Basilica of Sant’Andrea Mantua: Visiting Hours, Tickets, and History
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction
Situated in the heart of Mantua, Italy, the Basilica of Sant’Andrea is a crowning jewel of Renaissance architecture, religious devotion, and the city’s illustrious Gonzaga heritage. Commissioned in 1472 by Ludovico III Gonzaga and designed by the visionary Leon Battista Alberti, the basilica is celebrated for enshrining the revered relic of the “Preziosissimo Sangue di Cristo” (Most Precious Blood of Christ), a treasure that has drawn pilgrims for centuries. Alberti’s design harmoniously blends classical Roman elements—such as its triumphal arch-inspired façade and monumental barrel vault—with Renaissance ideals of proportion and humanism. The basilica is not only a spiritual sanctuary but also a cultural beacon, home to significant works of art, including frescoes by Andrea Mantegna. This comprehensive guide explores the basilica’s historical development, architectural highlights, spiritual significance, visitor information, and practical tips to ensure a rewarding visit to one of Mantua’s most treasured sites (Spotting History; Atlas Obscura; Kalata).
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background
- Religious and Cultural Significance
- Visiting Information
- Architectural and Artistic Highlights
- Rituals, Festivals, and Community Events
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Summary and Final Tips
- Sources and Further Reading
Historical Background
Origins and Patronage
Construction of the Basilica of Sant’Andrea began in 1472 under Marquis Ludovico III Gonzaga, on the site of a former Benedictine monastery. The project was entrusted to Leon Battista Alberti, a leading Renaissance architect and theorist. The original bell tower, dating to 1414, remains attached to the basilica (Spotting History; Ars Artis).
Architectural Innovation
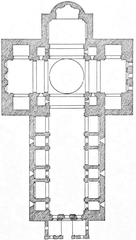
Alberti’s vision was groundbreaking: the basilica features a Latin cross plan, a vast barrel-vaulted nave reminiscent of the ancient Basilica of Maxentius in Rome, and a façade modeled after the Roman Arch of Trajan at Ancona. The façade’s central arch, flanking pilasters, and classical pediment established a new Renaissance standard for church architecture (Spotting History). Side chapels open through alternating arches, replacing traditional aisles and enhancing spatial unity.
Construction Timeline and Additions
The initial construction phase concluded in 1494, but the basilica was not fully completed until 1790. Later additions include the transepts and crypt (1597) and the crowning dome, designed by Filippo Juvarra and built between 1732 and 1782 (Atlas Obscura).
Religious and Cultural Significance
The Precious Blood Relic
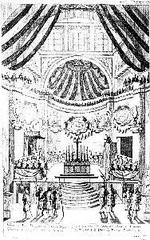
According to tradition, the Roman centurion Longinus, who pierced Christ’s side, collected earth soaked in Jesus’ blood and brought it to Mantua (kalata.it; mondayfeelings.com). Hidden for centuries, the relic was rediscovered after a vision of Saint Andrew revealed its location. Today, it is preserved in sacred vessels in the crypt beneath a marble octagon in front of the main altar. The relic is presented annually during the Good Friday procession (isharethese.com).
Pilgrimage and Liturgy
The basilica’s status as a major pilgrimage site since the Middle Ages has shaped Mantua’s economic and spiritual life. Pilgrims have long venerated the relic, believed to offer spiritual blessings and healing. The basilica remains a focal point for Holy Week, parish life, and special liturgies (kalata.it).
Artistic and Civic Importance
Sant’Andrea was a grand expression of the Gonzaga dynasty’s patronage, serving both as a coronation site and a symbol of their power (wikipedia; finestresullarte.info). The basilica houses masterpieces by Andrea Mantegna (whose tomb is here), Pisanello, and others, and played a key role in Mantua’s recognition as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (mondayfeelings.com; kalata.it).
Visiting Information
Hours and Days of Operation
- Tuesday to Sunday: 9:00 AM – 12:30 PM, 3:00 PM – 6:00 PM
- Closed: Mondays & major public holidays
Hours may change during religious events. Always confirm via the official website or tourist information before visiting.
Tickets and Admission
- Entry: Free of charge; donations are welcome to support maintenance.
- Guided Tours: Available for a fee; book online or on-site.
- Special Exhibitions: Separate ticketing may apply.
Accessibility
- Wheelchair Access: Ramps at the main entrance; accessible restrooms.
- Additional Assistance: Contact the basilica in advance for specific needs.
Getting There
- Location: Piazza Mantegna, central Mantua—within walking distance from the main train station (Mantova).
- Parking: Limited paid parking nearby; public transport and walking are recommended.
Nearby Attractions
- Palazzo Ducale: Former seat of the Gonzaga family, rich in Renaissance art.
- Rotonda di San Lorenzo: Mantua’s oldest church.
- Piazza delle Erbe: Lively square with shops and cafes.
- Palazzo Te: Renowned for Mannerist architecture and art.
Travel Tips
- Best Time to Visit: Weekday mornings or late afternoons for fewer crowds.
- Photography: Allowed without flash; professional equipment requires permission.
- Dress Code: Modest attire is recommended as the basilica is an active place of worship.
Architectural and Artistic Highlights
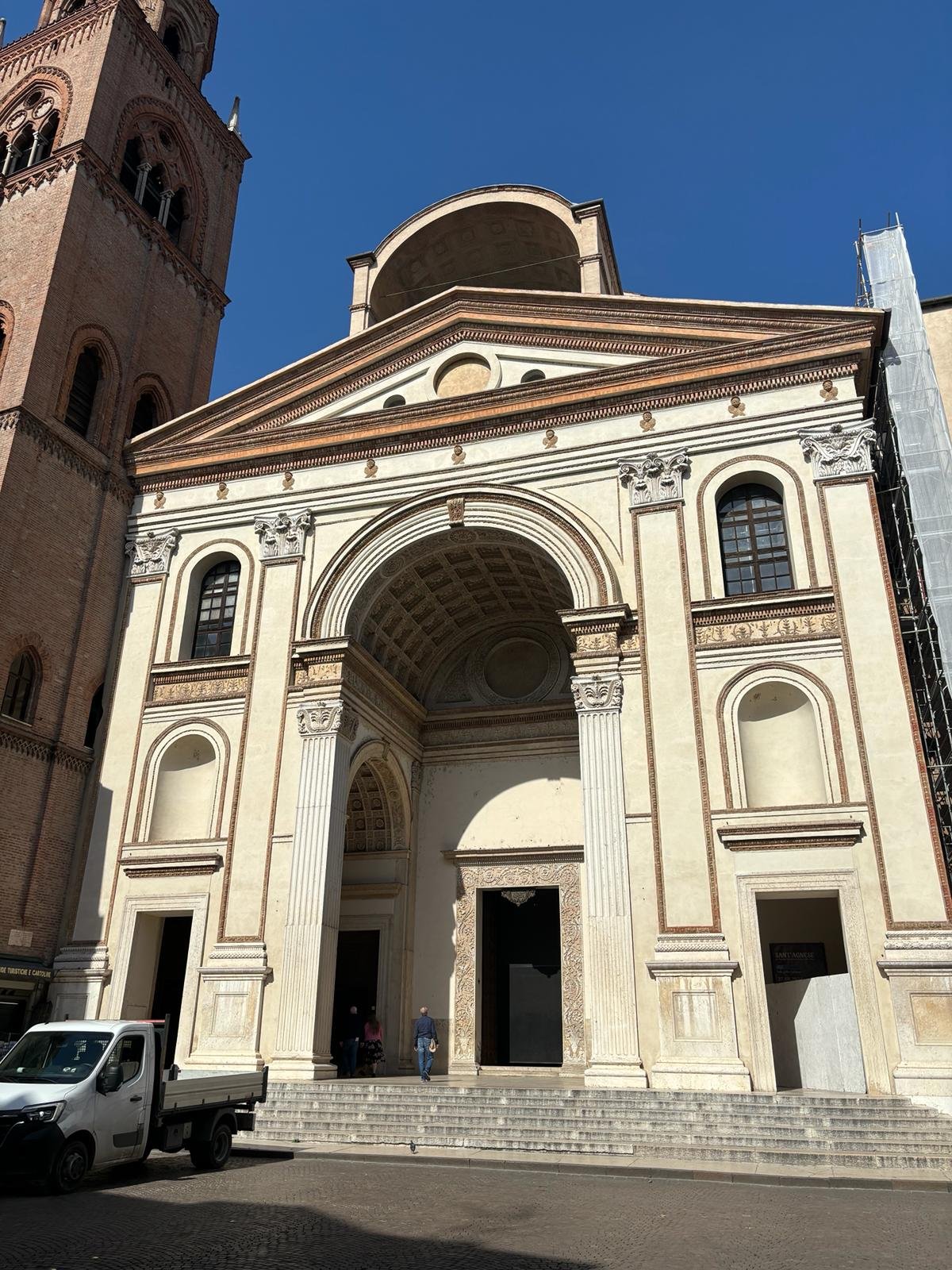
Façade and Exterior
Alberti’s façade, inspired by Roman triumphal arches, commands Piazza Mantegna with its massive central arch, Corinthian pilasters, and classical pediment. The façade is slightly smaller than the basilica itself, designed to heighten the sense of space upon entering.
Interior and Vaulting
The Latin cross plan features a monumental barrel vault—18 meters wide, the largest since antiquity. Side chapels between the massive piers allow an uninterrupted view of the altar and relic. The coffered ceiling and geometric marble floors exemplify Renaissance harmony and order (architecturallife.com).
Artistic Treasures
- Andrea Mantegna’s Tomb: First chapel on the left, marked by a marble bust.
- San Longino Chapel: Houses Mantegna’s “San Sebastiano” fresco.
- Chapel of the Sacred Blood: Richly decorated with frescoes and stuccoes narrating the relic’s story.
Baroque enhancements, including the ornate marble high altar, seamlessly blend with the Renaissance foundation.
Rituals, Festivals, and Community Events
Good Friday Procession
The annual Good Friday procession features the public display of the sacred vessels containing Christ’s blood, drawing large crowds (isharethese.com).
Pilgrimage and Group Visits
Organized pilgrimages and parish groups can arrange special access to the crypt and guided tours (kalata.it).
Cultural Events
The basilica occasionally hosts concerts, art exhibitions, and community gatherings, strengthening its role in Mantua’s cultural life (shegoesthedistance.com).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the visiting hours?
A: Tuesday to Sunday, 9:00 AM – 12:30 PM and 3:00 PM – 6:00 PM; closed Mondays.
Q: Is there an admission fee?
A: Entry is free; guided tours and special events may require tickets.
Q: Is the basilica accessible for visitors with disabilities?
A: Yes; wheelchair ramps and accessible facilities are available.
Q: Can I take photos inside?
A: Non-flash photography is permitted; professional equipment requires permission.
Q: Are guided tours available?
A: Yes; book online or at the entrance.
Q: What is the significance of the relic?
A: The basilica houses relics believed to be the Blood of Christ, central to its spiritual and pilgrimage importance.
Summary and Final Tips
The Basilica of Sant’Andrea is a living testament to Renaissance genius, religious tradition, and Mantua’s civic identity. From Alberti’s architectural innovations and the spiritual draw of the Precious Blood relic to its role in Mantua’s UNESCO World Heritage status, the basilica offers a profound experience for pilgrims, art lovers, and travelers alike. Visitors can expect accessible facilities, expert-led guided tours, and proximity to other Renaissance landmarks. For the best experience, check hours in advance, consider a guided tour, and explore the historic surroundings.
Sources and Further Reading
- Spotting History: Basilica of Sant’Andrea
- Ars Artis: Basilica of Sant’Andrea in Mantua
- Kalata: Basilica and Dome of Sant’Andrea
- Monday Feelings: What to Do in Mantua
- Atlas Obscura: Basilica St. Andrea Sacred Vessels
- Mantua Tourism Official Site
- Wikipedia: Basilica of Sant’Andrea, Mantua
- Finestre sull’Arte: Mantua Travel
- I Share These: Basilica di Sant’Andrea
- She Goes the Distance: Mantua, Italy
- Architectural Life: Tradition and Innovation