Visiting Al-Azhar Mosque in Al Nozha: Hours, Tickets, and History
Date: 17/07/2024
Introduction
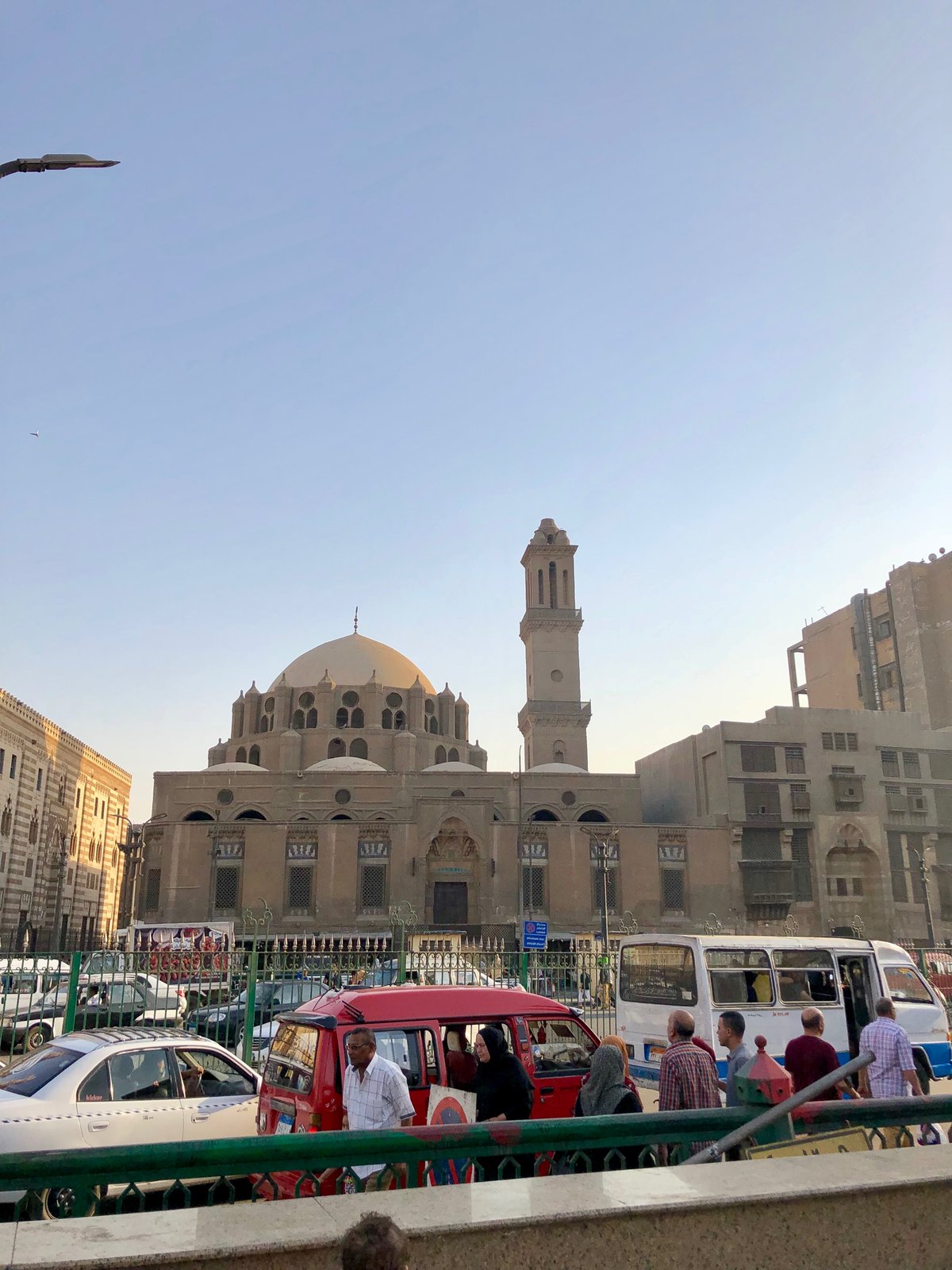
Standing as a monumental piece of Islamic heritage in the heart of Cairo, Al-Azhar Mosque is more than just a place of worship; it is a vibrant symbol of Islamic scholarship and architectural brilliance. Established in 970 AD by the Fatimid Caliphate, the mosque’s name, ‘Al-Azhar,’ translates to ‘the radiant,’ reflecting its enduring role in the dissemination of knowledge and culture (Discover the Historical Significance and Visitor Tips for Al-Azhar Mosque in Cairo). Over the centuries, Al-Azhar has evolved from a modest Friday mosque into one of the world’s oldest continuously operating universities, attracting scholars and students from across the globe (Exploring Al-Azhar Mosque - A Journey Through Its Architectural Splendor and History). This comprehensive guide delves into the rich historical significance, architectural splendor, and practical visitor tips for exploring Al-Azhar Mosque, offering a detailed look at one of Cairo’s most iconic landmarks.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Significance of Al-Azhar Mosque
- Exploring Al-Azhar Mosque’s Architecture
- Visitor Information
- Nearby Attractions
- Accessibility
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Historical Significance of Al-Azhar Mosque
Early Years and Evolution into a Seat of Learning
Founded in 970 AD by the Fatimid Caliphate, a dynasty of Ismaili Shia Muslims, the mosque quickly evolved into a center of scholarship, earning its name “Al-Azhar,” meaning “the blossoming” or “the radiant,” for its role in disseminating knowledge. Initially built as a Friday mosque for the new Fatimid capital, Al-Azhar’s transformation into a university began in 988 AD. Fatimid Caliph al-Aziz Billah established regular lectures on various Islamic sciences, attracting scholars and students from across the Muslim world. This marked the birth of Al-Azhar University, one of the oldest continuously operating universities globally.
A Legacy Forged Through Dynasties
Throughout the centuries, Al-Azhar witnessed the rise and fall of dynasties, each leaving its mark on the mosque’s architectural and intellectual landscape.
- The Fatimids (969-1171 AD) - Laid the foundation, establishing the mosque and its initial madrasas (schools).
- The Ayyubids (1171-1250 AD) - Focused on Sunni Islam’s resurgence, modifying some Fatimid architectural elements.
- The Mamluks (1250-1517 AD) - A golden age for Al-Azhar, marked by significant expansions, the addition of minarets, and the establishment of new study circles.
- The Ottomans (1517-1914 AD) - Continued patronage, further expanding the mosque and integrating it into the Ottoman education system.
Al-Azhar’s Role in Resisting Colonial Influence
Al-Azhar’s influence extended beyond religious scholarship. It played a pivotal role in resisting French occupation in the late 18th century. Scholars and students actively participated in uprisings, using the mosque as a platform for mobilizing resistance. This cemented Al-Azhar’s image as a symbol of national identity and defiance against foreign rule.
Modernization and Continued Relevance
The late 19th and 20th centuries saw Al-Azhar undergo modernization efforts. Egyptian reformer Muhammad Abduh played a key role in introducing modern subjects into the curriculum, bridging traditional Islamic teachings with contemporary thought. This ensured Al-Azhar’s continued relevance in a rapidly changing world.
Al-Azhar Today - A Global Center of Islamic Learning
Today, Al-Azhar Mosque and University remain a beacon of Islamic scholarship, attracting students from all corners of the globe. It stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of Islamic learning and its ability to adapt and thrive through centuries of change. Visiting Al-Azhar is not just about admiring its architectural grandeur; it’s about connecting with a living history of knowledge, faith, and resilience.
Exploring Al-Azhar Mosque’s Architecture
The Fatimid Foundation (970-972 AD)
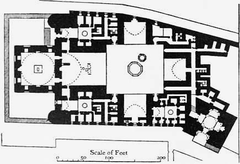
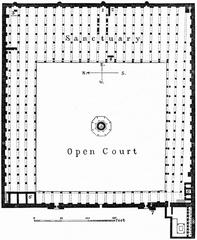
The mosque’s initial construction, commissioned by the Fatimid Caliph al-Mu’izz li-Din Allah, was completed in 972 AD. This original structure, though much smaller than the present-day mosque, established the basic layout. It featured:
- Hypostyle Hall - A vast prayer hall characterized by rows of columns supporting the roof, a typical feature of mosque architecture in that era.
- Central Courtyard (Sahn) - An open-air courtyard surrounded by arcades, serving as a transition space and a place for ablutions.
- Original Minarets - Two minarets were part of the initial construction, although they no longer exist in their original form.
Expansions and Additions Across Dynasties
Over the centuries, Al-Azhar Mosque witnessed significant expansions and additions under various rulers and dynasties:
- The Fatimids - Caliph al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah, known for his patronage of scholarship, expanded the mosque and formally established it as a center of learning in 989 AD.
- The Mamluks - This era (13th-16th century) saw the addition of several significant elements:
- Domes - The iconic dome over the mihrab (prayer niche) was built by Sultan al-Nasir Muhammad (1293-1341). Other domes were added later by different Mamluk rulers, each showcasing unique architectural styles.
- Minarets - The Mamluks added several minarets, each reflecting the architectural preferences of the sponsoring Sultan. Notable examples include the minaret of Qaytbay (1483) with its intricate stonework and the minaret of Sultan al-Ghuri (1510) known for its height and imposing structure.
- Madrasas (Religious Schools) - Various Mamluk Sultans added their own madrasas within the mosque complex, each dedicated to teaching specific Islamic schools of thought. These madrasas, with their own courtyards and student lodgings, contributed to the mosque’s evolving architectural landscape.
- The Ottomans - During their rule (16th-18th century), the Ottomans further expanded the mosque. Significant additions include:
- The Gate of Amir al-Hajj - This grand entrance, built by Abd al-Rahman Katkhuda in 1754, features impressive Ottoman architectural elements.
- Renovations and Restorations - The Ottomans undertook several restoration projects, preserving the mosque’s structural integrity and enhancing its beauty.
Architectural Styles and Influences
Al-Azhar Mosque beautifully showcases a blend of architectural styles:
- Fatimid - The original structure reflected the simplicity and elegance of Fatimid architecture, with its emphasis on geometric designs and the use of materials like marble and stucco.
- Mamluk - The Mamluk period brought about a more elaborate and ornate style. The minarets, with their multi-tiered designs and intricate carvings, exemplify Mamluk architectural prowess. The domes, often decorated with geometric patterns and calligraphy, are another hallmark of this era.
- Ottoman - The Ottoman influence is evident in the mosque’s later additions, particularly the Gate of Amir al-Hajj. This period introduced elements like slender minarets with conical roofs, pointed arches, and the use of Iznik tiles in decorative patterns.
Modern Restorations and Preservation
In recent times, Al-Azhar Mosque has undergone extensive restoration work to preserve its historical and architectural significance. These efforts, often supported by international organizations, focus on:
- Structural Reinforcement - Strengthening the foundations and walls to withstand the test of time and environmental factors.
- Conservation of Artwork - Restoring the intricate carvings, stucco decorations, and calligraphy that adorn the mosque’s interior and exterior.
- Modern Amenities - Integrating modern facilities like lighting and sound systems while maintaining the mosque’s architectural integrity.
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours
Al-Azhar Mosque is open to visitors daily from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM. However, it is closed during prayer times, so plan your visit accordingly.
Ticket Prices
Admission to Al-Azhar Mosque is free, but donations are appreciated to help with the mosque’s upkeep and preservation efforts.
Travel Tips
- Dress Code - Modest clothing is required for both men and women. Women should cover their heads with a scarf.
- Footwear - Shoes must be removed before entering the mosque, so wearing easy-to-remove footwear is recommended.
- Guided Tours - Consider hiring a local guide to enrich your experience with detailed historical and cultural insights.
Nearby Attractions
While visiting Al-Azhar Mosque, consider exploring other nearby historical sites in Cairo:
- Khan El Khalili Bazaar - A bustling market offering traditional crafts, jewelry, and souvenirs.
- The Egyptian Museum - Home to an extensive collection of ancient Egyptian artifacts.
- Sultan Hassan Mosque - Another architectural marvel located nearby.
Accessibility
Al-Azhar Mosque is accessible to all visitors, but those with mobility issues may find some areas challenging due to the mosque’s historic architecture. It is advisable to contact the mosque administration in advance to make necessary arrangements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the Al-Azhar Mosque visiting hours?
A: The mosque is open daily from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM, except during prayer times.
Q: Is there an entrance fee for Al-Azhar Mosque?
A: Admission is free, but donations are appreciated.
Q: What should I wear when visiting Al-Azhar Mosque?
A: Modest clothing is required. Women should cover their heads with a scarf.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes, hiring a local guide is recommended for a richer experience.
Conclusion
Al-Azhar Mosque is not merely an architectural marvel but a living testament to the enduring legacy of Islamic scholarship and resilience. From its foundation in the Fatimid era to its expansions under the Mamluks and Ottomans, and its modern-day relevance, Al-Azhar stands as a beacon of knowledge and faith (Visitor Information and Tips for Al-Azhar Mosque). Visitors to this historic site will find themselves immersed in a blend of art, history, and spirituality, making it a must-visit destination in Cairo. Whether you’re drawn by its architectural beauty, its scholarly heritage, or its cultural significance, Al-Azhar Mosque offers a unique and enriching experience. For more travel tips and updates, follow us on our social media channels or download our mobile app Audiala to explore more about Cairo’s historical sites.