Visiting Parco Archeologico Di Egnazia: Hours, Tickets, and Tips
Date: 31/07/2024
Introduction
Discover the Parco Archeologico di Egnazia, an extraordinary archaeological park nestled along the Adriatic coast between Monopoli and Savelletri in the Puglia region of Italy. This site, with its roots stretching back to the Bronze Age, offers an unparalleled glimpse into the rich tapestry of history that has shaped the region. From early human settlements and the Iron Age invasions by the Iapigi to the prosperity of the Roman era and the subsequent decline and abandonment, Egnazia’s historical layers are both deep and diverse. Rediscovered in 1912, the site has since been a focal point of archaeological research, revealing significant insights into the lives and cultures of ancient civilizations (Beautiful Puglia, Summer in Italy). Whether you are a history enthusiast eager to delve into the past or a casual tourist seeking a picturesque and culturally enriching experience, Parco Archeologico di Egnazia promises to captivate and educate. This guide will provide you with comprehensive information on the site’s historical significance, visitor logistics, and practical travel tips, ensuring a fulfilling visit to this remarkable destination.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Overview
- Visitor Information
- The National Archaeological Museum of Egnazia
- Christian Basilicas and Other Structures
- The Baths and Engineering Marvels
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Historical Overview
Early Settlements and Bronze Age
The Parco Archeologico di Egnazia is a site of immense historical significance. The earliest human settlements in Egnazia date back to the 13th century BC during the Bronze Age. This period saw the establishment of a simple village composed of huts, marking the beginning of human habitation in the area (Beautiful Puglia).
Iron Age and the Iapigi Invasion
In the 11th century BC, during the Iron Age, Egnazia experienced an invasion by the Iapigi, a civilization originating from the Balkans. This invasion marked a significant shift in the cultural and social dynamics of the region. The Iapigi brought with them new technologies and cultural practices that influenced the development of Egnazia (Beautiful Puglia).
Messapian Era
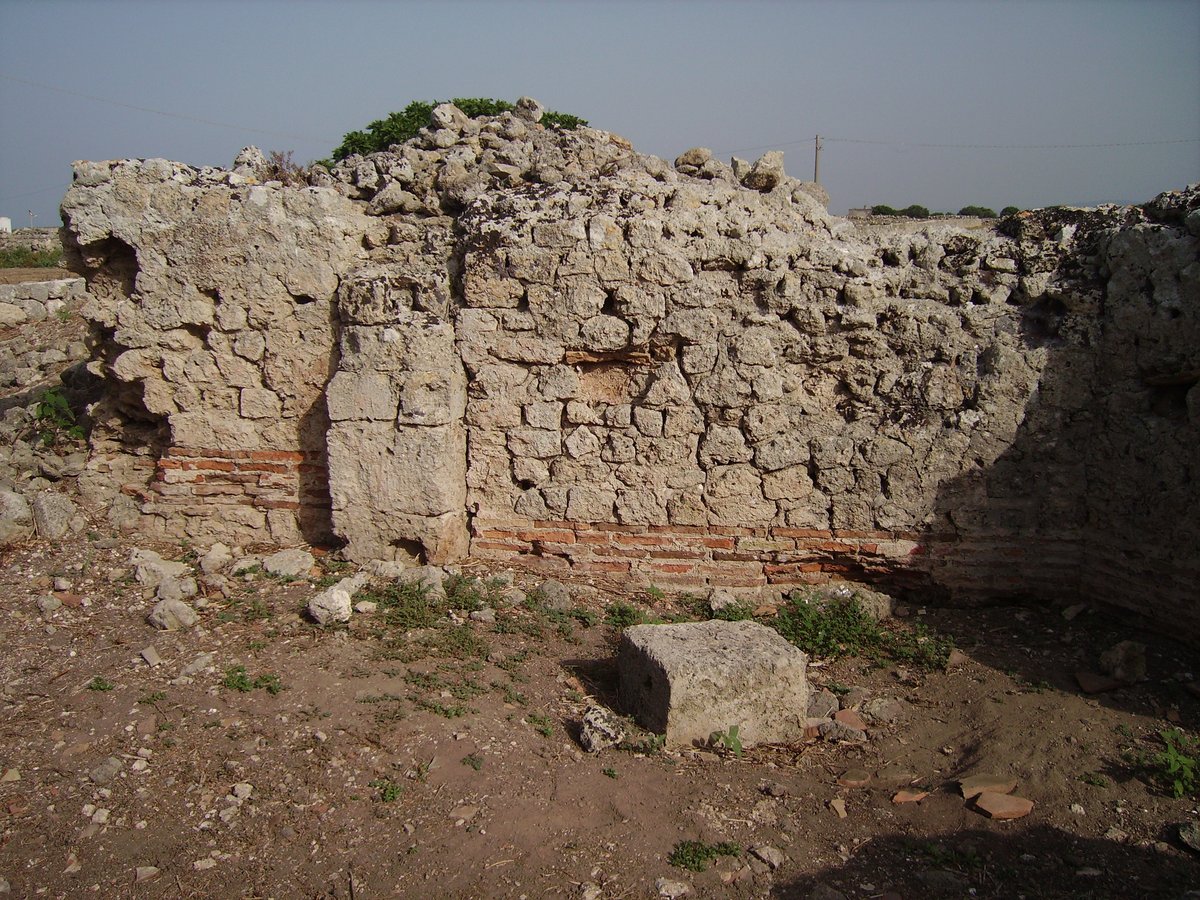
By the 8th century BC, the Messapians, an Italic tribe, had taken control of Egnazia. The Messapian period is notable for the construction of extensive defensive walls that surrounded the urban area, covering approximately 40 hectares. These walls, which are 2 kilometers long and 7 meters high, are among the most well-preserved structures from this era. The Messapians ruled Egnazia until the arrival of the Romans at the end of the 3rd century BC (Beautiful Puglia).
Roman Conquest and Prosperity
The Roman conquest of Egnazia marked the beginning of a period of significant growth and prosperity for the town. Declared a municipality by the Romans, Egnazia’s strategic location allowed it to flourish as a center of trade and commerce. The construction of the Via Traiana, a road linking Rome to Brindisi, further enhanced Egnazia’s importance as a trade hub. The Romans also improved the port facilities, making Egnazia a crucial seaport (Beautiful Puglia).
Architectural and Cultural Developments
During the Roman period, Egnazia saw the construction of several monumental structures, including the forum, amphitheater, and various Christian basilicas. The forum served as the center of public life, while the amphitheater hosted various public spectacles. The Christian basilicas, built between the 4th and 6th centuries AD, are notable for their architectural and artistic significance. The Episcopal Basilica, with its baptistery and mosaic floors, is a must-see for visitors (Italia.it).
Decline and Abandonment
Despite its prosperity during the Roman period, Egnazia faced several challenges following the fall of the Roman Empire. The town suffered attacks from various groups, including the Visigoths, Saracens, and Turks. These invasions weakened Egnazia, leading to its eventual abandonment in the 10th century AD. The once-thriving town became a “dead place,” forgotten until its rediscovery in 1912 (Beautiful Puglia).
Rediscovery and Archaeological Excavations
The rediscovery of Egnazia in 1912 marked the beginning of extensive archaeological investigations. These excavations have uncovered only a small portion of the site, but they have revealed significant insights into the town’s history. Among the notable discoveries are the tracks of the Via Traiana, the ancient amphitheater, and the forum. The archaeological park today offers visitors a glimpse into the rich history of Egnazia, with many well-preserved remains from both the Messapian and Roman periods (Summer in Italy).
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Tickets
The Parco Archeologico di Egnazia is open to visitors throughout the year, but hours may vary depending on the season. It is advisable to check the official website or contact the park directly for the most up-to-date information on visiting hours and ticket prices.
Travel Tips
- Getting There: The park is located between Monopoli and Savelletri, easily accessible by car or public transportation.
- Nearby Attractions: Include other historical sites in Monopoli and enjoy the beautiful Adriatic coast.
- Guided Tours: Consider booking a guided tour to gain deeper insights into the history and significance of the site.
- Photography: Don’t forget to bring your camera; the park offers numerous photographic spots, especially at sunset.
Accessibility
The park is designed to be accessible to all visitors, but it is recommended to check specific accessibility options in advance.
The National Archaeological Museum of Egnazia
The National Archaeological Museum of Egnazia, named after Giuseppe Andreassi, is located within the archaeological park. The museum houses a vast collection of artifacts spanning from the Bronze Age to the Middle Ages. Among the exhibits are ceramics, vases, and other valuable items from the Messapian and Roman periods. Notable artifacts include a marble head from the Roman period depicting the god Attis, an altar for sacrifices to oriental deities, and the mosaic of the Three Graces (Italia.it).
Christian Basilicas and Other Structures
The Christian basilicas within the park are significant for their historical and architectural value. The Episcopal Basilica, with its baptistery, and the Southern Basilica, once adorned with mosaic floors, are key highlights. These structures provide insights into the religious practices and architectural styles of the period between the 4th and 6th centuries AD (Italia.it).
The Baths and Engineering Marvels
The archaeological park also features the remains of Roman baths, equipped with a calidarium, tepidarium, swimming pool, marble baths, statues, mosaics, and sitting rooms. The laconicum, a room used for perspiration baths by dry hot air, is a testament to the advanced engineering skills of the Romans. The heat in the baths was managed through a sophisticated system of pipes and holes in the walls, showcasing the ingenuity of Roman engineering (Imagina Puglia).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the visiting hours for Parco Archeologico di Egnazia?
Visiting hours vary by season. It is best to check the official website or contact the park directly for the most accurate information.
How much do tickets cost for Parco Archeologico di Egnazia?
Ticket prices can vary, so it is advisable to check the official website or contact the park for the latest information on ticket prices.
Are guided tours available?
Yes, guided tours are available and can provide valuable insights into the history and significance of the site.
Is Parco Archeologico di Egnazia accessible?
The park is designed to be accessible, but it is recommended to verify specific accessibility options in advance.
Conclusion
From its Bronze Age origins to its Roman prosperity, the Parco Archeologico di Egnazia is a treasure trove of history. The archaeological park and museum provide valuable insights into the town’s past, making it a must-visit destination for history enthusiasts and tourists alike. Don’t miss the chance to explore this fascinating site and immerse yourself in the rich history of Egnazia.
References
- Beautiful Puglia, n.d., Retrieved from https://www.beautifulpuglia.com/egnazia/
- Summer in Italy, n.d., Retrieved from https://www.summerinitaly.com/guide/egnazia
- Italia.it, n.d., Retrieved from https://www.italia.it/en/puglia/brindisi/national-archeological-museum-egnazia-giuseppe-andreassi-fasano
- Imagina Puglia, n.d., Retrieved from https://imaginapuglia.com/points-of-interest/egnazia-national-archaeological-museum-park/
- The Magic of Puglia, n.d., Retrieved from https://www.themagicofpuglia.com/blog/egnazia-a-worthwhile-daytrip
- Understanding Italy, n.d., Retrieved from https://www.understandingitaly.com/egnazia.html
- Savoring Italy, n.d., Retrieved from https://www.savoringitaly.com/monopoli-travel-guide/
- Musei Puglia, n.d., Retrieved from https://museipuglia.cultura.gov.it/musei/museo-archeologico-nazionale-e-parco-archeologico-di-egnazia/