Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, Boston, United States
Date: 19/07/2024
Introduction
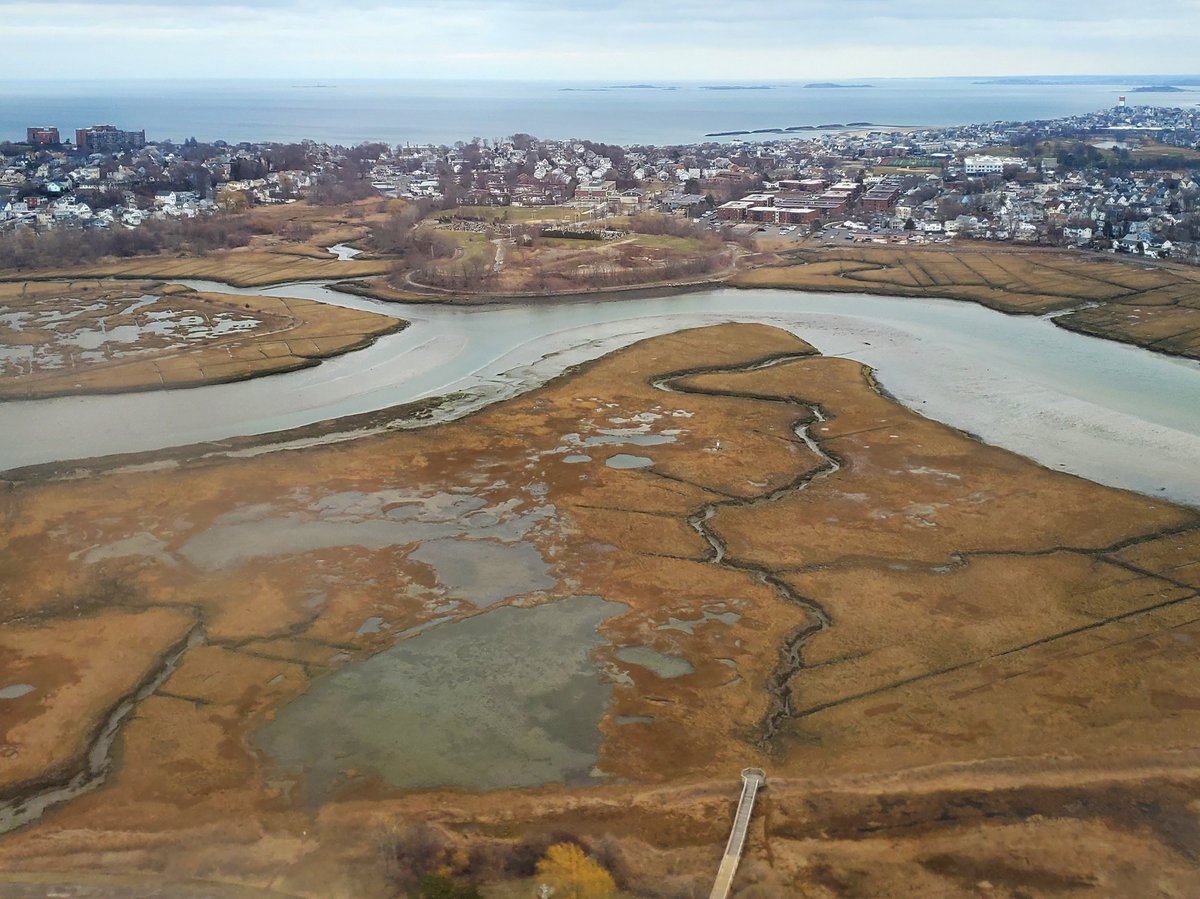
Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, located in East Boston, Massachusetts, is a captivating destination that combines natural beauty with significant historical and ecological value. Covering approximately 350 acres, it is the largest remaining salt marsh in the Boston area, offering a unique habitat for a diverse range of flora and fauna (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Historically, the marsh has been a vital resource for the Native American tribes of the Massachusett and Pawtucket peoples, providing sustenance and materials for their daily lives. The arrival of European settlers in the 17th century marked the beginning of significant land-use changes, transforming the fertile marshland into agricultural grounds (Massachusetts Historical Society). Industrialization and urban development further impacted the area, yet portions of the marsh remained undisturbed, serving as a refuge for wildlife and a natural flood control system (Boston Harbor Islands Partnership). Recognizing its ecological importance, the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation (DCR) designated Belle Isle Marsh as a reservation in 1985, aiming to protect and restore its health (Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation). This comprehensive guide will explore the rich history, ecological significance, and practical visitor information about Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, making it an essential resource for anyone planning a visit.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Early History and Indigenous Presence
- Colonial Era and Land Use Changes
- Industrialization and Urban Development
- Conservation Efforts and Establishment as a Reservation
- Ecological Significance
- Biodiversity and Wildlife Habitat
- Cultural and Recreational Importance
- Visitor Information - Tickets and Hours
- Practical Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
- Ongoing Conservation and Restoration Efforts
- Future Challenges and Opportunities
- FAQ Section
- Conclusion
Early History and Indigenous Presence
Belle Isle Marsh Reservation is a significant natural area with a history dating back thousands of years. Originally inhabited by the Native American tribes of the Massachusett and Pawtucket peoples, the marshland was a vital source of sustenance and materials for their daily lives, offering abundant resources like fish, shellfish, and plant materials.
Colonial Era and Land Use Changes
With the arrival of European settlers in the 17th century, Belle Isle Marsh began to change. Part of a larger area known as “Noddle’s Island,” granted to Samuel Maverick in 1624, the settlers recognized the marsh’s fertile soil and altered the land for agricultural purposes, constructing dikes and drainage systems (Massachusetts Historical Society).
Industrialization and Urban Development
The 19th and early 20th centuries brought industrialization and urban development to Boston, impacting Belle Isle Marsh. Construction of railroads, roads, and residential areas led to encroachment on the marshland. Despite industrial waste and pollution, portions of the marsh remained undisturbed, serving as a refuge for wildlife and a natural flood control system (Boston Harbor Islands Partnership).
Conservation Efforts and Establishment as a Reservation
In 1985, growing awareness of environmental issues led to Belle Isle Marsh being designated as a reservation by the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation (DCR). This aimed to protect the remaining marshland from further development and restore its ecological health (Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation).
Ecological Significance
Belle Isle Marsh, covering approximately 350 acres, is the largest remaining salt marsh in the Boston area. Salt marshes provide numerous ecological benefits, serving as nurseries for fish and shellfish, supporting diverse bird species, and acting as natural filters for pollutants. They also mitigate climate change impacts by absorbing carbon dioxide and buffering against storm surges and flooding (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration).
Biodiversity and Wildlife Habitat
The biodiversity of Belle Isle Marsh is one of its most significant attributes. It supports a variety of plant and animal species, many of which are rare or endangered. Birdwatchers can observe species like the snowy egret, great blue heron, and the endangered saltmarsh sparrow. The marsh is also home to numerous fish species, including striped bass and flounder (Mass Audubon).
Cultural and Recreational Importance
Belle Isle Marsh offers cultural and recreational value for the local community, providing opportunities for birdwatching, hiking, and nature photography. Educational programs and guided tours help visitors learn about the marsh’s history, ecology, and conservation efforts. The marsh also serves as an outdoor classroom for local schools and universities (Friends of Belle Isle Marsh).
Visitor Information - Tickets and Hours
Belle Isle Marsh Reservation is open to the public year-round from dawn to dusk. There is no admission fee, making it an accessible destination for everyone. Visitors are encouraged to check the official DCR website for any updates on visiting hours or special events.
Practical Travel Tips and Nearby Attractions
When planning your visit, consider bringing binoculars for birdwatching and comfortable shoes for hiking. Nearby attractions include Revere Beach and the Boston Harbor Islands, offering additional outdoor activities and scenic views. The marsh is accessible via public transportation, with the closest MBTA station being Suffolk Downs on the Blue Line.
Ongoing Conservation and Restoration Efforts
Preservation of Belle Isle Marsh requires continuous monitoring and management. The DCR, along with local environmental organizations and volunteers, work tirelessly on restoration projects such as removing invasive species, replanting native vegetation, and improving water quality (Environmental Protection Agency).
Future Challenges and Opportunities
Belle Isle Marsh faces challenges like climate change, sea-level rise, and urban development pressures. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovative conservation strategies and community engagement. Continued research and collaboration will be essential in ensuring the marsh’s long-term health (The Nature Conservancy).
Conclusion
Belle Isle Marsh Reservation stands as a testament to successful conservation efforts and the enduring importance of natural habitats within urban landscapes. Its rich history, from being a vital resource for indigenous peoples to withstanding the pressures of industrialization, highlights its resilience and ecological significance. Today, the marsh serves as a sanctuary for diverse plant and animal species, offering visitors a unique opportunity to connect with nature through activities such as birdwatching, hiking, and educational programs. The ongoing conservation efforts by the DCR and local organizations ensure that Belle Isle Marsh will continue to thrive, addressing challenges such as climate change and urban development. As a cherished part of Boston’s natural landscape, Belle Isle Marsh provides not only a peaceful retreat for nature enthusiasts but also an outdoor classroom for learning about the importance of wetland ecosystems. Whether you’re visiting for a day or exploring the wider Boston area, Belle Isle Marsh offers an enriching and memorable experience for all (Friends of Belle Isle Marsh).
FAQ Section
Q - What are the visiting hours for Belle Isle Marsh Reservation?
A - The reservation is open year-round from dawn to dusk.
Q - Is there an admission fee to enter Belle Isle Marsh?
A - No, there is no admission fee.
Q - What activities can I do at Belle Isle Marsh?
A - Visitors can enjoy birdwatching, hiking, and nature photography. Guided tours and educational programs are also available.
Q - How can I reach Belle Isle Marsh by public transportation?
A - The closest MBTA station is Suffolk Downs on the Blue Line.
Q - Are there any nearby attractions?
A - Yes, nearby attractions include Revere Beach and the Boston Harbor Islands.
References
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, Massachusetts Historical Society
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, Boston Harbor Islands Partnership
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, Mass Audubon
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, Friends of Belle Isle Marsh
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, Environmental Protection Agency
- Comprehensive Guide to Visiting Belle Isle Marsh Reservation, 2024, The Nature Conservancy