Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Insights of Gwalior Fort
Date: 17/07/2024
Introduction
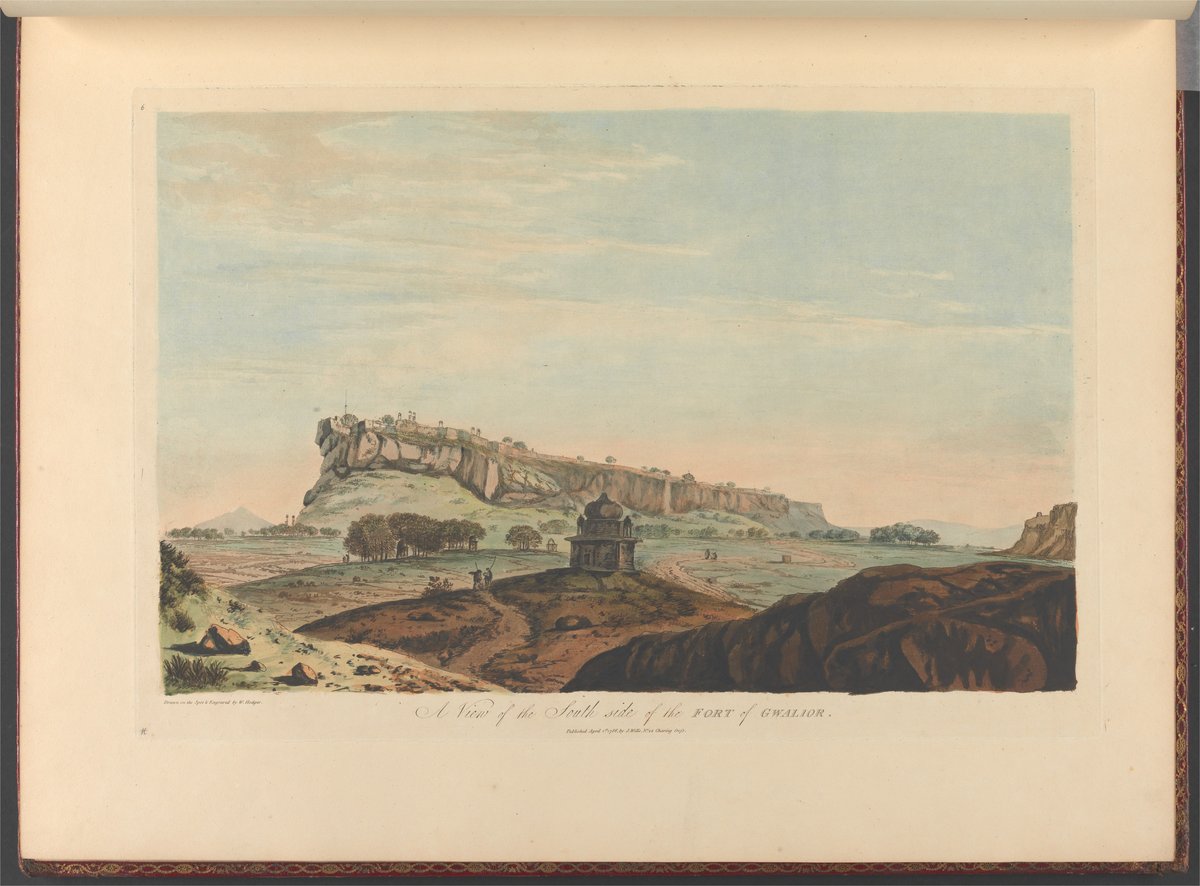
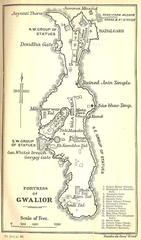
Gwalior Fort, often hailed as the “Gibraltar of India,” is a monumental fortress located in Gwalior, India. Renowned for its rich history and architectural grandeur, the fort stands as a testament to the diverse cultural influences that have shaped the region over centuries. The origins of Gwalior Fort are steeped in legend, dating back to the 3rd century CE when a local chieftain named Suraj Sen was cured of leprosy by sage Gwalipa, leading to the fort’s construction in gratitude (Discover the Majestic Gwalior Fort). The fort’s strategic location on a rocky hilltop not only provided natural defense but also made it a coveted prize for various dynasties, including the Tomars, Mughals, and Marathas (Exploring Gwalior Fort). Today, Gwalior Fort is a must-visit historical site, offering visitors a glimpse into India’s architectural and historical legacy, with highlights such as the Man Mandir Palace, Gujari Mahal, and the Sas-Bahu Temples (Essential Visitor Tips for Gwalior Fort).
Table of Contents
- [Introduction](#introductionintroduction)
- [History of Gwalior Fort](#history-of-gwalior-forthistory-of-gwalior-fort)
- [Early History and Founding](#early-history-and-foundingearly-history-and-founding)
- [The Tomar Dynasty](#the-tomar-dynastythe-tomar-dynasty)
- [Mughal Era](#mughal-eramughal-era)
- [Maratha and British Periods](#maratha-and-british-periodsmaratha-and-british-periods)
- [Architectural Marvels](#architectural-marvelsarchitectural-marvels)
- [Man Mandir Palace](#man-mandir-palaceman-mandir-palace)
- [Gujari Mahal](#gujari-mahalgujari-mahal)
- [Temples](#templestemples)
- [Teli Ka Mandir](#teli-ka-mandirteli-ka-mandir)
- [Sas-Bahu Ka Mandir](#sas-bahu-ka-mandirsas-bahu-ka-mandir)
- [Historical Significance](#historical-significancehistorical-significance)
- [Political Prison](#political-prisonpolitical-prison)
- [Indian Rebellion of 1857](#indian-rebellion-of-1857indian-rebellion-of-1857)
- [Visitor Information](#visitor-informationvisitor-information)
- [Visiting Hours and Ticket Prices](#visiting-hours-and-ticket-pricesvisiting-hours-and-ticket-prices)
- [Travel Tips](#travel-tipstravel-tips)
- [Nearby Attractions](#nearby-attractionsnearby-attractions)
- [Accessibility](#accessibilityaccessibility)
- [Preservation and Restoration Efforts](#preservation-and-restoration-effortspreservation-and-restoration-efforts)
- [FAQ Section](#faq-sectionfaq-section)
- [Conclusion](#conclusionconclusion)
- [References](#referencesreferences)
History of Gwalior Fort
Early History and Founding
Gwalior Fort’s origins are shrouded in legend. According to folklore, Suraj Sen, a local chieftain, was cured of leprosy by the sage Gwalipa and built the fort in gratitude. This legend dates back to the 3rd century CE.
The Tomar Dynasty
The Tomar dynasty, particularly under the rule of Raja Man Singh Tomar (1486-1516), made significant architectural contributions. Man Singh Tomar is renowned for constructing the Man Mandir Palace, a stunning example of Rajput architecture.
Mughal Era
In the early 16th century, the fort fell into the hands of the Mughal Emperor Babur. Babur’s memoirs, the “Baburnama,” describe the fort as a “pearl amongst fortresses.” The Mughals retained control over Gwalior Fort for several decades, using it as a prison for political prisoners.
Maratha and British Periods
In the 18th century, the fort came under Maratha control, specifically the Scindia dynasty. The Scindias made Gwalior their capital. During the British colonial period, the fort played a crucial role in the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Architectural Marvels
Gwalior Fort is a treasure trove of architectural marvels, reflecting diverse cultural influences.
Man Mandir Palace
Built by Raja Man Singh Tomar, the Man Mandir Palace is adorned with intricate carvings and vibrant tiles depicting scenes from Hindu mythology. It also features underground chambers used as prisons during the Mughal era.
Gujari Mahal
Gujari Mahal was built by Raja Man Singh Tomar for his beloved queen, Mrignayani. It now houses an archaeological museum, showcasing artifacts from the region.
Temples
The fort complex is home to several ancient temples, each with unique architectural styles and historical significance.
- Teli Ka Mandir - Dating back to the 9th century, it features a blend of North Indian and Dravidian architectural styles.
- Sas-Bahu Ka Mandir - Dedicated to Vishnu, this 11th-century temple complex consists of two adjacent temples known for their intricate carvings.
Historical Significance
Political Prison
During the Mughal era, the fort served as a political prison for high-profile prisoners, including the Mughal prince Salim (later Emperor Jahangir).
Indian Rebellion of 1857
The fort played a crucial role during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. The recapture of the fort by the British marked a significant turning point in the rebellion.
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Ticket Prices
- Visiting Hours: The fort is open from 6:00 AM to 5:30 PM daily.
- Ticket Prices: The entry fee is INR 75 for Indian citizens and INR 250 for foreign nationals. Children below the age of 15 can enter for free.
Travel Tips
- Guided Tours: Hiring a local guide can enhance your visit.
- Footwear: Wear comfortable footwear for walking and climbing.
- Hydration: Carry water bottles, especially during the summer months.
- Photography: The fort offers numerous picturesque spots. Note that the use of tripods and professional equipment may require special permission.
Nearby Attractions
- Jai Vilas Palace Museum: Home to the Scindia family, this museum showcases European architecture and royal artifacts.
- Sun Temple: A modern temple inspired by the Sun Temple at Konark.
Accessibility
The fort is accessible by road, and local transport options are available from the city. However, the terrain can be challenging for visitors with mobility issues.
Preservation and Restoration Efforts
Over the centuries, Gwalior Fort has undergone several restoration and preservation efforts to maintain its architectural integrity. The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has played a crucial role in these efforts, conducting extensive conservation work to preserve the fort’s historical and architectural heritage.
FAQ Section
Q - What are the visiting hours for Gwalior Fort? A - The fort is open from 6:00 AM to 5:30 PM daily.
Q - How much are the tickets for Gwalior Fort? A - The entry fee is INR 75 for Indian citizens and INR 250 for foreign nationals. Children below the age of 15 can enter for free.
Q - Are guided tours available? A - Yes, hiring a local guide is recommended for a more informative experience.
Q - What is the best time to visit Gwalior Fort? A - The best time to visit is during the winter months (October to March).
Conclusion
Gwalior Fort is not just an architectural marvel but a symbol of India’s rich history. From its legendary founding to its role in pivotal historical events, the fort offers a unique glimpse into the past. Efforts by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) ensure its preservation for future generations. Whether you’re a history enthusiast or a casual tourist, Gwalior Fort promises an unforgettable experience (Discover the Majestic Gwalior Fort).
References
- Discover the Majestic Gwalior Fort - History, Visiting Hours, and More, 2024 Discover the Majestic Gwalior Fort
- Exploring Gwalior Fort - History, Architecture, and Visitor Information, 2024 Exploring Gwalior Fort
- Essential Visitor Tips for Gwalior Fort - Entry Fees, Timings, and More, 2024 Essential Visitor Tips for Gwalior Fort