Castaic Power Plant Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Travel Guide
Date: 04/07/2025
Introduction
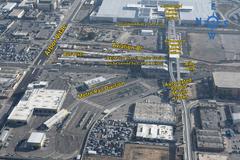
The Castaic Power Plant, located in the scenic northern reaches of Los Angeles County, is a crown jewel in California’s renewable energy and water management landscape. As a pivotal part of the California State Water Project, this pumped-storage hydroelectric facility harnesses the elevation difference between Pyramid Lake and Castaic Lake to generate over 1,200 megawatts of peak-load electricity. Its innovative design not only makes it one of the largest facilities of its kind in the western United States but also a landmark of engineering, environmental stewardship, and economic development.
While the power plant itself is generally closed to the public due to operational and security reasons, visitors can enjoy the adjacent Castaic Lake State Recreation Area, which offers numerous recreational activities including boating, fishing, hiking, and scenic views of the infrastructure. Special guided tours of the plant are occasionally available through professional and educational organizations, offering a rare behind-the-scenes look at this engineering marvel.
This comprehensive guide details the Castaic Power Plant’s history, engineering achievements, environmental and economic impacts, and practical visitor information. It will also answer frequently asked questions and provide tips for exploring the surrounding attractions. For further information, consult resources such as the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, California Department of Water Resources, and California State Parks.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- History and Planning
- Engineering and Construction
- Role in the California State Water Project
- Technological Innovations
- Economic and Regional Impact
- Environmental Impact
- Visitor Information
- Operational Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Call to Action
- References
History and Planning
Conceived in the mid-20th century, the Castaic Power Plant was developed to address Southern California’s growing need for electricity and water. It is a central component of the California State Water Project, which was initiated in the 1960s to transport water from Northern to Southern California while generating renewable energy (California Department of Water Resources). The Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) partnered with the state to construct the plant at the terminus of the West Branch of the California Aqueduct, utilizing the elevation drop between Pyramid and Castaic Lakes for hydroelectric generation (LADWP Castaic Power Plant).
Engineering and Construction
Construction began in the early 1970s, transforming the area into a sophisticated pumped-storage hydroelectric facility at a cost of $412 million (Los Angeles Times article). Massive feeder pipes, large enough for workers to walk through, channel water from Pyramid Lake to Castaic’s turbines. The plant features seven generators with a combined capacity of 1,247 MW, making it one of the largest in the region (LADWP Power Generation).
A unique aspect of the plant is its pumped-storage design: it not only generates electricity but also pumps water uphill during off-peak hours, effectively storing energy for later use.
Role in the California State Water Project
As the southernmost hydroelectric facility of the California State Water Project (California State Water Project Overview), the Castaic Power Plant plays a dual role. It generates electricity as water drops from Pyramid Lake to Castaic Lake and supports water delivery. This synergy between water management and energy production helps balance the region’s electricity grid and supports recreational activities at Castaic Lake.
Technological Innovations
Since its commissioning in 1978, the plant has been upgraded with advanced control systems, improved turbine efficiency, and enhanced safety protocols. Its reversible pump-turbines are crucial for storing excess renewable energy and balancing the intermittent supply from sources like wind and solar (LADWP Sustainability Initiatives).
Economic and Regional Impact
The Castaic Power Plant has contributed significantly to the regional economy by creating thousands of jobs during construction and supporting skilled employment for ongoing operations. Its reliable electricity supply has underpinned the growth of industry and residential communities. Additionally, the integration with Castaic Lake has created a thriving recreational destination (Castaic Lake Recreation).
Environmental Impact
Hydrological and Ecosystem Effects
The facility uses Pyramid and Castaic Lakes as reservoirs, which, while supporting water supply and recreation, have altered natural habitats and flow regimes (Water Power Magazine). Reservoir creation has submerged ecosystems and transformed the landscape, affecting biodiversity.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Water Quality
Hydropower is generally cleaner than fossil fuels, but reservoirs can emit methane and affect water quality through nutrient accumulation and reduced oxygen levels (WorldRef Insights).
Visual and Landscape Alteration
The infrastructure—tunnels, penstocks, and dams—has changed the region’s appearance, but mitigation measures like habitat restoration are in place (Water Power Magazine).
Aquatic Ecosystem Concerns
Artificial reservoirs and modified flows can disrupt aquatic life, though fish passage is less of a concern at Castaic compared to traditional river dams (WorldRef Insights).
Social and Community Considerations
While constructed in a sparsely populated area, the plant’s development reflects growing attention to community engagement and environmental justice (WorldRef Insights; LADWP SLTRP Meeting Summary).
Visitor Information
Accessibility and Tours
The Castaic Power Plant is not open for general public tours, but special visits can be arranged for professional or educational groups through organizations such as ASME or AIAA (Ekwestrel Engineering). These tours require advance RSVP and government-issued identification. The adjacent Castaic Lake State Recreation Area is open to the public year-round.
Visiting Hours and Tickets
- Castaic Power Plant: No regular public hours or ticket sales. Special tours only.
- Castaic Lake State Recreation Area: Open daily, typically 6:00 AM – 10:00 PM; fees may apply for parking and activities (California State Parks).
Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Location: Near Castaic, CA, about 45 miles northwest of downtown Los Angeles. Access by I-5.
- Nearby: Castaic Lake for boating, hiking, and fishing; Pyramid Lake, Santa Clarita, and Vasquez Rocks for additional recreation and sightseeing.
Practical Tips for Tours
- Monitor professional organization and LADWP announcements for tour opportunities.
- Arrive early and prepared for security screening.
- Wear sturdy, closed-toe shoes; hard hats may be provided.
- Bring water and minimal belongings.
- Photography is restricted; always ask permission.
- Some tour areas may challenge those with claustrophobia or mobility issues.
Operational Practices
The plant operates on a daily pump and generate cycle, coordinated with grid operators to optimize energy storage and release. Maintenance is ongoing to ensure reliability and compliance with safety standards (LADWP SLTRP Meeting Summary).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I tour the Castaic Power Plant?
A: Public tours are not available, but special arrangements can be made for educational or professional groups.
Q: What are the visiting hours for Castaic Lake State Recreation Area?
A: The park is generally open from 6:00 AM to 10:00 PM daily.
Q: Are there fees to visit the recreation area?
A: Yes, vehicle day-use and activity fees apply. Check the official park website for current details.
Q: Is the area accessible for visitors with disabilities?
A: The recreation area provides accessible trails, picnic sites, and restrooms.
Q: What should I bring for a tour?
A: Government-issued ID, sturdy shoes, water, and minimal personal items.
Call to Action
The Castaic Power Plant continues to play a vital role in California’s clean energy and water resource management, supporting both the electricity grid and regional recreation. While general public tours are rare, the surrounding recreation area offers abundant opportunities to experience the intersection of engineering and nature.
For updates on plant tours, regional energy news, and curated guides, download the Audiala app and follow us on social media. For more information, visit the LADWP official site, California Department of Water Resources, and California State Parks.
References
- California Department of Water Resources
- LADWP Castaic Power Plant
- Los Angeles Times article
- LADWP Power Generation
- California State Water Project Overview
- LADWP Sustainability Initiatives
- Castaic Lake Recreation
- Water Power Magazine Spotlight on Pumped Storage
- WorldRef Insights on Hydro Power Environmental Impact
- LADWP SLTRP Meeting Summary
- Ekwestrel Engineering Castaic Lake Hydroelectric Power Plant Facility
- LAist Article on Castaic Power Plant
- ThinkNest Future of Castaic Power Plant
- CLUI Castaic Power Plant