A Complete Guide to Aqua Marcia: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Rome’s Historical Sites
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction: The Legacy of Aqua Marcia in Rome
Aqua Marcia stands as one of ancient Rome’s crowning engineering achievements. Built between 144 and 140 BCE, it was commissioned by the Roman Senate to address the capital’s ever-growing need for clean, abundant water. Overseen by the praetor Quintus Marcius Rex, this aqueduct stretched approximately 91 kilometers (57 miles), making it the longest among Rome’s legendary aqueducts. Funded by Rome’s military victories, notably the conquest of Corinth and Carthage, Aqua Marcia embodied both Roman innovation and prosperity.
Renowned for delivering water of exceptional purity and coldness from the Anio valley, the aqueduct’s design featured underground channels, monumental arches, and advanced inspection shafts—testament to Roman engineering prowess. Today, the remains of Aqua Marcia, especially at the Parco degli Acquedotti and other open-air sites, offer a fascinating journey into the city’s urban and technological evolution. This guide provides everything you need to plan your visit, including historical background, practical travel tips, ticketing information, and recommendations for nearby attractions (Wikipedia, SpottingHistory, Parco degli Acquedotti official tourism page).
Table of Contents
- Origins and Construction
- Engineering and Route
- Technical Achievements and Innovations
- Water Quality and Distribution
- Historical Significance and Legacy
- Visiting Aqua Marcia: Hours, Tickets & Travel Tips
- Nearby Attractions and Events
- FAQs: Aqua Marcia Visiting Essentials
- Preservation and Modern Relevance
- Plan Your Visit & Stay Connected
- Sources
Origins and Construction
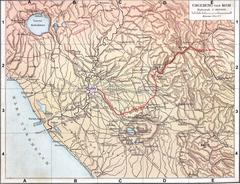
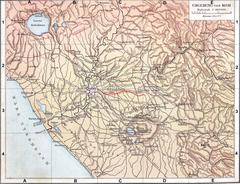
Aqua Marcia emerged as a response to the failing capacity of earlier aqueducts like Aqua Appia and Aqua Anio Vetus, which had become insufficient due to age and illegal diversions. The Senate chose Quintus Marcius Rex for this ambitious project, leveraging the spoils of recent conquests to fund a new aqueduct of unprecedented length and complexity (Wikipedia). Its source in the Anio valley was carefully selected for water quality, and the route, at 91 kilometers, made Aqua Marcia the longest of Rome’s ancient aqueducts (SpottingHistory).
Engineering and Route
Aqua Marcia’s water originated between Arsoli and Marano Equo in the Anio valley, east of Rome. The aqueduct was predominantly underground for its first 80 kilometers, safeguarding quality and minimizing evaporation. As it neared the city, it rose onto monumental arches for the final 11 kilometers—a pioneering feature that became a model for later aqueducts (Wikipedia). The route included engineering feats like bridges (Ponte Lupo, Ponte San Pietro) and tunnels, skillfully navigating the challenging terrain.
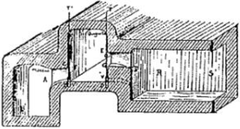
Technical Achievements and Innovations
Among the “four great aqueducts of Rome,” Aqua Marcia introduced several technical milestones. It was the first to enter the city on a grand arcade, maintaining a precise gradient for optimal water flow. Regularly spaced inspection shafts (putei) and service tunnels, like the 230-meter-long Bullica tunnel, demonstrated a commitment to maintenance and longevity (SpottingHistory).
Water Quality and Distribution
Aqua Marcia’s water was famed for its coldness and purity. According to ancient commissioner Frontinus, its daily flow was among the highest in Rome, supplying essential water for public baths, fountains, and households. The aqueduct’s branches served both the Quirinal and Capitoline hills, with additional distribution reservoirs near the present-day Via XX Settembre (Wikipedia).
Historical Significance and Legacy
The construction of Aqua Marcia marked a turning point in urban development, enabling Rome’s rapid growth and supporting its iconic public baths. Over centuries, it endured periods of neglect, with emperors occasionally restoring its capacity due to private diversions. Its route was reused by later waterworks, such as the Acqua Felice in the Renaissance, and many original arches and bridges still stand as a testament to its builders (SpottingHistory).
Visiting Aqua Marcia: Hours, Tickets & Travel Tips
Visiting Hours & Entry
Aqua Marcia’s remains are predominantly open-air archaeological sites, especially at Parco degli Acquedotti, and are accessible year-round. There is no entrance fee to visit the visible arches and ruins.
- Parco degli Acquedotti: Open daily, generally from 7:00 AM to sunset (turismoroma.it).
- Other Sites: Outdoor sections are accessible during daylight hours for safety and preservation.
Accessibility
- Terrain is mostly flat but can be uneven near ruins.
- Some paths are wheelchair accessible, but check local details for specific areas.
Getting There
- By Metro: Line A (Lucio Sestio, Giulio Agricola, or Subaugusta stations), followed by a short walk.
- By Bus: Multiple lines serve the area from central Rome.
- By Car: Limited parking; public transport is recommended.
Guided Tours & Best Photography Spots
- Guided Tours: Available through local providers, often combining Aqua Marcia with other aqueducts and archaeological parks.
- Best Photography: Monumental arches at golden hour, especially at Parco degli Acquedotti and Ponte Lupo, provide stunning backdrops (myadventuresacrosstheworld.com).
Nearby Attractions and Events
Combine your visit with:
- Appian Way (Via Appia Antica): Explore ancient roads, tombs, and catacombs.
- Baths of Caracalla: A monumental bath complex once supplied by branches of Aqua Marcia.
- Porta Maggiore: A major city gate where several aqueducts converged.
- Special Events: Occasional open-air concerts, reenactments, and guided walks—check the Parco Regionale dell’Appia Antica website for updates.
FAQs: Aqua Marcia Visiting Essentials
Q: Are tickets required to visit Aqua Marcia?
A: No, most visible sections are free to visit. Guided tours may require a fee.
Q: What are the best visiting hours?
A: Daylight hours—early morning or late afternoon—for comfort and photos.
Q: Is public transport available?
A: Yes, Metro Line A and several buses serve the main sites.
Q: Are guided tours recommended?
A: Yes, for in-depth history and best site access.
Q: Is the park family-friendly?
A: Absolutely, with open spaces for children and group visits.
Preservation and Modern Relevance
Sections of Aqua Marcia continue to shape Rome’s landscape and heritage. The aqueduct’s source still contributes to Rome’s water supply, and its route offers an enduring lesson in ancient infrastructure (Wikipedia). Conservation efforts protect the arches and bridges for future generations, while modern studies of Roman materials inspire today’s engineers.
Plan Your Visit & Stay Connected
- Plan Ahead: Review opening hours, check weather, and download digital guides for a richer experience.
- Use the Audiala App: Access audio guides, maps, and real-time updates for Rome’s historical sites.
- Stay Informed: Follow official park and tourism websites, and check social media for events and tips.
Summary & Recommendations
Aqua Marcia, with its towering arches and storied past, offers a vivid connection to Rome’s ancient ingenuity and civic spirit. Its remains, especially at Parco degli Acquedotti, are freely accessible and surrounded by other historical landmarks that deepen any visit to the Eternal City. For the best experience:
- Visit during daylight for safety and optimal photography.
- Wear comfortable shoes and bring water/snacks.
- Consider a guided tour for expert insights.
- Respect the site’s archaeological integrity.
Aqua Marcia is more than a monument—it’s a living chapter in Rome’s ongoing story of innovation, resilience, and cultural achievement. For more information, consult sources like Wikipedia, SpottingHistory, and the Parco degli Acquedotti tourism guide.
Sources and Official Links for Further Information
- Aqua Marcia, Wikipedia
- SpottingHistory: Aqua Marcia
- Parco degli Acquedotti official tourism page
- Wanted in Rome: Rome’s Ancient Aqueducts
- Appia Antica Regional Park
- myadventuresacrosstheworld.com: Parco degli Acquedotti guide
- historytools.org: Acqua Marcia – The Lifeblood of Ancient Rome
- engineeringrome.org: Aqua Marcia as Roman Infrastructure