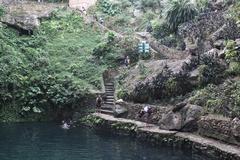Visiting Cenote Zací in Valladolid: A Complete Guide
Date: 25/07/2024
Introduction
Cenote Zací, situated in the vibrant town of Valladolid, Yucatán, Mexico, is a stunning natural sinkhole that blends remarkable natural beauty with deep historical roots. A visit to Cenote Zací offers an immersive experience featuring crystal-clear waters, ancient Mayan significance, and colonial history. Derived from the Mayan word for ‘White Hawk,’ Cenote Zací has been a crucial water source and a sacred site for the Mayan civilization (Wikipedia). The cenote was not only a lifeline for the ancient Mayans but also a battlefield for indigenous warriors against Spanish conquistadors, marking it as a symbol of resistance (Wikipedia). Today, it stands as a popular tourist destination offering a blend of recreational activities like swimming and cliff jumping, along with cultural experiences such as dining at the on-site restaurant and exploring the charming colonial town of Valladolid. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Cenote Zací, including its historical significance, visitor information, safety guidelines, and tips to ensure an enjoyable and environmentally responsible visit.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background
- Modern-Day Significance
- Visitor Tips and Nearby Attractions
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Historical Background
Mayan Origins and Significance
Cenote Zací holds a rich historical significance dating back to the ancient Mayan civilization. The name “Zací” translates to “White Hawk” in the Mayan language, a nod to the Mayan settlement that once thrived in this area (Wikipedia). The cenote was a crucial water source for the Mayans, who considered these natural sinkholes sacred. The Mayans believed cenotes were portals to the underworld and often used them for rituals and offerings to their gods.
The Capul Clan and the Conquistadors
The historical significance of Cenote Zací extends beyond its Mayan roots. It was the site where the Capul clan, a group of indigenous warriors, fought against the first Spanish conquistadors. This battle marked a significant moment in the region’s history, symbolizing the resistance of the native population against foreign invaders (Wikipedia).
The Founding of Valladolid
The city of Valladolid, where Cenote Zací is located, was founded in 1543 by Spanish settlers. The cenote played a vital role in the early development of the city, serving as its primary water source. The Spanish colonizers recognized the importance of the cenote and incorporated it into their urban planning, ensuring that the city had a reliable supply of fresh water (Wikipedia).
The Cenote’s Role in Colonial Times
During the colonial period, Cenote Zací continued to be an essential resource for the inhabitants of Valladolid. The cenote’s water was used for drinking, cooking, and irrigation, making it a lifeline for the city’s residents. The Spanish also built infrastructure around the cenote, including staircases carved from the rock, to facilitate access to the water (Atlas Obscura).
Modern-Day Significance
Architectural Features
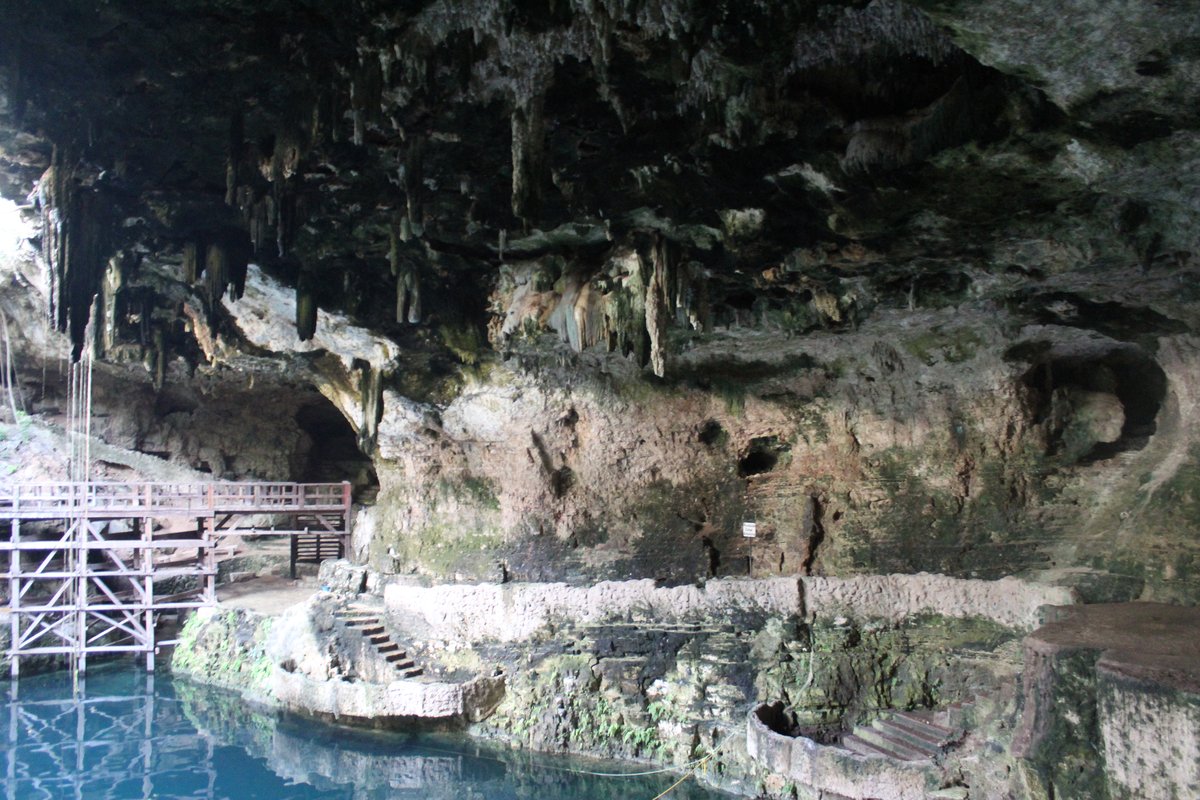
Cenote Zací is a semi-open cenote, meaning it has both exposed and subterranean sections. The cave is approximately 150 feet across and 260 feet deep, with much of its depth filled with water. The cenote’s partially collapsed cavern creates a unique and picturesque setting, with stalactites hanging from the ceiling and lush vegetation surrounding the water (Atlas Obscura).
Cultural and Recreational Activities
Today, Cenote Zací is not only a historical site but also a hub for recreational activities. Visitors can enjoy swimming in the cenote’s cool, clear waters, which are home to eyeless black fish. For the more adventurous, cliff-jumping from various heights around the cenote is a popular activity. The cenote also features an on-site restaurant, where visitors can enjoy local cuisine and gain free entrance to the cenote if their bill exceeds 200 pesos (Jonny Melon).
Visiting Hours and Tickets
Cenote Zací is open daily from 8:30 am to 5:30 pm. The entrance fee is affordable, at around 30 Mexican Pesos (approximately $1.50 USD), making it accessible to a wide range of tourists (Cenotes Mexico).
Preservation and Tourism
Efforts have been made to preserve the natural beauty and historical significance of Cenote Zací. However, the cenote faces challenges related to conservation and environmental protection. The proximity to municipal sewer pipes has raised concerns among some tourists, highlighting the need for ongoing efforts to maintain the cenote’s water quality and natural environment (Atlas Obscura).
Visitor Tips and Nearby Attractions
Travel Tips
- Best Time to Visit: Early morning or late afternoon to avoid crowds and enjoy the tranquil atmosphere.
- What to Bring: Swimsuit, towel, water shoes, and biodegradable sunscreen to protect the cenote’s ecosystem.
- Getting There: Valladolid is easily accessible by bus or car from major cities like Cancún and Mérida.
Nearby Attractions
- Convent of San Bernardino de Siena: A historical landmark showcasing colonial architecture and local history.
- Calzada de los Frailes: A picturesque street lined with colorful buildings, shops, and restaurants.
- Cenote Dzitnup: Another beautiful cenote located just a short drive from Valladolid, perfect for a day trip.
FAQ
What are the visiting hours for Cenote Zací?
Cenote Zací is open daily from 8:30 am to 5:30 pm.
How much are the tickets for Cenote Zací?
The entrance fee is approximately 30 Mexican Pesos (around $1.50 USD).
Can you swim in Cenote Zací?
Yes, visitors can swim in the cenote’s cool, clear waters.
Are there guided tours available?
While Cenote Zací does not offer official guided tours, local guides can often be found in Valladolid to provide tours of the city and its attractions.
Is Cenote Zací family-friendly?
Yes, the cenote is suitable for visitors of all ages, although children should be supervised at all times.
Conclusion
Cenote Zací’s historical background is a testament to its enduring significance in the region. From its origins as a sacred Mayan site to its role in colonial times and its current status as a tourist attraction, the cenote has played a vital role in the history and culture of Valladolid. Its unique architectural features, cultural activities, and ongoing preservation efforts make it a must-visit destination for anyone exploring the Yucatán Peninsula. For more travel tips and updates, consider checking out our mobile app Audiala, related posts, or following us on social media.