Guide to Visiting Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Florence, Italy
Date: 19/07/2024
Introduction
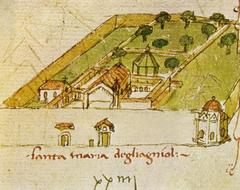
Nestled in the picturesque hills of Florence, Italy, the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri is an institution that represents both the historical depth and cutting-edge advancements in the field of astronomy. Established in 1872 by Giovanni Battista Donati, a pioneering astronomer known for his work on comets and spectroscopy, the observatory has been instrumental in expanding our understanding of the universe (INAF Arcetri). Over the decades, the observatory has been a site of groundbreaking research, from early advancements in spectroscopy to modern studies in radio astronomy and exoplanet research.
The observatory’s location on the hill of Arcetri was chosen for its optimal conditions for astronomical observations, such as its elevation and originally low light pollution. This ideal setting has allowed the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri to make significant contributions to various fields of astrophysics, including solar physics, stellar spectroscopy, and radio astronomy. Notable figures like Antonio Abetti and his son Giorgio Abetti have played crucial roles in the observatory’s development, further enhancing its reputation in the global scientific community (Antonio Abetti, Solar Physics).
Today, the observatory is part of Italy’s National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), facilitating collaborations with leading research institutions worldwide and access to state-of-the-art technology (INAF). Visitors to the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri can expect an enriching experience, with guided tours, educational programs, and special events that showcase the observatory’s rich history and ongoing research efforts. Whether you are an astronomy enthusiast or a casual visitor, the observatory offers a unique glimpse into the cosmos and the scientific endeavors that make astronomical discoveries possible.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Establishment and Early Years
- Contributions to Spectroscopy
- The Role of Antonio Abetti
- The Solar Physics Era
- The Advent of Radio Astronomy
- Modern Developments and Research
- Notable Achievements and Discoveries
- Visitor Information
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Discover the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri - History, Visiting Hours, and More
Establishment and Early Years
The Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, established in 1872 by Giovanni Battista Donati, has a rich history. Donati’s vision was to create a state-of-the-art facility to advance the study of astrophysics. The observatory was strategically placed on the hill of Arcetri for its optimal conditions for astronomical observations due to its elevation and originally low light pollution (INAF Arcetri).
Contributions to Spectroscopy
One of the early significant contributions of the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri was in the field of spectroscopy. Giovanni Battista Donati himself was a pioneer in this area, and his work laid the foundation for future research at the observatory. Spectroscopy, the study of the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation, became a crucial tool for astronomers to understand the composition and properties of celestial objects (Spectroscopy History).
The Role of Antonio Abetti
Antonio Abetti, who succeeded Donati as the director of the observatory in 1894, played a pivotal role in its development. Abetti was instrumental in modernizing the observatory’s equipment and expanding its research capabilities. Under his leadership, the observatory acquired new telescopes and instruments, which allowed for more precise and detailed observations. Abetti’s tenure also saw an increase in international collaborations, further enhancing the observatory’s reputation in the global scientific community (Antonio Abetti).
The Solar Physics Era
In the early 20th century, the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri became a hub for solar physics research. The observatory’s scientists made significant contributions to the understanding of solar phenomena, including sunspots, solar flares, and the solar corona. This period was marked by the work of Giorgio Abetti, Antonio Abetti’s son, who made substantial advancements in the study of the Sun (Solar Physics).
World War II and Post-War Reconstruction
The observatory faced challenges during World War II, disrupting research activities and causing damage to some facilities. However, the post-war period saw efforts to rebuild and modernize the observatory, supported by new funding and international collaborations. This era also marked the beginning of the observatory’s involvement in radio astronomy (WWII Impact on Science).
The Advent of Radio Astronomy
The mid-20th century saw the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri expand its research into radio astronomy. This new branch of astronomy, which studies celestial objects at radio frequencies, opened up new avenues for exploration and discovery. The observatory established a radio astronomy division and began constructing radio telescopes to complement its optical instruments (Radio Astronomy).
Modern Developments and Research
In recent decades, the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri has continued to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of astronomical research. It is now part of the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), facilitating greater collaboration with other research institutions and access to cutting-edge technology. The observatory’s current research focuses on various topics, including star formation, galaxy evolution, and the search for exoplanets (INAF).
Notable Achievements and Discoveries
Throughout its history, the Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri has been associated with numerous significant achievements and discoveries:
- Discovery of Comet Donati: Giovanni Battista Donati’s discovery of the comet that bears his name in 1858 was a landmark event. The comet provided valuable data for the study of cometary physics (Comet Donati).
- Solar Eclipse Observations: Detailed observations of solar eclipses have contributed to a better understanding of the Sun’s structure and behavior, crucial in studying the solar corona and solar flares (Solar Eclipses).
- Advancements in Stellar Spectroscopy: The observatory’s work in stellar spectroscopy has provided insights into the composition and properties of stars, refining models of stellar evolution (Stellar Spectroscopy).
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours
The observatory is open to the public on select days. Check their official website for the latest visiting hours.
Tickets
Admission prices vary depending on the type of visit (self-guided tours, guided tours, special events). Purchase tickets in advance to ensure availability (Tickets).
Guided Tours
Enhance your visit with a guided tour led by expert astronomers who can provide in-depth insights into the observatory’s history and current research (Guided Tours).
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
While visiting the observatory, explore other historical sites in Florence:
- Florence Cathedral: A masterpiece of Renaissance architecture, located just a short distance from the observatory.
- Piazzale Michelangelo: Offers stunning panoramic views of Florence, perfect for a post-visit stroll.
- Palazzo Pitti and Boboli Gardens: Explore the rich history and beautiful gardens of this grand palace.
Accessibility
The Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri strives to be accessible to all visitors. If you have specific accessibility needs, contact the observatory in advance to ensure a smooth visit (Accessibility).
Educational and Public Outreach
The observatory hosts public lectures, workshops, and educational programs aimed at fostering interest in astronomy and science. These initiatives are designed to engage the public and inspire the next generation of astronomers and scientists (Public Outreach).
Preservation of Historical Instruments
The observatory takes pride in preserving its historical instruments and artifacts. Many of the original telescopes and scientific instruments used by Donati, Abetti, and other pioneering astronomers are still housed at the observatory. These historical pieces provide a tangible link to the observatory’s storied past (Historical Instruments).
FAQ
- What are the visiting hours? The visiting hours vary; check the official website for the most up-to-date information.
- How much do tickets cost? Ticket prices vary based on the type of visit; see the official website for details.
- Are guided tours available? Yes, guided tours are available and are highly recommended for a comprehensive experience.
- What are some nearby attractions? Florence Cathedral, Piazzale Michelangelo, and Palazzo Pitti and Boboli Gardens are all nearby.
Conclusion
The Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri stands as a testament to the enduring human quest for knowledge and understanding of the universe. Its rich history, marked by significant contributions to various fields of astronomy, continues to inspire and inform contemporary scientific endeavors. Plan your visit today and immerse yourself in the fascinating world of astronomy.
References
- INAF Arcetri. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.arcetri.inaf.it/
- Antonio Abetti. (n.d.). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/biography/Antonio-Abetti
- Solar Physics. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/journal/11207
- INAF. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.inaf.it/en
- Exoplanet Exploration. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/
- ELT. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://elt.eso.org/