Purana Qila Visiting Hours, Ticket Prices, and Historical Significance
Date: 17/08/2024
Introduction
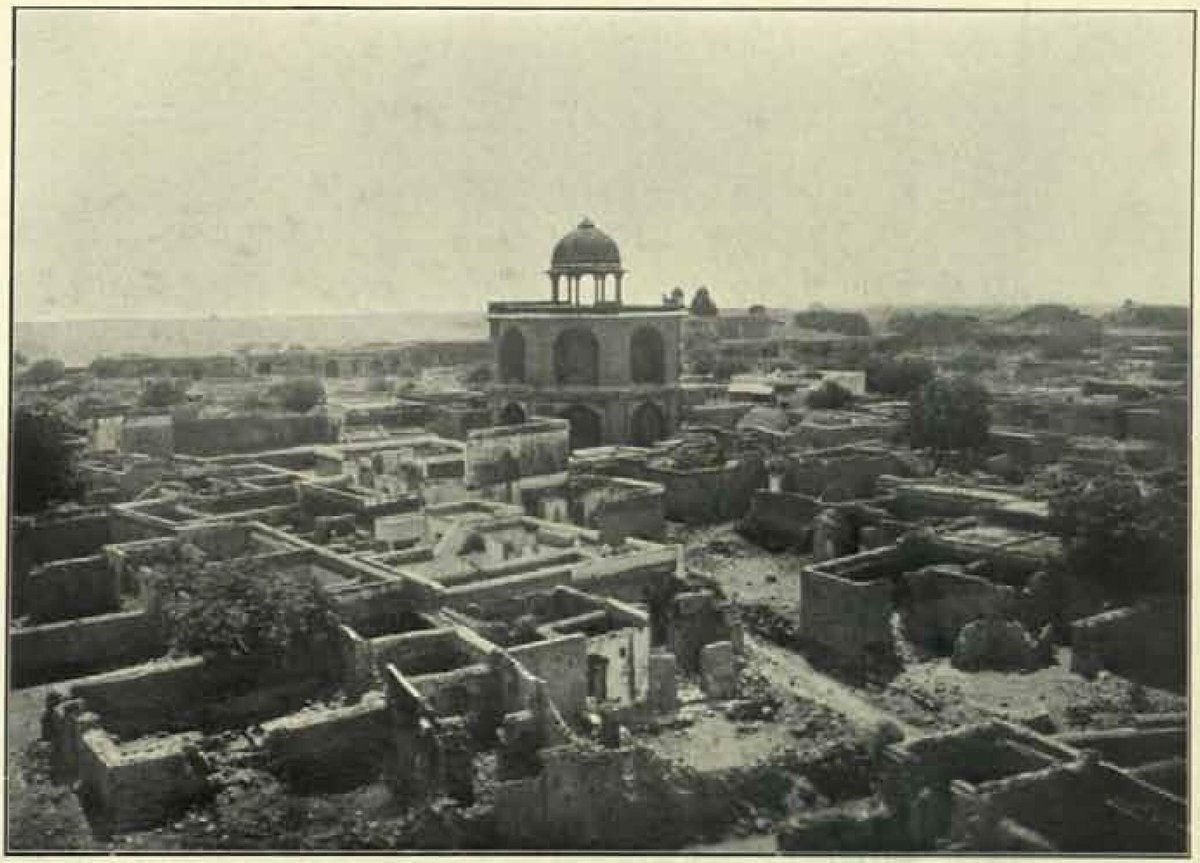
Purana Qila, often referred to as the Old Fort, is one of New Delhi’s most iconic historical landmarks, embodying the rich tapestry of India’s ancient and medieval heritage. The fort’s origins are shrouded in legend, with some historians identifying it as the site of Indraprastha, the ancient city mentioned in the Mahabharata, founded by the Pandavas over 2,500 years ago. Archaeological excavations have uncovered artifacts dating back to the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE, lending credence to its ancient roots (Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage).
The fort as it stands today primarily dates back to the 16th century, constructed under the direction of the Afghan ruler Sher Shah Suri and later completed by the Mughal Emperor Humayun. This amalgamation of Afghan and Mughal architectural influences is evident in the fort’s grand design, exemplified by structures such as the Qila-i-Kuhna Mosque and the Sher Mandal (Delhi Darshan).
Visitors to Purana Qila can explore its majestic gates, lush gardens, and the Archaeological Museum, which houses artifacts from various historical periods. The site is also a vibrant cultural hub, hosting light and sound shows, art exhibitions, and cultural festivals that bring the fort’s storied past to life (Citybit). Whether you’re a history enthusiast, a cultural explorer, or simply a traveler seeking to immerse yourself in the historical essence of Delhi, Purana Qila offers a captivating journey through time.
Table of Contents
Exploring Purana Qila: History, Visiting Hours, Tickets, and More
Ancient Origins and Mythological Connections
Purana Qila, also known as the Old Fort, is steeped in history that dates back over 2,500 years. According to legend, the site of Purana Qila is believed to be the ancient city of Indraprastha, which is mentioned in the Indian epic Mahabharata. Indraprastha was the capital city founded by the Pandavas, the protagonists of the epic. This connection to the Mahabharata lends Purana Qila a mythological significance that adds to its historical allure. Excavations at the site have revealed layers of habitation dating back to the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE, with pottery fragments that could date from approximately 1000-500 BCE (Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage).
Mughal and Afghan Influence
The current structure of Purana Qila primarily dates back to the 16th century. It was initially constructed by the Afghan king Sher Shah Suri during his reign from 1540 to 1545. Sher Shah Suri, after defeating the Mughal Emperor Humayun, decided to build a fort that would serve as a stronghold for his empire. The fort was later renovated and completed by Humayun after he recaptured Delhi from Sher Shah Suri’s successors in 1555 (Delhi Darshan).
Architectural Marvels
Purana Qila is a masterpiece of medieval architecture, showcasing a blend of Afghan and Mughal styles. The fort is spread over a vast area and encompasses notable structures such as the Qila-i-Kuhna Mosque, Sher Mandal, and Humayun’s Library. The Qila-i-Kuhna Mosque, built by Sher Shah Suri, is an exquisite example of Indo-Islamic architecture, known for its stunning domes and intricate designs. The mosque features stone inlay using red and yellow sandstone and white and black marble, stone carving, and tile work (Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage).
The Sher Mandal, initially conceived as a library by Sher Shah Suri, stands as a testimony to the evolving architectural styles of the period. Its octagonal design and distinct features make it a fascinating structure within the fort. Additionally, Humayun’s Library reflects a fusion of Persian and Indian architectural elements (Delhi Darshan).
Cultural and Heritage Significance
Purana Qila is not just a historical relic; it’s a vibrant hub of cultural and heritage activities. The fort plays host to various cultural events, including light and sound shows that narrate the history of Delhi and the fort. These events transport visitors back in time, allowing them to visualize the grandeur and history associated with the place. The sprawling lawns within the fort often serve as venues for cultural festivals, art exhibitions, and concerts, attracting artists and art enthusiasts from all corners (Delhi Darshan).
Visitor Information
- Visiting Hours: Purana Qila is open daily from 7:00 AM to 5:00 PM.
- Tickets: The entry fee for Indian citizens is INR 30, while for foreign visitors, it is INR 300. Children below the age of 15 can enter for free.
- Travel Tips: Visitors are advised to wear comfortable shoes as exploring the fort involves a considerable amount of walking. Carrying water and light snacks is also recommended.
- Nearby Attractions: Purana Qila is located near other historical sites like Humayun’s Tomb, India Gate, and the National Zoological Park.
Special Events and Guided Tours
Special events like cultural festivals and exhibitions often take place within the fort premises. Guided tours are available and can provide a more in-depth understanding of the fort’s history and architecture. These tours are conducted by knowledgeable guides who share fascinating anecdotes and lesser-known facts about Purana Qila.
Photographic Spots
Purana Qila offers numerous photographic opportunities. The Qila-i-Kuhna Mosque and Sher Mandal are particularly popular among photographers for their architectural beauty. The lush green lawns and the fort’s imposing walls provide stunning backdrops for memorable photos.
Archaeological Discoveries
Excavations at Purana Qila have unearthed a wealth of artifacts that provide insights into the historical and cultural evolution of the region. The Archaeological Museum within the fort houses these artifacts, which include pottery, figurines, glassware, tiles, and Mughal period Chinese porcelain. These discoveries highlight the continuous habitation and historical significance of the site over millennia (Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage).
Strategic Importance
The strategic importance of Purana Qila is underscored by its location and design. The fort’s walls form a rectangle with a perimeter of about 1.9 kilometers. The eastern side was originally bounded by the Yamuna River, which provided a natural defense. The fort’s gateways, including the Bada Darwaza and Talaaqi Darwaza, are imposing structures that served both defensive and ceremonial purposes. The Bada Darwaza, most likely built under Humayun, features inlay patterns in sandstone and marble, stone carving, and tile work. The Talaaqi Darwaza, with its incised plaster and tile detail, adds to the fort’s architectural grandeur (Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage).
Preservation Efforts
Efforts by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and other heritage organizations are underway to preserve and restore the fort, ensuring that future generations can appreciate its architectural splendor and historical importance. These efforts include maintaining the structural integrity of the fort, conserving its intricate designs, and promoting its cultural significance through various events and exhibitions (Delhi Darshan).
FAQ
- What are the visiting hours for Purana Qila?
- Purana Qila is open daily from 7:00 AM to 5:00 PM.
- How much are tickets for Purana Qila?
- The entry fee for Indian citizens is INR 30, while for foreign visitors, it is INR 300. Children below the age of 15 can enter for free.
- Are guided tours available?
- Yes, guided tours are available and provide a more in-depth understanding of the fort’s history and architecture.
- What are some nearby attractions?
- Nearby attractions include Humayun’s Tomb, India Gate, and the National Zoological Park.
Conclusion
Purana Qila stands as a living testament to Delhi’s ancient past and its resilience through the ages. As visitors explore its majestic structures and vast expanse, they can feel the whispers of history echoing through time. A visit to Purana Qila is not merely a journey into the past; it’s an experience that connects us with the roots of a city that has stood witness to the rise and fall of empires, making it an integral part of India’s rich cultural tapestry.
References
- Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage. (n.d.). Purana Qila. Retrieved from Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage
- Delhi Darshan. (n.d.). Purana Qila: A Glimpse into Delhi’s Timeless Past. Retrieved from Delhi Darshan
- Citybit. (n.d.). Purana Qila. Retrieved from Citybit