Emporium Rome Italy: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Sites Guide
Date: 04/07/2025
Introduction: The Emporium’s Legacy in Rome
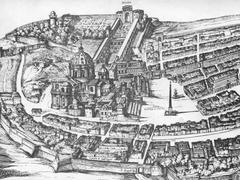
Situated along the left bank of the Tiber River in the heart of Rome’s Testaccio district, the Emporium remains one of the city’s most evocative yet under-explored archaeological sites. Established in the 2nd century BCE, this ancient river port was integral to Rome’s economic might, handling the flow of essential goods such as grain, olive oil, and wine from the empire’s farthest reaches. Supported by monumental infrastructure—like the Porticus Aemilia and the Horrea Galbana warehouses—the Emporium was a center of commerce and logistics for over four centuries. Adjacent to this port, Monte Testaccio (Monte dei Cocci) stands as a unique archaeological site: an artificial hill created from millions of discarded amphorae, bearing silent witness to the scale of Rome’s ancient trade.
Today, the Emporium’s open-air remains, alongside the vibrant Testaccio neighborhood, invite visitors to experience both Rome’s imperial history and its dynamic contemporary culture. This guide provides comprehensive details on the Emporium’s historical significance, archaeological features, practical visitor information—including hours, tickets, and accessibility—as well as nearby attractions and travel tips.
For more on visiting and guided tours, see Turismo Roma’s Widespread Museum of Testaccio and Rome Actually’s Testaccio Neighborhood Guide.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- History and Significance
- Archaeological Features: What to See
- Decline, Rediscovery, and Cultural Legacy
- Practical Visitor Information
- Visitor Experiences and Tours
- Nearby Attractions
- Tips and Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- References
History and Significance
Origins and Role in Ancient Rome
The Emporium emerged in the 2nd century BCE as Rome outgrew its earlier river port near the Forum Boarium. Its new location in Testaccio, with direct access to the Tiber, allowed for the efficient unloading, warehousing, and distribution of goods arriving from Ostia and the Mediterranean. The site’s vast warehouses—such as the Horrea Galbana and the Porticus Aemilia—stored key commodities that sustained Rome’s burgeoning population and construction projects.
The Emporium not only handled the city’s food supply but also underpinned Rome’s status as an imperial capital, facilitating trade networks that stretched across the Mediterranean. Its economic influence lasted into late antiquity, shaping both the city’s urban landscape and its social development (Turismo Roma).
Monte Testaccio: Rome’s Amphorae Hill
A unique legacy of the Emporium is Monte Testaccio, an artificial mound comprised of some 53 million discarded olive oil amphorae. This “mountain of potsherds” stands as a lasting testament to the scale of Roman imports and the city’s consumption patterns. The fragments—often stamped with information about origin and contents—provide invaluable data for archaeologists studying Rome’s commercial history and logistics (Emporium Rome).
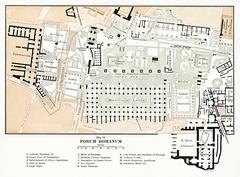
Archaeological Features: What to See
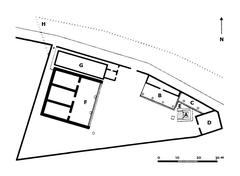
- Ancient Quays and Embankments: Large blocks of travertine and tufa, visible at river level, formed the port’s docking platforms. Some bear ancient inscriptions related to trade and transport (Stanford Nash Collection).
- Warehouses (Horrea): Remnants of the massive storage complexes that held grain, oil, and wine.
- Porticus Aemilia: One of the largest covered warehouses of the ancient world, with sections accessible on Via Rubattino.
- Monte Testaccio: The amphorae hill, accessible via guided tours, offers insights into ancient waste management and trade.
- Archaeological Panels and Digital Resources: Educational panels and mobile apps help visitors understand the site’s layout and history (Turismo Roma).
Decline, Rediscovery, and Cultural Legacy
The Emporium’s fortunes waned by the 3rd century CE, as river silting and changing trade routes reduced its importance. The area became agricultural land during the Middle Ages. Its true significance was rediscovered in the 19th century, when Pope Pius IX authorized excavations revealing the scale of the ancient port and the artificial origins of Monte Testaccio.
Today, the Emporium is a focal point for local heritage initiatives, such as the Widespread Museum of Testaccio, which integrates open-air archaeology, community events, and digital resources to engage both residents and visitors (Turismo Roma).
Practical Visitor Information
Location and Access
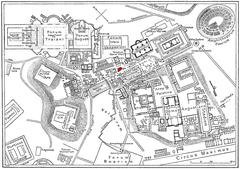
- Address: Lungotevere Testaccio, in front of number 11; main access via Via L. Ghiberti 19 (Nuovo Mercato Testaccio).
- Neighborhood: Testaccio, south of Rome’s historic center, near Aventine Hill.
Visiting Hours and Tickets
- Emporium Archaeological Area: The open-air remains are generally accessible 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, at no charge.
- Monte Testaccio and Restricted Areas: Access to the amphorae hill and some warehouse interiors is by guided tour only, typically available through local archaeological groups.
- Guided Tours and Special Events: Tours and events require advance booking and may charge between €5–€15 per person.
- Booking: Individual and group visits to restricted areas can be arranged via [email protected]; schools should contact [email protected].
- Official Hours: For up-to-date hours, tour schedules, and temporary events, check Turismo Roma and Rome Actually.
Accessibility
- Physical Access: The upper promenade along Lungotevere Testaccio is wheelchair accessible and offers views of the ruins. Embankment steps and river-level areas have uneven surfaces and may be slippery after rain.
- Public Transport: Closest metro: Piramide (Line B). Major bus lines: 23, 280, 170. Roma Ostiense train station is nearby.
- Parking: Limited; public transport is recommended.
Facilities
- Restrooms: Available in nearby cafés and Testaccio Market.
- Food & Drink: Testaccio Market and local eateries offer Roman specialties.
- Shops & ATMs: Scattered throughout the neighborhood.
Visitor Experiences and Tours
- Guided Walking Tours: Local operators offer in-depth tours focusing on the Emporium, Monte Testaccio, and the district’s industrial heritage.
- Widespread Museum of Testaccio: An open-air museum experience, with educational panels, digital resources, and thematic itineraries (Turismo Roma).
- Photography: Best light is at sunrise and sunset; drones require permits.
- Family-Friendly Activities: Educational zones and interactive programs for children are sometimes available during special events.
Nearby Attractions
- Monte Testaccio: The amphorae hill—guided tours recommended.
- Pyramid of Cestius: A striking 1st-century BCE pyramid tomb near Porta San Paolo.
- Porta San Paolo & Museo della Via Ostiense: Explore ancient roads and the history of Rome’s trade.
- Cimitero Acattolico (Non-Catholic Cemetery): Resting place of poets Keats and Shelley.
- Aventine Hill: Renowned for gardens, churches, and panoramic views.
- Testaccio Market: Authentic Roman food and a lively atmosphere.
Tips and Frequently Asked Questions
Travel and Safety Tips
- Footwear: Wear sturdy shoes for cobblestones and uneven terrain (Full Suitcase).
- Water & Sun Protection: Bring a refillable bottle, hat, and sunscreen.
- Security: Testaccio is generally safe, but standard city precautions apply (Rome on Foot).
- Best Time to Visit: Spring and autumn are ideal; summer days can be hot and crowded (Rome Hacks).
- Amenities: No facilities at the site itself; use nearby cafés or the market.
FAQs
Q: Is there an entrance fee to visit the Emporium?
A: The outdoor site is free and open to the public. Guided tours or special events may require tickets.
Q: What are the Emporium’s visiting hours?
A: The open-air area is accessible at all times. Guided tours run on fixed schedules—check official sources for details.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, through local operators and during special events. Booking in advance is recommended.
Q: Is the site accessible for people with disabilities?
A: The upper promenade is accessible; some lower areas have uneven surfaces.
Q: How do I get there?
A: By metro (Piramide, Line B), bus (23, 280, 170), or train (Roma Ostiense). Public transport is advisable due to limited parking.
Conclusion
The Emporium is a vital and atmospheric window into ancient Rome’s commercial lifeblood and urban ingenuity. Its monumental quays, warehouses, and the amphorae hill of Monte Testaccio reveal the city’s role as a global trade hub. Modern Testaccio, with its lively markets, restaurants, and cultural events, provides an ideal backdrop for exploring this unique archaeological site.
Whether you are a history enthusiast, urban explorer, or curious traveler, the Emporium offers flexible, free access and the chance to discover Rome’s past in a living neighborhood. Make the most of your visit by joining a guided tour, downloading the Widespread Museum of Testaccio app, and exploring nearby attractions. For the latest information, always consult official tourism websites and local resources.
Start your journey today and uncover the stories of Rome’s ancient river port!
References
- Visiting the Emporium in Rome: History, Hours, Tickets, and Nearby Attractions
- Visiting the Emporium in Rome: Hours, Tickets, and Historical Insights
- Emporium Rome: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Guide to Rome’s Ancient River Port
- Emporium Rome: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Guide to Rome’s Historic River Port
- Stanford Nash Collection: The Emporium—Rome’s Largest Inland Port
- Romewise: Accessible Rome
- Help Tourists in Rome: Accessible Travel Tips
- Full Suitcase: Tips for Planning a Trip to Rome
- Mama Loves Rome: First Time Rome Tips
- Rome on Foot: Rome Safety Tips
- Rome Hacks: Rome in July
- Trips & Leisure: Tips for Traveling to Rome, Italy
- Italia.it: Rome and the Jubilee 2025—History and Meaning
- Romeing: Rome Events in July
- Past Pathways: Best Archaeological Sites to Visit in Rome