Pyramid of Cestius Rome: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Significance
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
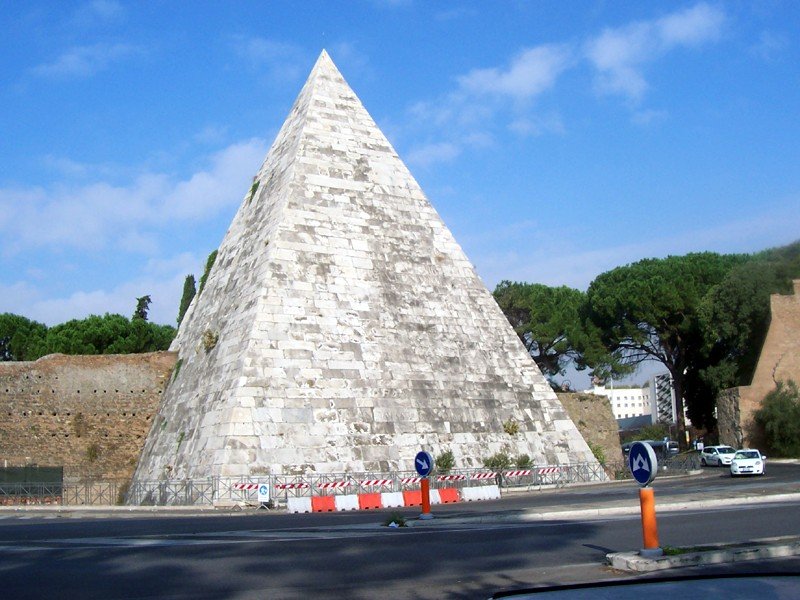
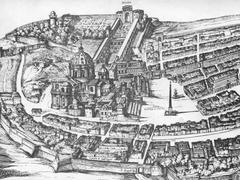
The Pyramid of Cestius is one of Rome’s most distinctive ancient monuments, embodying both Roman engineering ingenuity and the Egyptian architectural influence that swept through Rome after the conquest of Egypt by Octavian Augustus. Constructed as the tomb of Gaius Cestius between 18 and 12 BCE, this gleaming marble pyramid is an enduring testament to Rome’s imperial ambitions, cosmopolitan tastes, and fascination with the cultures it absorbed. The monument is seamlessly integrated into the Aurelian Walls near the Porta San Paolo, creating a striking juxtaposition of Roman and Egyptian styles. Today, it stands as a remarkably well-preserved reminder of the Augustan era and a compelling site for visitors interested in history, art, and architecture (Turismo Roma; Rome Holidays; Wanted in Rome).
This guide provides an in-depth look at the Pyramid of Cestius, covering its history, architectural features, restoration efforts, practical visitor information, and travel tips to help you make the most of your visit.
Contents
- Historical Background
- Origins and Construction
- Historical Context and Evolution
- Other Roman Pyramids
- Architectural Features
- Structure and Dimensions
- Decorative Elements
- Interior Frescoes
- Preservation and Restoration
- Visiting the Pyramid of Cestius
- Hours and Tickets
- Accessibility
- Guided Tours
- Nearby Attractions and Travel Tips
- Visitor FAQs
- Conclusion and Summary
- References
Historical Background
Origins and Construction
Commissioned as the tomb of Gaius Cestius, a wealthy magistrate and member of the Epulones religious college, the pyramid was built between 18 and 12 BCE, during a period when Egyptian culture was highly fashionable in Rome after the defeat of Cleopatra and Mark Antony (Turismo Roma; Rome Holidays). Cestius’s will demanded that the pyramid be completed within 330 days, a stipulation enforced by the threat of his heirs losing their inheritance if the work was delayed (Ancient Origins).
Historical Context and Evolution
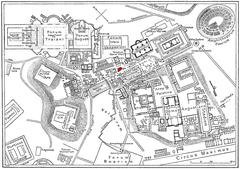
The pyramid was originally built outside Rome’s city limits, as Roman law forbade burials within the city. In the late 3rd century CE, it was fortuitously incorporated into the newly constructed Aurelian Walls, which greatly aided its preservation (Turismo Roma; Rome Holidays). For centuries, its true origin was forgotten, and it was mistakenly believed to be the tomb of Remus, the legendary founder of Rome’s twin. The rediscovery of its inscriptions in the 17th century restored its historical identity (Ancient Origins).
Other Roman Pyramids
The Pyramid of Cestius was not unique in Rome—other pyramidal tombs existed, such as the Meta Romuli, which was demolished in the late 15th century to provide marble for St. Peter’s Basilica (Turismo Roma; Ancient Origins).
Architectural Features
Structure and Dimensions
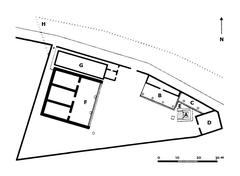
The pyramid stands 36.4 meters (119 feet) high with a square base measuring about 29.6 meters (97 feet) per side. Its steep profile more closely resembles Nubian pyramids than the broad-based Egyptian pyramids of Giza, reflecting the diverse influences in play during the Augustan period (Turismo Roma; Ancient Origins). The core is brick-faced concrete—a Roman specialty—while the exterior is clad in luminous Carrara marble (Rome Holidays).
Decorative Elements
The pyramid once stood within a walled enclosure, marked at each corner by columns (now lost but described in ancient accounts). Latin inscriptions on two faces commemorate Gaius Cestius and the rapid completion of the project. A later inscription records 17th-century restoration efforts (Ancient Origins).
Interior Frescoes
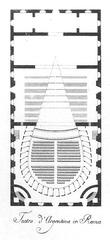
The burial chamber, a small barrel-vaulted room about 5.95 x 4.10 x 4.80 meters, is decorated with delicate Augustan-era frescoes depicting nymphs and winged Victories. Although looted in antiquity, significant portions of these frescoes survive; they were restored in 2015 (Turismo Roma; Ancient Origins).
Preservation and Restoration
The pyramid owes its survival to its integration into the Aurelian Walls. Over the centuries, it has undergone several restoration campaigns: notably in the 17th century under Pope Alexander VII, and most recently between 2011 and 2014, funded by Japanese entrepreneur Yuzo Yagi. These efforts have stabilized the structure, cleaned the marble, and preserved the interior frescoes (Wanted in Rome; Wellesley College). Wartime damage, such as bullet and shrapnel marks from WWII, remain visible as a testament to the monument’s enduring presence (Wellesley College).
Visiting the Pyramid of Cestius
Hours and Ticket Information
- Exterior viewing: The pyramid’s exterior can be admired at any time, 24/7, from the street or the adjacent Protestant Cemetery (Romewise).
- Protestant Cemetery: Entry is via donation. Check the official cemetery website for current opening hours.
- Interior access: The burial chamber is accessible only through guided tours, usually on the third and fourth weekends of each month (except August). Tours must be booked in advance due to limited group sizes (Wanted in Rome; Coop Culture). Tickets are modestly priced, with discounts for select groups.
Accessibility
The exterior and surrounding area are largely accessible to visitors with mobility challenges. The interior, however, is accessed via narrow stairs and corridors and may be unsuitable for those with limited mobility. It is advisable to contact tour providers regarding specific needs (Rome Holidays).
Guided Tours and Special Events
Guided tours are the only way to visit the interior and are available in Italian and sometimes English. These tours provide in-depth historical and architectural insights. Occasionally, the site hosts special cultural events—check local tourism listings and Coop Culture for updates.
Getting There
- Metro: Take Line B to Piramide station, adjacent to the site.
- Train: Roma Ostiense station is nearby.
- Bus/Tram: Multiple lines serve the area.
- Walking: The pyramid is a short walk from Testaccio and Porta San Paolo.
Parking is limited; public transport is recommended (Romewise; Colosseum Rome Tickets).
Nearby Attractions
- Protestant Cemetery: Resting place of John Keats and Percy Bysshe Shelley.
- Porta San Paolo and Museo della Via Ostiense: Explore ancient gates and museums.
- Testaccio District: Known for authentic Roman cuisine and culture.
- Basilica of Saint Paul Outside the Walls: Another major historical site nearby.
Visitor FAQs
Q: What are the visiting hours for the Pyramid of Cestius?
A: Exterior viewing is possible at any time. Interior access is by guided tour, typically on the third and fourth weekends of the month. Check official sources for updates.
Q: How much are tickets?
A: Exterior viewing is free. Interior tours require advance booking and a modest ticket fee.
Q: Is the site accessible for people with disabilities?
A: The exterior is accessible; the interior may pose challenges due to stairs and narrow passages.
Q: Can I take photos inside the pyramid?
A: Photography is encouraged outside. Interior photography may be restricted to protect the frescoes.
Q: How do I get there?
A: The site is next to Piramide metro station and well served by public transport.
Conclusion and Summary
The Pyramid of Cestius is a captivating symbol of Rome’s cosmopolitan history, blending Egyptian and Roman styles in a monument that is both architecturally unique and remarkably well-preserved. Its integration into the Aurelian Walls, rare interior frescoes, and ongoing conservation efforts make it a must-see for visitors interested in ancient history. The adjacent Protestant Cemetery, Porta San Paolo, and vibrant Testaccio district further enrich the visitor experience.
To maximize your visit, check official tourism resources for the latest opening hours and ticketing information. Enhance your journey with guides like the Audiala app, and explore related historical sites to deepen your understanding of Rome’s heritage. For regular updates, follow official channels and social media platforms.
References and Further Reading
- Pyramid of Cestius: History, Architecture, and Visitor’s Guide to Rome’s Unique Monument (Turismo Roma)
- The Pyramid of Cestius: A Unique Roman Landmark (Rome Holidays)
- Pyramid of Cestius in Rome: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Insights (The Brain Chamber)
- Pyramid of Cestius Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Guide to Rome’s Historical Sites (Romewise)
- Rome’s Pyramid of Cestius and How to Visit (Wanted in Rome)
- Restoration and Conservation of the Pyramid of Cestius (The Archaeologist)
- Pyramid of Cestius - Wikipedia
- Pyramid of Cestius Conservation (Wellesley College)
- Pyramid of Cestius - Civitavecchia Port Mobility
- Protestant Cemetery Official Website
- Coop Culture Official Website