Daughters of Jacob Bridge: Comprehensive Visiting Guide, Historical Overview, and Ticket Information
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
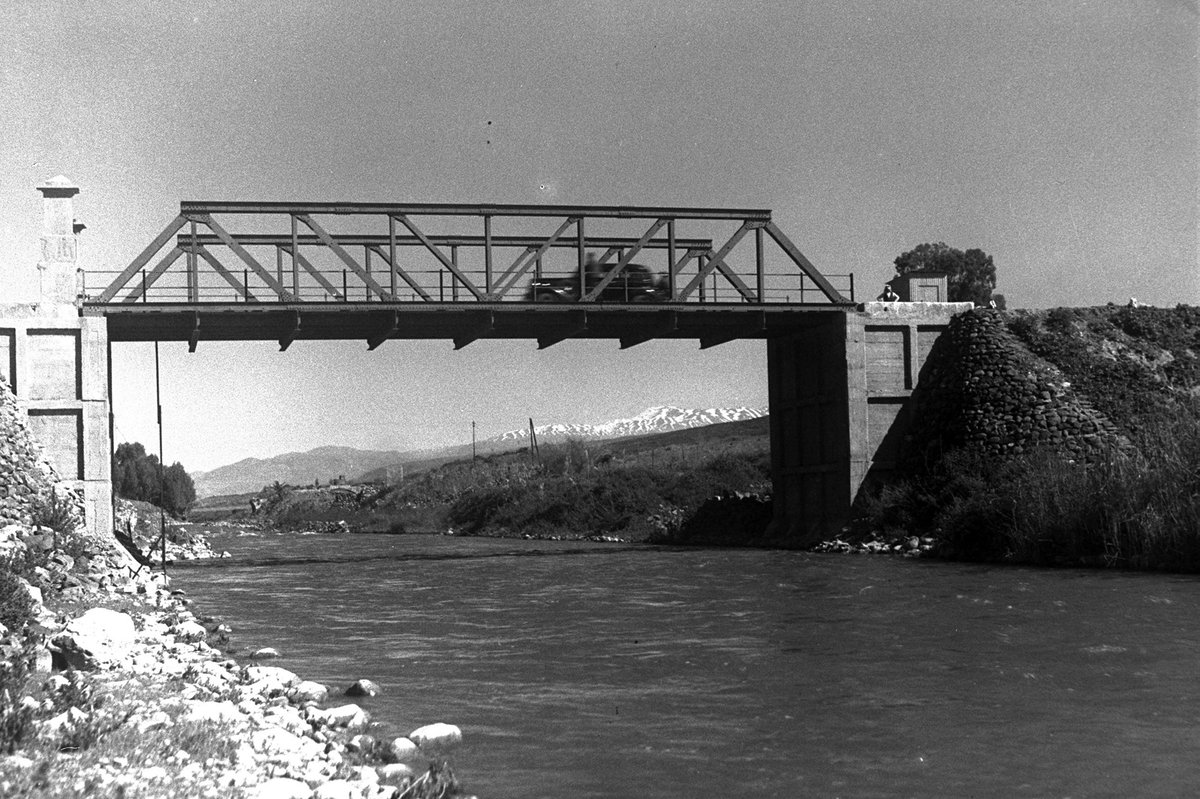
The Daughters of Jacob Bridge, known locally as Gesher Bnot Ya’akov (גשר בנות יעקב), is among Northern Israel’s most important historical and cultural landmarks. Spanning the upper Jordan River, this ancient crossing has served as a strategic link between the Galilee and the Golan Heights for thousands of years. As one of the oldest known inhabited sites in the Levant—tracing human activity back nearly 780,000 years—the bridge blends archaeological richness, dramatic history, and opportunities for adventure. This guide provides a detailed overview of the bridge’s history, practical visitor information (including visiting hours and ticketing), accessible travel tips, and recommendations for nearby attractions. Whether your interests lie in archaeology, outdoor adventure, or simply appreciating scenic landscapes, the Daughters of Jacob Bridge is a must-see destination in Northern Israel.
For the latest updates and official visitor information, consult the Israel Nature and Parks Authority (INPA), Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA), and Israel Ministry of Tourism (Israel Travel).
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Overview
- Architectural and Archaeological Features
- Cultural and Religious Significance
- Visiting Information
- Nearby Attractions
- Visitor Experience and Practical Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Visuals and Media
- Conclusion
- References and Further Reading
Historical Overview
Early Settlement and Ancient Empires
Archaeological excavations confirm that the area around the Daughters of Jacob Bridge has been inhabited since the Lower Paleolithic era, approximately 780,000 years ago. Flint tools and Acheulean hand axes found at the site indicate it was a gathering point for early humans. The bridge’s location at a natural ford made it a crucial crossing for ancient trade, migration, and military routes—especially as part of the Via Maris, which connected Egypt with Mesopotamia (Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs, BibleWalks).
Medieval and Crusader Periods
During the Crusader era (12th–13th centuries CE), the bridge was fortified and became known as “Pont des Filles de Jacob” or Jacob’s Ford (Latin: Vadum Iacob). It was the site of the Chastelet fortress, a critical stronghold that witnessed fierce battles between Crusaders and Saladin’s forces, culminating in its destruction in 1179. The Mamluks later reconstructed the bridge with stone arches and added a fortified caravanserai (khan) to shelter travelers—a testament to the site’s enduring strategic value (Encyclopaedia Judaica).
Ottoman Era and Modern Military Events
Under Ottoman administration (1517–1917), the bridge continued to serve as a vital crossing for trade, administration, and pilgrimage. European explorers like Victor Guérin documented its historic and biblical associations in the 19th century (PEF Survey of Western Palestine). The site is linked to the biblical patriarch Jacob, who, according to tradition, crossed the Jordan River nearby (Genesis 32:22).
In the 20th century, the bridge played pivotal roles in military conflicts: British and Australian forces crossed it during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I (Australian War Memorial), and the bridge was repeatedly destroyed and rebuilt during the “Night of the Bridges” in 1946, the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, and later regional conflicts (Yad Vashem).
Architectural and Archaeological Features
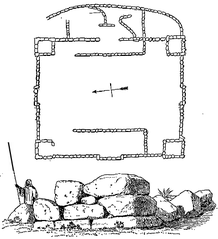
The present-day remains of the Daughters of Jacob Bridge reflect multiple phases of construction and repair. Notable architectural features include:
- Basalt Arches: Three to four pointed arches constructed from local basalt, each spanning 8–10 meters. The full length of the bridge is about 40–50 meters.
- Foundations: Deep-set to withstand floods and heavy use by caravans and armies.
- Decorative Details: Limestone inscriptions and carving provide visual contrast to the dark basalt.
- Defensive Structures: Remnants of Crusader gatehouses, Mamluk towers, and evidence of a moat and drawbridge on the western approach.
- Khan (Caravanserai): Thick basalt walls and vaulted ceilings provided protection and shelter for travelers.
- Archaeological Layers: Finds include Acheulean tools, Roman coins, Crusader and Mamluk inscriptions, and Ottoman ceramics (Israel Antiquities Authority, Israel Nature and Parks Authority).
Cultural and Religious Significance
The bridge holds significance for Jewish, Christian, and Islamic traditions due to its biblical association with Jacob. The name “Daughters of Jacob” may stem from medieval legends or linguistic interpretations. The surrounding landscape and bridge itself have functioned as a symbolic passage between regions, cultures, and religions (Jewish Virtual Library).
Visiting Information
Hours and Ticketing
- Opening Hours: Generally open daily, 8:00 AM–5:00 PM (hours may vary in summer or on holidays).
- Admission: Free for general entry. Fees may apply for guided tours and special events.
- Adventure Activities: Tickets required for rappelling, rope climbing, and the bungee swoop. Book online or on-site (advance booking recommended, especially in peak season) (Israel Extreme).
Accessibility and Travel Tips
- Location: Easily accessible by car via Highway 91, with ample parking on-site.
- Public Transport: Reachable by regional bus from Safed and Tiberias.
- Accessibility: Paved paths, ramps, and accessible restrooms support visitors with mobility challenges.
- Best Time to Visit: Spring and autumn for mild weather and scenic landscapes. Summer can be hot—bring sun protection and water.
Guided Tours and Adventure Activities
- Guided Tours: Available on weekends or by appointment. Run by expert archaeologists and local operators.
- Adventure Options: Rappelling, commando-style rope climbs, and bungee swoops over the Jordan River—all supervised by certified professionals with safety equipment (Israel Extreme).
- Custom Packages: Available for groups and families, including meals and multi-activity bundles.
Nearby Attractions
- Hula Valley Nature Reserve: Renowned for birdwatching and wetland hiking.
- Tel Dan Archaeological Site: Ancient city ruins and lush nature trails.
- Black Canyon (Nakik HaShachor): Adventure canyoning and hiking.
- Dalton Cliff and Abirim Stalactite Cave: Additional options for adventure and exploration.
Visitor Experience and Practical Tips
- Amenities: Restrooms, shaded seating, picnic areas, and reliable mobile coverage.
- Safety: All adventure activities are supervised; first aid is available on-site.
- Photography: Multiple scenic viewpoints—ideal for photos at sunrise or sunset.
- Environmental Care: Respect local flora and fauna, dispose of waste properly, and follow staff guidelines for sustainable tourism.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the visiting hours for the Daughters of Jacob Bridge?
A: Typically 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM daily, but check official sites for seasonal updates.
Q: Is there an entrance fee?
A: General admission is free. Adventure activities and special tours require tickets.
Q: How do I purchase activity tickets?
A: Online via the official booking platform or on-site (advance booking recommended).
Q: Is the site accessible for visitors with disabilities?
A: Yes. There are paved paths and accessible restrooms, though some uneven terrain exists.
Q: Are children allowed to participate in adventure activities?
A: Most activities have age or height restrictions—confirm with operators before booking.
Q: What other sites are nearby?
A: Hula Valley Nature Reserve, Tel Dan, Black Canyon, and Dalton Cliff.
Visuals and Media
- Alt text: Ruins of the Daughters of Jacob Bridge featuring basalt arches over the Jordan River in Northern Israel.
- Interactive map of the bridge location and nearby attractions
- Official social media channels and virtual tours feature galleries and videos with optimized alt tags for accessibility.
Conclusion
The Daughters of Jacob Bridge is much more than an ancient crossing—it is a testament to the region’s layered history, blending archaeological marvels, military intrigue, and natural beauty. With its well-preserved ruins, engaging adventure activities, and accessible facilities, it appeals to history buffs, families, and thrill-seekers alike. Ongoing conservation and educational programs by the Israel Nature and Parks Authority and Israel Antiquities Authority ensure that this landmark remains an enduring symbol of Northern Israel’s heritage.
Plan your visit today to experience the Daughters of Jacob Bridge firsthand. For the most up-to-date information on tours, activities, and events, download the Audiala app and explore official resources. Your journey through history and adventure awaits!
References and Further Reading
- Daughters of Jacob Bridge Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Guide to Northern Israel’s Iconic Monument, 2025, Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs)
- Archaeological Reports on Daughters of Jacob Bridge, Israel Antiquities Authority (Israel Antiquities Authority)
- Biblical and Historical Context, BibleWalks (BibleWalks)
- Crusader and Medieval History, Encyclopaedia Judaica (Jewish Virtual Library)
- 19th Century and Ottoman Era Documentation, PEF Survey of Western Palestine (Palestine Exploration Fund)
- Military History and World War I Role, Australian War Memorial (Australian War Memorial)
- 20th Century Conflicts and Reconstructions, Yad Vashem (Yad Vashem)
- Recent Archaeological Discoveries, Haaretz (Haaretz)
- Official Site and Conservation Efforts, Israel Nature and Parks Authority (Israel Nature and Parks Authority)
- Visiting Information and Adventure Activities, Israel Extreme (Israel Extreme)
- General Tourism and Travel Tips, Israel Ministry of Tourism (Israel Ministry of Tourism)
- Wikipedia: Daughters of Jacob Bridge (Wikipedia)