Visiting the Botanical Garden of Rome: Hours, Tickets, and Tips
Date: 18/07/2024
Introduction
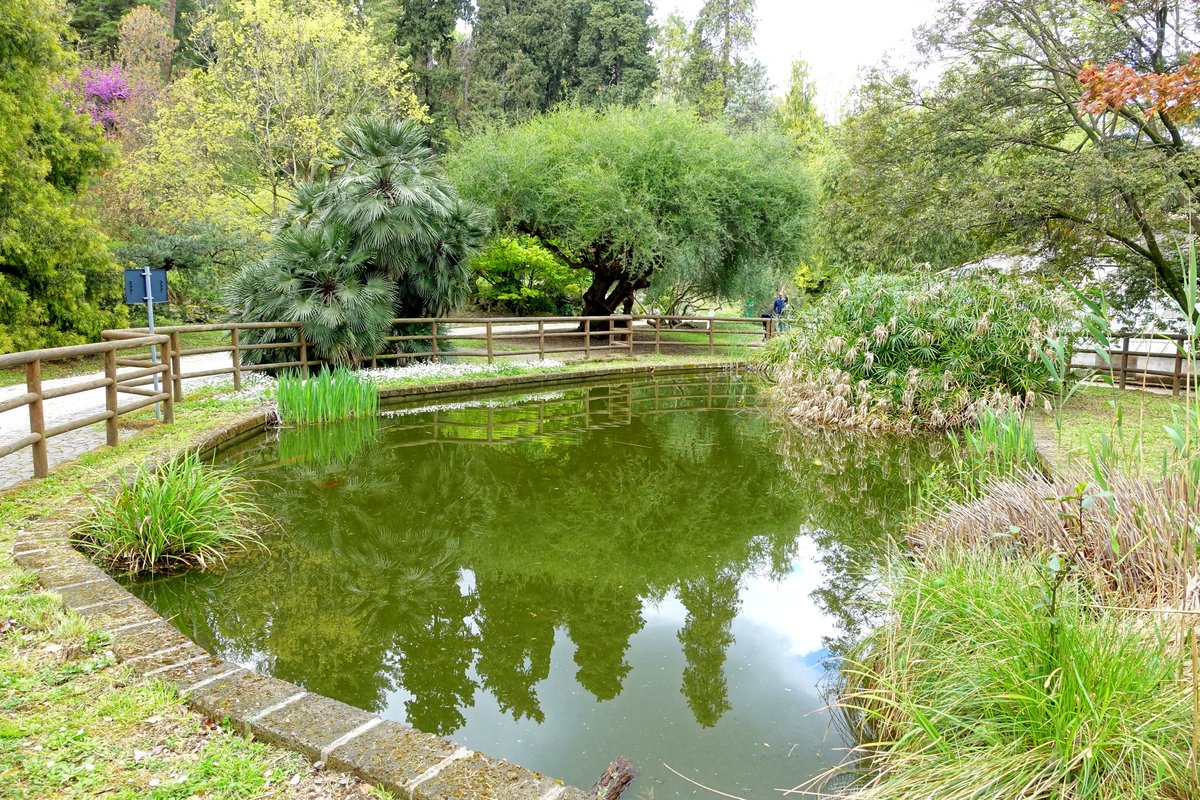
Nestled in the heart of Rome, the Botanical Garden of Rome, or “Orto Botanico di Roma,” provides a serene escape from the bustling city, offering visitors a unique blend of historical significance, scientific research, and breathtaking natural beauty. Established in 1883 and managed by the Sapienza University of Rome, this lush sanctuary boasts a rich history that spans centuries, tracing its origins back to the 13th century when Pope Nicholas III created a medicinal garden near the Vatican. The garden’s relocation to Janiculum Hill in the 16th century under Pope Sixtus V marked its transformation into a hub for scientific study, mirroring Europe’s broader trend of establishing botanical gardens for plant classification and research. Throughout its history, the garden has undergone significant expansions and modernizations, including the addition of specialized sections for medicinal plants, succulents, and tropical species in the 19th century and the construction of new greenhouses in the early 20th century. In recent decades, the Botanical Garden of Rome has emphasized conservation and sustainability, playing a crucial role in the study and preservation of plant biodiversity. Visitors can enjoy leisurely strolls through beautifully landscaped grounds, participate in guided tours, and engage in educational programs, making it an ideal destination for families, history buffs, plant enthusiasts, and those seeking a peaceful retreat in the heart of Rome (Botanical Garden of Rome).
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- History of the Botanical Garden of Rome
- Recent Developments and Conservation Efforts
- Visitor Information
- Notable Collections and Features
- Visitor Experience
- Conclusion
- FAQ
History of the Botanical Garden of Rome
Origins and Early Development
The Botanical Garden of Rome’s origins trace back to the Renaissance period. Initially established in 1883, its roots go even deeper, to the 13th century when Pope Nicholas III created a medicinal garden near the Vatican. This early garden was dedicated to cultivating medicinal plants, reflecting the era’s focus on the healing properties of flora.
In the 16th century, Pope Sixtus V relocated the garden to Janiculum Hill, marking its transformation into a center for scientific study. The garden’s new location provided ample space for collecting and studying diverse plant species, aligning with the broader European trend of establishing botanical gardens as hubs for plant classification and research.
19th Century Expansion
The 19th century was a period of significant growth for the Botanical Garden of Rome. In 1883, the garden moved to its current location on the grounds of the Palazzo Corsini in the Trastevere district. This move, facilitated by the Italian government after Italy’s unification, allowed for the cultivation of a wider variety of plant species.
Under the direction of notable botanists like Pietro Romualdo Pirotta, the garden introduced numerous exotic plants and established specialized sections, including areas for medicinal plants, succulents, and tropical species. The garden also became a center for botanical research and education, affiliated with the University of Rome.
20th Century Modernization
The 20th century saw further modernization and scientific advancements. Significant renovations in the early 1900s improved infrastructure and expanded collections. New greenhouses were built for tropical and subtropical plants, and the garden’s layout was redesigned for both aesthetic appeal and research functionality.
A notable addition was the Japanese Garden in 1956, part of a cultural exchange between Italy and Japan. Featuring traditional elements like a koi pond, stone lanterns, and bonsai trees, it remains one of the garden’s most popular attractions.
Recent Developments and Conservation Efforts
In recent decades, the Botanical Garden of Rome has emphasized conservation and sustainability. Managed by the Sapienza University of Rome, various initiatives have been implemented to preserve its diverse plant collections and promote environmental awareness.
Key conservation efforts include the Mediterranean Garden, showcasing unique flora of the Mediterranean region. This section highlights the importance of preserving native plant species and their habitats amidst climate change and habitat destruction.
Additionally, the garden has become a hub for scientific research, with ongoing studies in plant physiology, ecology, and genetics. Researchers are involved in international collaborations, contributing to global understanding of plant biodiversity and conservation.
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Tickets
The Botanical Garden of Rome is open year-round. Visiting hours vary by season, so it’s advisable to check the official website for current hours and any special closures. General admission is €8, with discounts available for students, seniors, and groups. Children under six can enter for free. Special rates may apply during events.
Guided Tours and Special Events
Guided tours are available and provide in-depth insights into the garden’s history, collections, and ongoing research. The garden also hosts special events, including art exhibitions, concerts, and cultural festivals, making it a vibrant part of Rome’s cultural life.
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
Located in the Trastevere district, the garden is easily accessible by public transport, with several bus and tram lines stopping nearby. Nearby attractions include the Palazzo Corsini and the historic Trastevere neighborhood, offering plenty of opportunities for a full day of exploration.
Accessibility
The Botanical Garden of Rome is committed to providing access to all visitors. Pathways are well-maintained, and facilities are available for those with mobility challenges. It’s advisable to contact the garden in advance for specific accessibility information.
Notable Collections and Features
- The Palm Grove - Home to a diverse collection of palm species from around the world, highlighting their ecological and economic importance.
- The Rose Garden - Featuring a wide variety of rose species and hybrids, showcasing the beauty and diversity of this beloved flower.
- The Greenhouses - Housing an extensive collection of tropical and subtropical plants, including orchids, ferns, and carnivorous plants.
- The Arboretum - Dedicated to the study and conservation of trees and shrubs, featuring diverse species from different parts of the world.
Visitor Experience
Visitors can enjoy leisurely strolls through beautifully landscaped grounds, educational tours, and workshops. Each season offers a unique display of flora, with spring and early summer being particularly popular times to visit.
For those interested in deeper insights, guided tours provide a comprehensive understanding of the garden’s development and its role in botanical research. Educational programs for children and adults make it an ideal destination for families and school groups.
Conclusion
The Botanical Garden of Rome is a living testament to the rich history and ongoing evolution of botanical science. Its diverse collections, historical significance, and commitment to conservation make it a must-visit destination for anyone interested in the natural world. For more information, including visiting hours and ticket prices, visit the official website.
FAQ
-
What are the visiting hours for the Botanical Garden of Rome?
- Visiting hours vary by season. Check the official website for current hours.
-
How much are tickets to the Botanical Garden of Rome?
- General admission is €8, with discounts for students, seniors, and groups. Children under six may enter for free.
-
Are guided tours available?
- Yes, guided tours are available and provide in-depth insights into the garden’s history and collections.
-
Is the garden accessible for visitors with mobility challenges?
- Yes, the garden is committed to accessibility. Pathways are well-maintained, and facilities are available. Contact the garden in advance for specific information.
-
What nearby attractions can I visit?
- Nearby attractions include the Palazzo Corsini and the historic Trastevere neighborhood.
References
- Botanical Garden of Rome, Sapienza University of Rome https://web.uniroma1.it/ortobotanico/en
- Orto Botanico di Roma, Sapienza University of Rome https://web.uniroma1.it/ortobotanico/