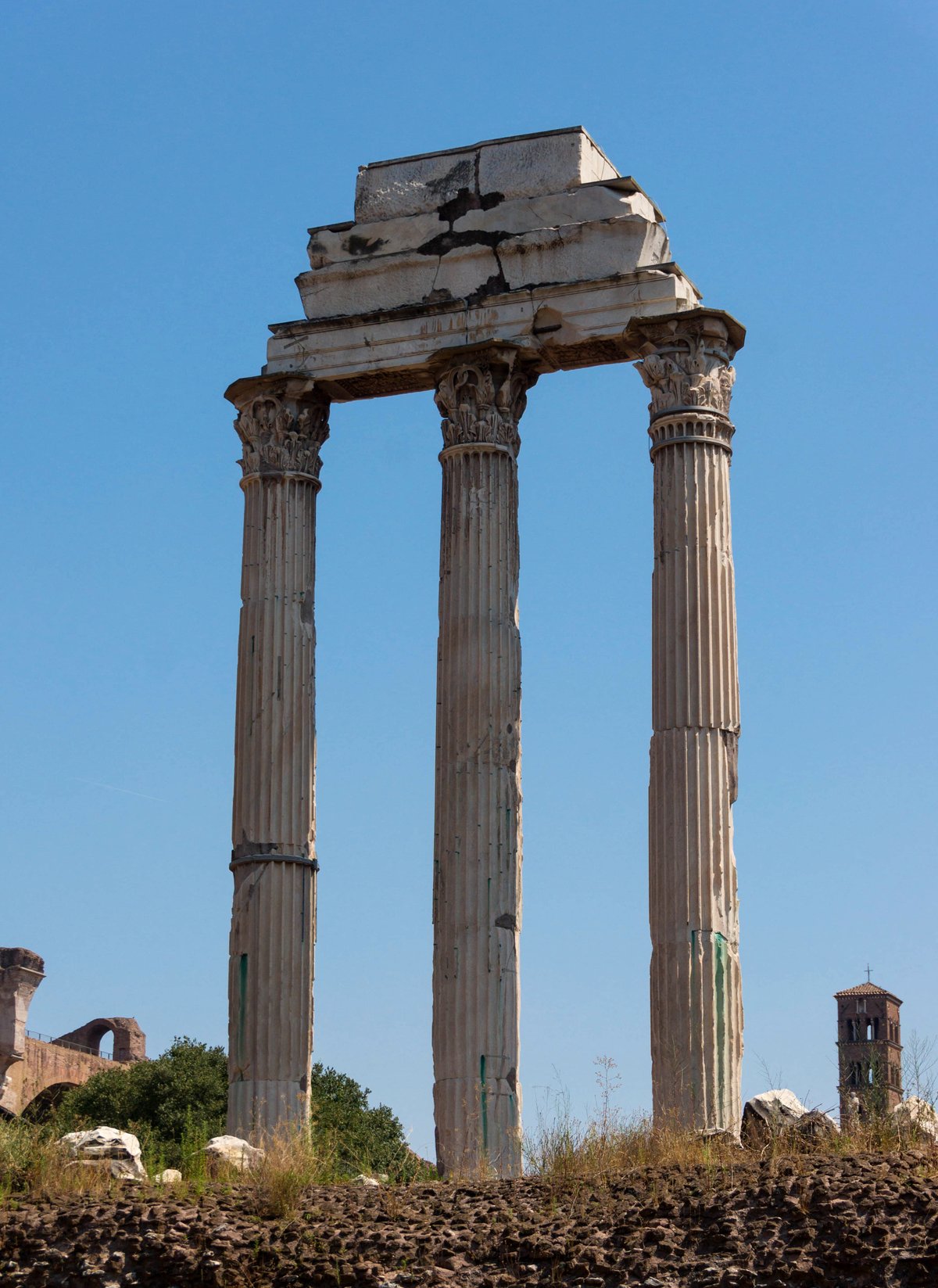
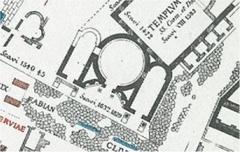
The temple remained in a state of neglect for centuries until it was rediscovered during the Renaissance. Archaeological excavations in the 19th and 20th centuries revealed the temple’s foundations and surviving architectural elements, including three Corinthian columns that still stand today. These columns, often referred to as the ‘Three Columns,’ have become an iconic symbol of the Roman Forum and a testament to the grandeur of ancient Roman architecture (Wikipedia).
Modern Significance and Visitor Information
Modern Significance
Today, the Templum Castoris is a popular tourist attraction and an important archaeological site. Visitors to the Roman Forum can explore the temple’s remains and gain insight into the religious and civic life of ancient Rome. The temple’s surviving columns and podium provide a glimpse into the architectural splendor of the Roman Republic and Empire.
The Templum Castoris is also a valuable resource for historians and archaeologists studying the evolution of Roman religious practices and architectural styles. Ongoing research and conservation efforts aim to preserve the temple’s remains and enhance our understanding of its historical significance.
Visiting Hours and Admission Fees
The Templum Castoris is part of the Roman Forum complex, and admission is included in a two-day combined ticket that also grants access to the Colosseum and Palatine Hill. The site is open daily, with varying hours depending on the season:
- Last Oct Sun - Feb 15: 8:30 am - 4:30 pm
- Feb 16 - Mar 15: 8:30 am - 5 pm
- Mar 16 - last Mar Sat: 8:30 am - 5:30 pm
- Last Mar Sun - Aug 31: 8:30 am - 7:15 pm
- Sep 1 - Sep 30: 8:30 am - 7 pm
- Oct 1 - Oct 24: 8:30 am - 6:30 pm
The site is closed on January 1, May 1, and December 25. Visitors are advised to check the official website for the most up-to-date information on opening hours and ticket prices (Sygic Travel).
The admission fees for the Roman Forum, including the Templum Castoris, are as follows:
- Adults: €12
- EU citizens (18-25): €7.50
- Online reservation fee: €2
These fees are subject to change, so it is recommended to verify the current prices on the official website before planning a visit (CoopCulture).
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Travel Tips: Wear comfortable shoes, as the Roman Forum is expansive and involves a lot of walking. Bring water and a hat, especially during the summer months, as there is limited shade.
- Nearby Attractions: While visiting the Templum Castoris, consider exploring other nearby historical sites such as the Colosseum, Palatine Hill, and the Arch of Titus.
- Accessibility: The Roman Forum has uneven terrain, which may be challenging for visitors with mobility issues. However, there are ramps and pathways designed to improve accessibility.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the best time to visit the Templum Castoris? A: The best time to visit is early in the morning or late in the afternoon to avoid the midday crowds and heat.
Q: Are guided tours available at the Templum Castoris? A: Yes, guided tours are available and are an excellent way to learn more about the history and significance of the temple.
Q: Is photography allowed at the Templum Castoris? A: Yes, photography is allowed, but tripods and professional equipment may require special permits.
Conclusion
Today, the Templum Castoris stands as a revered archaeological site and a popular tourist attraction, offering visitors a unique glimpse into the religious, social, and architectural history of ancient Rome. Although the temple fell into disrepair with the decline of the Roman Empire, its rediscovery during the Renaissance and subsequent archaeological excavations have preserved its legacy. The surviving Corinthian columns, often referred to as the ‘Three Columns,’ symbolize the enduring grandeur of Roman architecture and continue to captivate historians and tourists alike (Wikipedia).
Visiting the Templum Castoris provides an enriching experience, allowing one to explore the remnants of a site that once played a pivotal role in Roman society. With its inclusion in the Roman Forum complex, visitors can delve deeper into Rome’s ancient history, complemented by nearby attractions such as the Colosseum and Palatine Hill. By following practical tips on visiting hours, ticket information, and accessibility, one can fully appreciate the historical significance and architectural splendor of this iconic temple (CoopCulture). For more detailed planning and updates, visitors are encouraged to check official resources and travel guides.
References
- Wikipedia, 2023, Temple of Castor and Pollux Wikipedia
- CoopCulture, 2023, Heritage Information CoopCulture
- Sygic Travel, 2023, Temple of Castor and Pollux Sygic Travel