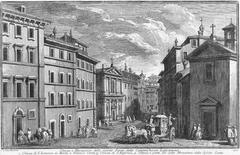Guide to Visiting Piazza del Campidoglio, Rome
Published Date: 17/07/2024
Introduction to Piazza del Campidoglio
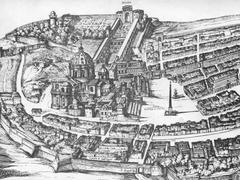
Piazza del Campidoglio, an exceptional blend of historical grandeur and architectural brilliance, is one of Rome’s most iconic landmarks. Situated on the Capitoline Hill, one of the seven hills of ancient Rome, this square has been a focal point of the city’s political and religious activities since antiquity. Designed by the legendary Michelangelo Buonarroti in the 16th century at the behest of Pope Paul III, the piazza was intended to showcase the magnificence of Rome to the visiting Holy Roman Emperor Charles V (Rome Reborn). Michelangelo’s innovative design features a harmonious trapezoidal layout, a grand staircase known as the Cordonata, and a central equestrian statue of Marcus Aurelius, which collectively create a space of extraordinary aesthetic and symbolic significance (Capitoline Museums). Over the centuries, Piazza del Campidoglio has evolved while retaining its historical essence, serving as a testament to Rome’s ability to blend its rich past with modern needs (Rome Art Lover). Visitors to this remarkable site can immerse themselves in a journey through time, exploring the Capitoline Museums’ vast collection of ancient and Renaissance art, and enjoying panoramic views of Rome’s historical landscape (Rome.net).
Table of Contents
- [Historical Background of Piazza del Campidoglio](#historical-background-of-piazza-del-campidogliohistorical-background-of-piazza-del-campidoglio)
- [Ancient Origins](#ancient-originsancient-origins)
- [Medieval Period](#medieval-periodmedieval-period)
- [Renaissance Transformation](#renaissance-transformationrenaissance-transformation)
- [Architectural Elements](#architectural-elementsarchitectural-elements)
- [The Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius](#the-equestrian-statue-of-marcus-aureliusthe-equestrian-statue-of-marcus-aurelius)
- [Symbolic Significance](#symbolic-significancesymbolic-significance)
- [Modern Developments](#modern-developmentsmodern-developments)
- [Visitor Information](#visitor-informationvisitor-information)
- [Visiting Hours and Tickets](#visiting-hours-and-ticketsvisiting-hours-and-tickets)
- [Travel Tips](#travel-tipstravel-tips)
- [Nearby Attractions](#nearby-attractionsnearby-attractions)
- [Accessibility](#accessibilityaccessibility)
- [Preservation Efforts](#preservation-effortspreservation-efforts)
- [Visitor Experience](#visitor-experiencevisitor-experience)
- [FAQ](#faqfaq)
- [Conclusion](#conclusionconclusion)
- [Call to Action](#call-to-actioncall-to-action)
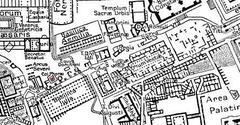
Historical Background of Piazza del Campidoglio
Ancient Origins
Piazza del Campidoglio, located on the Capitoline Hill, is one of the most historically significant sites in Rome. The Capitoline Hill, known as “Mons Capitolinus” in Latin, was one of the seven hills on which ancient Rome was founded. It served as the political and religious heart of the city. The hill was home to the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, the most important temple in ancient Rome, dedicated to the king of the gods (Rome Reborn).
Medieval Period
During the Middle Ages, the Capitoline Hill fell into disrepair. The once-grand temples and public buildings were abandoned or repurposed. The area became a maze of narrow streets and dilapidated structures. However, the hill retained its symbolic importance, and it was here that the Senate of Rome continued to meet. The medieval period saw the construction of the Palazzo Senatorio, which served as the seat of the municipal government (Capitoline Museums).
Renaissance Transformation
The transformation of Piazza del Campidoglio into its current form began in the 16th century under the direction of Michelangelo Buonarroti. In 1536, Holy Roman Emperor Charles V visited Rome, prompting Pope Paul III to commission Michelangelo to redesign the square to impress the emperor. Michelangelo’s design was revolutionary, featuring an innovative trapezoidal plan that created a sense of order and harmony. The centerpiece of the piazza was the equestrian statue of Marcus Aurelius, which Michelangelo relocated from the Lateran Palace (Michelangelo’s Rome).
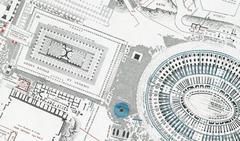
Architectural Elements
Michelangelo’s design included the construction of new buildings and the renovation of existing ones. The Palazzo Senatorio, originally built in the 12th century, was given a new façade and a grand double staircase. The Palazzo dei Conservatori and the Palazzo Nuovo were constructed to flank the square, creating a cohesive architectural ensemble. The buildings were adorned with classical elements, such as pilasters and cornices, reflecting the Renaissance revival of ancient Roman architecture (Great Buildings).
The Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius
The equestrian statue of Marcus Aurelius is one of the most iconic features of Piazza del Campidoglio. The statue dates back to the 2nd century AD and is the only surviving bronze statue of a pre-Christian Roman emperor. It was mistakenly believed to represent Constantine the Great, which likely saved it from being melted down during the Middle Ages. The statue was moved to the Capitoline Hill in 1538 as part of Michelangelo’s redesign. Today, the original statue is housed in the Capitoline Museums, and a replica stands in the piazza (Capitoline Museums).
Symbolic Significance
Piazza del Campidoglio holds immense symbolic significance for Rome and Italy. It represents the continuity of Rome’s history, from its ancient origins through the medieval period and into the Renaissance. The piazza is a testament to the city’s ability to reinvent itself while preserving its historical legacy. It also symbolizes the power and authority of the municipal government, which has been based on the Capitoline Hill for centuries (Rome Art Lover).
Modern Developments
In the 20th century, Piazza del Campidoglio underwent further changes to accommodate modern needs while preserving its historical integrity. The square was pedestrianized, and the surrounding buildings were restored. The Capitoline Museums, housed in the Palazzo dei Conservatori and the Palazzo Nuovo, were expanded to display a vast collection of ancient Roman art and artifacts. The piazza continues to be a focal point for civic events and ceremonies, reflecting its enduring importance in the life of the city (Rome.info).
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Tickets
The Piazza del Campidoglio is open to the public 24 hours a day. However, the Capitoline Museums have specific visiting hours. They are generally open from 9:30 AM to 7:30 PM, Tuesday through Sunday. Ticket prices for the museums vary, with standard tickets costing around €15. It is recommended to check the official website for the most up-to-date information on visiting hours and ticket prices (Capitoline Museums).
Travel Tips
When visiting Piazza del Campidoglio, it is advisable to wear comfortable shoes as the area includes cobblestone streets and stairs. The best time to visit is early in the morning or late in the afternoon to avoid large crowds. Guided tours are available and can provide valuable insights into the history and significance of the site.
Nearby Attractions
Piazza del Campidoglio is situated near several other historical sites in Rome. The Roman Forum, Colosseum, and Palatine Hill are all within walking distance. Visitors can easily spend an entire day exploring these iconic landmarks. Additionally, the nearby Piazza Venezia offers more historical and cultural experiences.
Accessibility
Piazza del Campidoglio is accessible to visitors with disabilities. Ramps and elevators are available to accommodate wheelchairs, and the Capitoline Museums offer services for visitors with special needs. It is recommended to contact the museums in advance to arrange any necessary accommodations.
Preservation Efforts
Preservation efforts have been crucial in maintaining the historical and architectural integrity of Piazza del Campidoglio. The Italian government and various cultural organizations have invested in the restoration and conservation of the buildings and artworks in the piazza. These efforts ensure that future generations can continue to appreciate the rich history and cultural significance of this iconic site (UNESCO).
Visitor Experience
Today, Piazza del Campidoglio is a must-visit destination for tourists in Rome. Visitors can explore the Capitoline Museums, which house an extensive collection of ancient Roman sculptures, paintings, and artifacts. The piazza offers stunning views of the Roman Forum and the city of Rome. Guided tours are available, providing insights into the history and significance of the site. The piazza is also a popular spot for photography, thanks to its beautiful architecture and panoramic views (Rome.net).
FAQ
Q: What are the visiting hours for Piazza del Campidoglio?
A: The piazza itself is open 24 hours, but the Capitoline Museums are open from 9:30 AM to 7:30 PM, Tuesday through Sunday.
Q: How much do tickets to the Capitoline Museums cost?
A: Standard tickets cost around €15. Check the official website for the most current prices.
Q: Are there guided tours available?
A: Yes, guided tours are available and recommended for a more in-depth understanding of the site’s history.
Q: Is Piazza del Campidoglio accessible to visitors with disabilities?
A: Yes, the piazza and the Capitoline Museums offer accessibility options, including ramps and elevators.
Conclusion
Piazza del Campidoglio is a remarkable example of Rome’s ability to blend its ancient heritage with Renaissance innovation. Michelangelo’s masterful design has created a space that is both historically significant and visually stunning. The piazza continues to be a symbol of Rome’s enduring legacy and a testament to the city’s rich cultural history. Visitors to Piazza del Campidoglio can experience the grandeur of ancient Rome, the elegance of the Renaissance, and the vibrant life of modern Rome, all in one extraordinary location (Rome Art Lover).
Call to Action
For more information on Rome’s historical sites, download our mobile app Audiala, check out other related posts on our website, or follow us on social media for updates and travel tips.
References and Further Reading
- Rome Reborn. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. Rome Reborn.
- Capitoline Museums. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. Capitoline Museums.
- Great Buildings. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. Great Buildings.
- Michelangelo’s Rome. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. Michelangelo’s Rome.
- Rome Art Lover. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. Rome Art Lover.
- Rome.net. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. Rome.net.
- Rome.info. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. Rome.info.
- UNESCO. (n.d.). Piazza del Campidoglio. UNESCO.