Visiting Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide in Düsseldorf: Hours, Tickets, and Tips
Publication Date: 23/07/2024
Introduction to Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide
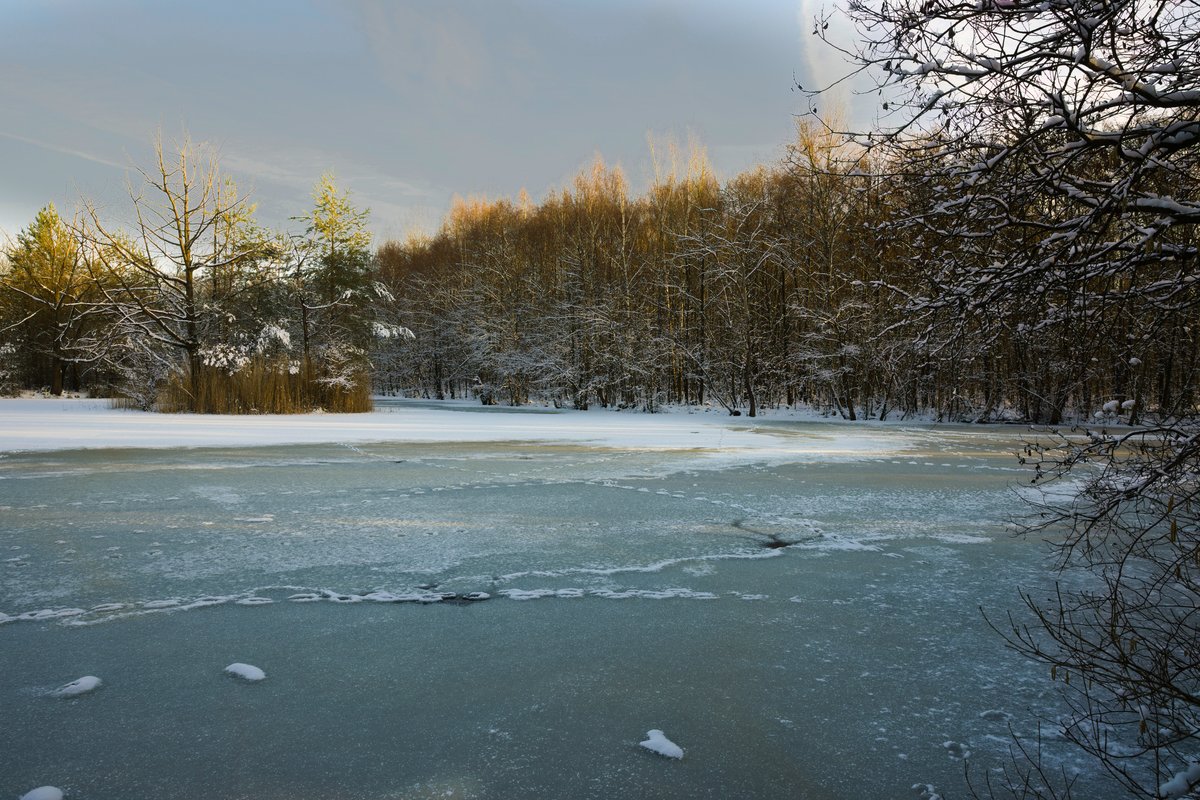
Nestled within the bustling cityscape of Düsseldorf, Germany, the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide stands as a testament to nature’s resilience and the enduring efforts of conservationists. This nature reserve, with its unique heathland, wetlands, and forested areas, offers a serene escape into a rich tapestry of biodiversity. Formed in the post-glacial period, the Ohligser Heide has been shaped by both natural processes and human activities over centuries (NABU). Conservation efforts began in earnest in the mid-20th century, leading to its designation as a nature reserve in 1953. Today, it is a sanctuary for rare and endangered species, supported by ongoing restoration projects and community involvement. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the Ohligser Heide’s history, ecological significance, and practical information for visitors, making it an indispensable resource for anyone planning to explore this natural gem.
What You Will Find in This Guide
- Introduction
- History of Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide
- Early History and Formation
- Human Influence and Land Use
- Industrialization and Urbanization
- Conservation Efforts
- Establishment as a Nature Reserve
- Restoration Projects
- Biodiversity Monitoring
- Community Involvement and Education
- Legal Protections
- Funding and Support
- Visitor Information
- Visiting Hours
- Tickets
- Travel Tips
- Nearby Attractions
- Accessibility
- Special Events and Guided Tours
- Photographic Spots
- Challenges and Future Directions
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Discover the History and Conservation Efforts of Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide in Düsseldorf
Introduction
Nestled in the vibrant city of Düsseldorf, Germany, the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide is a historical and ecological gem. This article delves into the rich history and ongoing conservation efforts of this unique nature reserve, as well as providing practical information for visitors.
History of Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide
Early History and Formation
The Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide, located in Düsseldorf, Germany, has a rich history that dates back to the post-glacial period. The area was originally formed by the retreat of glaciers, which left behind a landscape characterized by sandy soils and heathland vegetation. This unique environment provided a habitat for a variety of plant and animal species, some of which are now rare or endangered.
Human Influence and Land Use
Over the centuries, human activities have significantly influenced the Ohligser Heide. During the Middle Ages, the area was used for grazing livestock, which helped maintain the open heathland by preventing the encroachment of trees and shrubs. However, as agricultural practices evolved, the land was increasingly converted to farmland and forest, leading to a decline in the heathland habitat.
Industrialization and Urbanization
The industrialization of the 19th and 20th centuries brought further changes to the Ohligser Heide. The expansion of nearby cities, including Düsseldorf, led to increased pressure on the land for development and resource extraction. Sand and gravel mining became prevalent, further altering the landscape and threatening the native flora and fauna.
Conservation Efforts
Establishment as a Nature Reserve
Recognizing the ecological importance of the Ohligser Heide, conservation efforts began in earnest in the mid-20th century. In 1953, the area was officially designated as a nature reserve, known as the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide. This designation aimed to protect the unique heathland ecosystem and its biodiversity from further degradation.
Restoration Projects
Since its designation as a nature reserve, numerous restoration projects have been undertaken to rehabilitate the Ohligser Heide. These projects have focused on removing invasive species, reintroducing native plants, and managing the landscape to mimic traditional land-use practices that support heathland habitats. For example, controlled grazing by sheep has been reintroduced to help maintain the open heathland and prevent the growth of trees and shrubs.
Biodiversity Monitoring
Ongoing biodiversity monitoring is a crucial component of the conservation efforts at Ohligser Heide. Researchers and conservationists regularly conduct surveys to assess the health of the ecosystem and track the populations of key species. This data helps inform management decisions and ensures that conservation strategies are effective in preserving the area’s biodiversity.
Community Involvement and Education
Community involvement and education are also vital to the success of conservation efforts at Ohligser Heide. Local residents and visitors are encouraged to participate in volunteer activities, such as habitat restoration and species monitoring. Educational programs and guided tours are offered to raise awareness about the importance of the heathland ecosystem and the need for its protection.
Legal Protections
In addition to its designation as a nature reserve, the Ohligser Heide is protected by various national and international laws and regulations. These legal protections help safeguard the area from development and other activities that could harm its ecological integrity. For example, the European Union’s Habitats Directive and Birds Directive provide a framework for the conservation of habitats and species across member states, including Germany (European Commission).
Funding and Support
Conservation efforts at Ohligser Heide are supported by a combination of public and private funding. Government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private donors all contribute to the financial resources needed to carry out restoration projects, biodiversity monitoring, and educational programs. This collaborative approach ensures that the necessary resources are available to protect and preserve the Ohligser Heide for future generations.
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours
The Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide is open year-round. It is recommended to visit during daylight hours for the best experience.
Tickets
Entry to the nature reserve is free of charge.
Travel Tips
The reserve is easily accessible by public transport from Düsseldorf. Visitors can take a bus or train to the nearby stops and enjoy a short walk to the reserve.
Nearby Attractions
Explore other historical sites in Düsseldorf, such as the Königsallee street, the Altstadt (Old Town), and the Rheinturm (Rhine Tower).
Accessibility
The reserve has pathways suitable for walking, and some areas are accessible for wheelchairs and strollers.
Special Events and Guided Tours
Throughout the year, the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide hosts various events and guided tours. These include bird-watching tours, nature walks, and educational workshops. Check the official website for the latest schedule and booking information.
Photographic Spots
The Ohligser Heide offers stunning photographic opportunities with its diverse flora and fauna. Popular spots include the heathland during sunrise or sunset, and the bird observation points for capturing local wildlife.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the progress made in conserving the Ohligser Heide, several challenges remain. Climate change poses a significant threat to the heathland ecosystem, as changing temperatures and precipitation patterns can alter the habitat and affect the species that depend on it. Additionally, urbanization and development pressures continue to pose risks to the area.
To address these challenges, conservationists are exploring new strategies and approaches. For example, adaptive management techniques are being implemented to respond to changing environmental conditions and ensure the resilience of the ecosystem. Collaborative efforts with local communities, government agencies, and international organizations are also being strengthened to enhance the effectiveness of conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
The history and conservation efforts of the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide highlight the importance of protecting and preserving unique ecosystems. Through a combination of restoration projects, biodiversity monitoring, community involvement, and legal protections, significant progress has been made in safeguarding this valuable heathland habitat. However, ongoing efforts and adaptive strategies will be essential to address future challenges and ensure the long-term conservation of the Ohligser Heide.
FAQ
Q - What are the visiting hours for Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide?
A - The nature reserve is open year-round, and it is recommended to visit during daylight hours.
Q - Do I need tickets to enter the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide?
A - No, entry to the reserve is free of charge.
Q - How can I get to the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide?
A - The reserve is easily accessible by public transport from Düsseldorf. Visitors can take a bus or train to nearby stops and walk to the reserve.
Q - Are there any guided tours available?
A - Yes, the reserve offers guided tours, including bird-watching tours and nature walks. Check the official website for details.
Q - Is the Naturschutzgebiet Ohligser Heide accessible for wheelchairs and strollers?
A - Some areas of the reserve have pathways suitable for wheelchairs and strollers.
Sources and Further Reading
- NABU, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- BUND, ‘Naturschutzgebiete Ohligser Heide’
- European Commission, ‘Habitats Directive’
- Düsseldorf Tourism, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- Deutsche Bahn, ‘Route Planning’
- Nature Conservation Academy, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- BirdLife International, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- German Nature Photographers, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- Weather.com, ‘Ohligser Heide Weather’
- Düsseldorf Public Transport, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- Ohligser Heide Regulations, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- Ohligser Heide Tickets, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- Ohligser Heide Events, ‘Ohligser Heide’
- Düsseldorf, ‘Official Website’