Visiting Ben Ezra Synagogue in Cairo: Hours, Tickets, and Historical Insights
Date: 17/08/2024
Introduction
The Ben Ezra Synagogue, located in the Fustat district of Old Cairo, is one of Egypt’s most significant Jewish heritage sites. Once a Coptic Orthodox church, it was sold to the Jewish community in 882 CE and renamed after the renowned scholar Abraham ben Meir Ibn Ezra. This historic synagogue is world-famous for its association with the Cairo Geniza—a priceless collection of medieval Jewish manuscript fragments that has transformed our understanding of Jewish life and culture in the region (Egyptian Streets, Travel2Egypt).
Today, the Ben Ezra Synagogue serves as a museum and an enduring symbol of Egypt’s diverse cultural and religious fabric. This guide provides comprehensive information for visitors, including opening hours, ticket details, travel advice, and insights into the synagogue’s fascinating history and significance.
Visitor Information
Opening Hours
The Ben Ezra Synagogue is open to visitors Sunday to Thursday, from 9:00 AM to 4:00 PM. It is closed on Fridays and Saturdays in observance of the Jewish Sabbath and major Jewish holidays. Before visiting, it’s advisable to check for any special closures or updates via local tour operators or official sources (Encounterstravel).
Tickets and Admission
Admission is generally free, but donations are encouraged to support the ongoing preservation and restoration of this historical site. Guided tours may incur a fee and are highly recommended for those seeking deeper insights into the synagogue’s history and architecture.
How to Get There
The synagogue is situated in the Fustat area of Old Cairo, within the “Religions Complex” that also includes several significant Christian and Islamic sites. The nearest metro station is Mar Girgis, just a short walk from the synagogue. Taxis and local buses are also available for convenient access (Egypt Tours Portal).
Travel Tips
- Best Time to Visit: The most comfortable period is between November and February when Cairo’s weather is mild. Arriving early helps avoid crowds, especially during peak tourist season.
- Dress Code: Modest attire is required out of respect for the religious site. Women should cover their shoulders and knees; men are advised to avoid shorts.
- Photography: Allowed in most areas, but always check for signage or ask staff before taking photos.
- Accessibility: The synagogue is generally accessible, but some historic areas may be challenging for visitors with mobility issues.
Historical and Architectural Significance
Origins and Early History
Legend holds that the Ben Ezra Synagogue stands where baby Moses was found among the reeds—a story that adds biblical resonance to its location. Historically, after its sale in 882 CE, the site became the spiritual center for Cairo’s Jewish community, thriving as a place of worship, learning, and communal gathering (Egyptian Streets).
Architectural Features
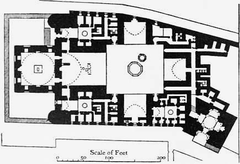
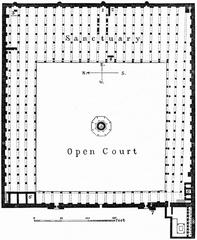
The synagogue’s design blends Jewish, Byzantine, Islamic, and Coptic architectural elements. Key features include a basilica-style hall, central nave, marble fixtures, and ornate wooden ceiling beams. Intricate geometric designs and decorative carvings, characteristic of Islamic art, adorn the interior, reflecting the multi-cultural influences of medieval Cairo (The Complete Pilgrim).
The Cairo Geniza Discovery
In the late 19th century, a hidden storeroom (geniza) was discovered within the synagogue, containing some 350,000 manuscript fragments in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Judeo-Arabic. These documents, many dating from the 11th to 13th centuries, offer unparalleled insights into the daily, economic, and religious lives of Jews in medieval Egypt. The majority of Geniza materials are now housed at the Cambridge University Library, with others distributed worldwide (Travel2Egypt).
Association with Maimonides
The celebrated philosopher and physician Maimonides lived nearby in Fustat from 1168 until his death in 1204. He led the Egyptian Jewish community and is referenced in several Geniza documents, including some in his own handwriting, adding further scholarly significance to the synagogue.
Fires, Decline, and Restoration
Ben Ezra Synagogue has survived numerous challenges over the centuries. Notable events include its destruction in the 12th-century fire set to prevent Crusader capture and various periods of decline where it was used only on special occasions. The structure seen today is largely the result of a comprehensive 19th-century rebuilding, preserving some original features like wooden furnishings and marble columns. Major restoration efforts—including a significant one completed in 2023—have ensured its continued preservation (The J).
Modern-Day Role and Educational Value
Today, the Ben Ezra Synagogue functions primarily as a museum, highlighting the contributions and history of Egypt’s once-thriving Jewish community. Informative displays and exhibits focus on the Geniza manuscripts, the synagogue’s architecture, and the broader context of Jewish life in Cairo (Horizon Travel Egypt).
The synagogue also fosters interfaith dialogue and cultural exchange, hosting educational programs, lectures, and community projects that promote tolerance and understanding. These initiatives have made it a valuable resource for both tourists and scholars, preserving the legacy of Egypt’s Jewish heritage.
Nearby Attractions
The Ben Ezra Synagogue is part of a rich historical landscape. Nearby sites include:
- The Hanging Church: Famous for its suspended nave and Coptic Christian heritage.
- Saints Sergius and Bacchus Church: Believed to be built on the site visited by the Holy Family during their flight into Egypt.
- Amr Ibn Al-As Mosque: The first mosque built in Egypt and Africa, representing early Islamic architecture.
- Coptic Museum: Showcasing Christian artifacts and art from Egypt’s Coptic community.
These attractions are within walking distance and can be combined into a full-day exploration of Old Cairo (Egypt Tours Portal).
Visitor Experience
A visit to the Ben Ezra Synagogue offers a journey through centuries of history. The tranquil, evocative atmosphere, coupled with the synagogue’s ornate architecture and wealth of historical artifacts, creates a memorable experience for anyone interested in Egypt’s diverse religious and cultural heritage. Guided tours provide further context, particularly about the Cairo Geniza and Jewish life in medieval Cairo.
Practical Tips
- Guided Tours: Highly recommended for an in-depth experience; often include nearby sites.
- Accommodation: Old Cairo offers options from luxury hotels (like Kempinski Nile Hotel) to budget hostels, suitable for all travelers.
- Local Cuisine: Don’t miss local specialties such as koshari, ful medames, and ta’ameya at nearby restaurants.
- Shopping: The Khan El Khalili market is ideal for souvenirs like handcrafted jewelry, papyrus art, and Egyptian spices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the synagogue’s opening hours?
A: Sunday–Thursday, 9:00 AM–4:00 PM. Closed Fridays and Saturdays (Encounterstravel).
Q: What is the cost of admission?
A: Admission is typically free; donations are encouraged.
Q: Is there a dress code?
A: Yes, modest dress is required.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, and they are highly recommended.
Q: How can I reach the synagogue?
A: By metro (Mar Girgis station), taxi, or bus.
Conclusion
The Ben Ezra Synagogue stands as a monument to Egypt’s rich and diverse history. Its unique blend of architecture, the invaluable Cairo Geniza manuscripts, and its enduring legacy as a center for faith and learning make it a must-visit destination in Cairo. Ongoing restoration and cultural initiatives ensure that its story will continue to inspire future generations. Plan your visit to this historic site to experience firsthand the remarkable tapestry of Egypt’s Jewish heritage (Horizon Travel Egypt, The J).
References
- Egyptian Streets: A Look at One of Egypt’s Oldest Jewish Temples: Ben Ezra
- Travel2Egypt: Ben Ezra Synagogue
- The J: Ben Ezra Synagogue in Cairo Reopens After Significant Restoration
- Horizon Travel Egypt: Ben Ezra Synagogue
- Encounterstravel: Synagogue Ben Ezra
- Egypt Tours Portal: Ben Ezra Synagogue
- The Complete Pilgrim: Ben Ezra Synagogue Cairo Geniza