Babylon Fortress: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and a Complete Guide to Cairo’s Historic Site
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
Babylon Fortress, located in the heart of Old Cairo, is a storied landmark representing the crossroads of Egypt’s ancient, Christian, Islamic, and Jewish heritage. Originating as an Egyptian settlement in the 3rd millennium BCE and reconstructed by the Romans, this fortress has played critical roles through the Byzantine, Arab, and Ottoman periods. Today, it houses some of Egypt’s most significant religious sites, including the Hanging Church and the Church of St. George, and is surrounded by a vibrant cluster of historic attractions.
This comprehensive guide covers Babylon Fortress visiting hours, ticketing details, accessibility, guided tour options, and practical travel tips. Whether you are a history enthusiast or a casual explorer, here’s how to make the most of your visit to one of Cairo’s top historical sites. (Discover Babylon Fortress; Babylon Fortress Visitor Guide; Babylon Fortress Historical Overview)
Table of Contents
- Babylon Fortress Overview: History and Significance
- Historical Development
- Main Attractions Inside and Nearby the Fortress
- Visitor Information
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Planning Your Visit: Practical Advice
- References and Further Reading
Babylon Fortress Overview: History and Significance
Babylon Fortress is a monumental structure that has stood at the center of Egypt’s capital for millennia. Its formidable Roman walls and towers once protected a key trade and military route along the Nile. Over the centuries, the fortress evolved into a religious and cultural hub, sheltering some of Egypt’s oldest churches and, later, significant Islamic and Jewish sites. Today, the area is known as Coptic Cairo and is celebrated for its unique blend of Roman architecture, Christian sanctuaries, and proximity to Islamic and Jewish landmarks.
Historical Development
Ancient Egyptian Origins
The site of Babylon Fortress was important long before the Romans arrived. Originally an Egyptian settlement near a canal linking the Nile to the Red Sea, it served as a strategic checkpoint for trade and military movement, eventually evolving into a fortified town.
Roman Construction
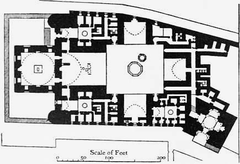
The current fortress structure dates primarily to the late 3rd and early 4th centuries CE, with major expansions under Emperor Diocletian. Roman engineers built massive limestone and mudbrick walls, rectangular bastions, and imposing gates. Some stonework incorporates blocks from earlier Pharaonic temples, blending ancient Egyptian and Roman craftsmanship. The fortress’s nickname, “Qasr El Shame” (Palace of Candles), derives from the candles that once illuminated its towers monthly. (Cairo Top Tours)
Byzantine and Coptic Era
During the Byzantine period, Babylon Fortress became a bastion for Egypt’s growing Coptic Christian community. Significant churches were constructed inside its walls, including the famed Hanging Church (Al-Muallaqa), built atop the south gate, and the Church of St. George. The area became an important pilgrimage site and center for Christian learning and worship.
Arab and Islamic Influence
Following the Arab conquest of Egypt in 641 CE, the fortress maintained its strategic and cultural importance. The first mosque in Africa, the Mosque of Amr ibn al-As, was founded nearby, marking the spread of Islam in Egypt. Despite the new Islamic governance, Christian communities continued to thrive within the fortress, exemplifying centuries of coexistence.
Ottoman Period and Modern Preservation
Babylon Fortress continued as a military and administrative center under successive rulers. Today, the site is under active preservation, with restoration projects ensuring its legacy endures for future generations.
Main Attractions Inside and Nearby the Fortress
The Hanging Church (Al-Muallaqa)
Perched above the fortress’s southern gate, this 5th-century church is renowned for its wooden nave and collection of over 100 ancient icons. Historically, it served as the seat of the Coptic Orthodox Pope. (Connolly Cove)
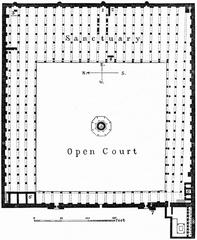
Church of St. George
A unique round church serving Cairo’s Greek Orthodox community. Its architecture blends Roman, Byzantine, and Coptic styles, and the church complex includes a museum and chapels. (Travel Hack Fun)
The Coptic Museum
Founded in 1908, the museum boasts the world’s most extensive collection of Coptic Christian artifacts, with manuscripts, textiles, icons, and architectural fragments on display. (The Complete Pilgrim)
Ben Ezra Synagogue
A short walk from the fortress, this is one of Egypt’s oldest synagogues, with origins in the 9th century.
Mosque of Amr ibn al-As
Egypt’s first mosque and a major Islamic landmark, located near the fortress.
Visitor Information
Opening Hours
Babylon Fortress and its associated sites are typically open daily from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM. Hours may vary during religious holidays or special events.
Tickets and Admission
- Babylon Fortress: Entrance to the fortress grounds is generally free.
- Churches: Some, like the Hanging Church and St. George Church, may request small donations or charge nominal entry fees.
- Coptic Museum: Admission is approximately 60–100 EGP for adults, with discounts for students and children.
- Advance Booking: Tickets for the Coptic Museum and guided tours can be purchased online or through reputable agencies to avoid queues. (ETL Travel)
Accessibility
The fortress features uneven terrain, cobblestones, and stairs. While some areas are accessible, others (such as tunnels and upper galleries) may pose challenges for those with limited mobility. The Coptic Museum offers wheelchair access and elevators.
Guided Tours
Guided tours, available in several languages, are highly recommended for historical context and architectural insights. Tours often include the fortress, Hanging Church, St. George Church, and the Coptic Museum. Tours last 1.5–2 hours. (touregyptclub.com)
Facilities and Amenities
- Restrooms: Available near the Coptic Museum and main entrances.
- Cafés & Shops: Small vendors offer refreshments and souvenirs.
- Security: The area is considered safe, with a visible police presence and standard bag checks at entrances.
Practical Travel Tips
- Best Time to Visit: Early morning or late afternoon for cooler temperatures and fewer crowds.
- Dress Code: Modest attire is recommended; shoulders and knees should be covered when entering religious sites.
- Photography: Permitted in outdoor areas; restrictions apply inside churches and the museum—ask for permission when in doubt.
- Hydration & Sun Protection: Bring bottled water, a hat, and sunscreen, especially in summer.
- Footwear: Wear comfortable, closed-toe shoes for walking on uneven surfaces.
- Language: Arabic is the official language, but English is widely spoken by staff and guides.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are Babylon Fortress visiting hours?
A: The fortress is open daily from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM, though hours may change during religious holidays.
Q: Do I need tickets to visit Babylon Fortress?
A: Entry to the fortress area is usually free; tickets are required for the Coptic Museum and some churches.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, guided tours are highly recommended and can be booked through local agencies or online.
Q: Is the site accessible for people with disabilities?
A: Some areas are accessible, but ancient structures and stairs may limit movement. The Coptic Museum is wheelchair-friendly.
Q: How do I get to Babylon Fortress?
A: The site is accessible via Cairo Metro (Mar Girgis Station, Line 1), taxis, and ride-hailing services.
Planning Your Visit
- Combine Your Visit: Include nearby attractions such as the Ben Ezra Synagogue and the Mosque of Amr ibn al-As.
- Use Public Transport: Parking is limited in Old Cairo; the metro is convenient and efficient.
- Stay Informed: Check the latest travel advisories, opening hours, and ticket prices before your visit.
- Download the Audiala App: For personalized tours, up-to-date information, and exclusive offers.
References and Further Reading
- Herasian Adventures: Coptic Cairo Ultimate Guide
- Cairo Egypt Tours: The Fortress of Babylon
- Academic Research on Babylon Fortress
- Actual Art: Babylon Fortress Architectural Study
- Encounters Travel Blog: Fortress of Babylon
- Travel Hack Fun: Coptic Cairo Guide
- ETL Travel: Babylon Fortress Guide
- The Complete Pilgrim: Babylon Fortress
- touregyptclub.com: Babylon Fortress
- jakadatoursegypt.com: Safety in Cairo
Summary and Next Steps
Babylon Fortress stands as a living testament to Egypt’s layered past, combining Roman engineering, Christian devotion, and multicultural influences within its ancient walls. By planning your visit around current Babylon Fortress visiting hours, securing tickets in advance, and following practical tips, you’ll enjoy a memorable and culturally rich experience. Don’t miss the opportunity to explore surrounding historical sites and deepen your appreciation of Cairo’s vibrant heritage.
For more travel insights, download the Audiala app, explore related guides, and follow us on social media for the latest updates and inspiration.