Bent Pyramid Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Historical Sites in Giza Governorate, Egypt
Date: 14/06/2025
Introduction: History and Cultural Significance of the Bent Pyramid
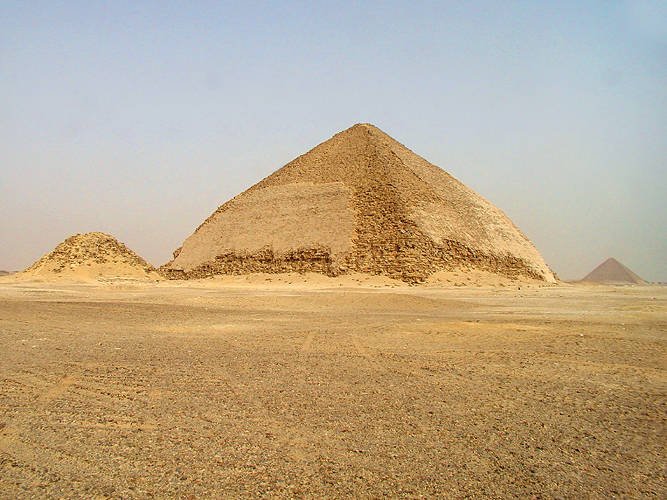
The Bent Pyramid, located in the Dahshur necropolis about 40 kilometers south of Cairo in Egypt’s Giza Governorate, is a monument of remarkable historical and architectural significance. Built during the reign of Pharaoh Sneferu around 2600 BCE, the pyramid is distinguished by its dual-angle design—its lower section rises steeply before transitioning abruptly to a gentler slope higher up. This unique geometry, which gave the pyramid its name, marks a critical phase in the transformation of ancient Egyptian funerary architecture from step-sided to smooth-sided pyramids, paving the way for iconic structures like the Great Pyramid of Giza.
The Bent Pyramid remains one of the best-preserved pyramids of the Old Kingdom, with much of its original polished limestone casing still intact. Its exceptional state of preservation offers visitors a rare opportunity to experience the craftsmanship and religious symbolism of ancient Egypt. The structure not only reflects architectural innovation but also embodies the cultural and spiritual values of ancient Egyptian society—demonstrating the links between kingship, cosmic order, and solar theology. Today, the Bent Pyramid is part of a larger mortuary complex, including the Red and Black Pyramids, enriching the experience for visitors interested in Egypt’s royal necropolises.
For further details and visitor resources, see egyptatours.com, paliparan.com, and ancientengineeringmarvels.com.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Origins and Historical Context
- Architectural Design and Construction Techniques
- Symbolic and Cultural Significance
- Archaeological Exploration and Preservation
- Visiting the Bent Pyramid: Practical Information
- FAQ
- Conclusion
- References
Origins and Historical Context
Commissioned by Pharaoh Sneferu of the Fourth Dynasty, the Bent Pyramid is a milestone in the evolution of pyramid construction, representing the transition from step-sided pyramids to true smooth-sided pyramids (egyptatours.com; paliparan.com). Its construction was a bold experiment in ancient engineering during an era of significant royal power and innovation.
Architectural Design and Construction Techniques
Unique Geometry and Structural Adaptation
The Bent Pyramid’s lower half ascends at a steep 54-degree angle, but midway, the slope shifts to a gentler 43 degrees, resulting in its distinctive “bent” profile (ancientengineeringmarvels.com). This change was likely a response to structural stress detected during construction, demonstrating the ancient Egyptians’ adaptability and technical skill.
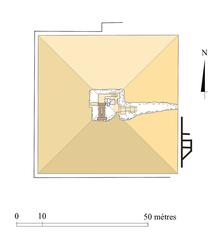
The pyramid stands approximately 105 meters tall, with a base length of 188.6 meters per side (encounterstravel.com). It features two entrance passages—on the north and west faces—each leading to separate corbelled chambers.
Materials and Interior Layout
Constructed mainly from local limestone, the core employs rougher blocks, while the outer casing consists of fine Tura limestone, much of which remains in place today (paliparan.com). The interior includes multiple chambers and passages, with two main burial chambers accessible via separate entrances (encounterstravel.com). Corbelled vaults support the immense weight of the structure above.
Symbolic and Cultural Significance
The Bent Pyramid is pivotal in the progression from step pyramids to the true pyramids. Its design not only influenced Sneferu’s later Red Pyramid but also laid the foundation for subsequent royal tombs (egyptatours.com; paliparan.com). Some scholars interpret its bent form as a symbol of sun rays, reflecting the religious and cosmological beliefs of the time (egyptatours.com). The monument testifies to the enduring legacy of Sneferu’s architectural experimentation.
Archaeological Exploration and Preservation
Early exploration by John Perring, Flinders Petrie, and others laid the groundwork for modern research (egyptbestvacations.com). Restoration efforts have focused on stabilizing the structure and preserving the limestone casing. The pyramid was reopened to visitors in 2019 after extensive conservation (egyptatours.com), balancing access with protection (ancientengineeringmarvels.com).
Modern preservation uses techniques like ground-penetrating radar, 3D scanning, and muon radiography to monitor and maintain the structure (egyptinsights.com; thebrainchamber.com). Visitor management, including limits on daily entries, helps safeguard the monument’s integrity (encounterstravel.com).
Visiting the Bent Pyramid: Practical Information
Visiting Hours
The Bent Pyramid is typically open daily from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM. Hours can vary seasonally or due to conservation work, so always confirm with official sources before your visit (thetouristchecklist.com).
Tickets and Admission
General admission tickets grant access to the Dahshur Necropolis, with an additional fee for entering the pyramid’s interior. As of 2025, interior access costs around $20 USD (tripsinegypt.com). Discounts may apply for students, seniors, and children. Tickets can be purchased on-site or through select online providers.
Accessibility
The site features uneven ground and narrow, steep passages. While the exterior is partially accessible, the interior is challenging for those with mobility limitations (tripsinegypt.com). The nearby Red Pyramid offers slightly easier access.
Travel Tips
- Visit in the cooler months (October to April) for comfort.
- Wear lightweight, modest clothing, sturdy shoes, and bring water and sun protection.
- Early morning visits are best for cooler temperatures and fewer crowds.
- Photography is generally allowed, but flash and tripods may be restricted.
Getting There
Dahshur is about 40 kilometers south of Cairo, accessible by taxi, private car, or organized tours. Public transit is limited, so arranging transportation in advance is recommended (thetouristchecklist.com).
Guided Tours
Hiring a local guide enriches your visit with historical context and navigation assistance. Many operators offer combined tours of Dahshur’s pyramids in multiple languages.
Nearby Attractions
- Red Pyramid: The first successful smooth-sided pyramid, also by Sneferu.
- Black Pyramid: A later, mud-brick royal tomb.
- Saqqara: Home to Djoser’s Step Pyramid, north of Dahshur (trip.com).
Conservation and Community Engagement
The Bent Pyramid has benefited from decades of conservation, including structural stabilization and casing repair (egyptinsights.com). Ongoing challenges include erosion, climate effects, and visitor impact (thebrainchamber.com). Visitor numbers are managed to protect sensitive areas. Local communities participate in heritage management, and sustainable tourism practices are encouraged (localguidetoegypt.com).
International collaborations with UNESCO and research institutions support ongoing preservation and educational initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the Bent Pyramid’s visiting hours?
A: Usually from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM; check for seasonal or conservation-related changes.
Q: How much do tickets cost?
A: General admission covers Dahshur Necropolis; interior access is an extra fee. Discounts may be available.
Q: Is the Bent Pyramid accessible for those with mobility impairments?
A: Accessibility is limited inside the pyramid due to steep, narrow passages.
Q: Can I take photos inside the pyramid?
A: Photography is allowed in most areas, but flash and tripods are often restricted.
Q: What other sites are nearby?
A: The Red Pyramid, Black Pyramid, and Saqqara are all within reach for a broader exploration of Egypt’s funerary monuments.
Conclusion
The Bent Pyramid is a testament to ancient Egyptian ingenuity and spiritual vision. Its unique architecture marks a turning point in pyramid design, and its exceptional preservation provides a direct link to the past. With careful planning—considering visiting hours, ticketing, accessibility, and respectful behavior—visitors enjoy a tranquil, immersive experience distinct from the busier Giza Plateau.
Ongoing conservation ensures that this monument remains accessible for future generations, and community engagement supports both preservation and local livelihoods. By following guidelines and embracing sustainable tourism, you contribute to the ongoing protection of Egypt’s ancient heritage.
For further updates, travel tips, and historical background, consult resources such as egyptatours.com, and consider using the Audiala app for real-time information.
Visual and Interactive Resources
- High-quality images and virtual tours are available through official Egyptian heritage websites.
- Interactive maps help plan your visit and highlight key features and nearby attractions.
References
- Bent Pyramid: A Complete Visitor’s Guide to Cairo’s Historic Architectural Marvel
- Dahshur Pyramid
- The Bent Pyramid
- Bent Pyramid, Dahshur: Visitor Guide
- The Bent Pyramid of Dahshur
- Visiting the Bent Pyramid: Your Guide to Dahshur’s Unique Ancient Wonder
- Bent Pyramid Visiting Hours, Tickets, and Conservation
- Bent Pyramid: Archaeological and Preservation Overview
- Bent Pyramid Visitor Information
- Dahshur Pyramids: A Local’s Guide
- Bent Pyramid Reviews and Visitor Insights
For more travel tips, updates, and multimedia resources, download the Audiala app and follow us on social media. Explore our related articles for a deeper dive into Egypt’s historical sites.