Visiting Hours and Tickets for the Pyramid of Djedefre, 6th of October, Egypt
Date: 01/08/2024
Introduction
Discover the enigmatic Pyramid of Djedefre, a lesser-known but historically significant monument from ancient Egypt. Situated at Abu Rawash, Egypt’s northernmost pyramid site, this pyramid offers a fascinating glimpse into the architectural and cultural innovations of the Fourth Dynasty. Constructed between 2566 and 2558 BC, the Pyramid of Djedefre was intended to be the final resting place of Pharaoh Djedefre, the son of Khufu, who is renowned for building the Great Pyramid of Giza. Unlike its more famous counterparts, Djedefre’s pyramid incorporates unique construction techniques and materials, such as the utilization of mudbrick and pink granite, which set it apart from other pyramids of its time (Egypt Tours Portal, Ancient Egypt Online).
Despite its current ruined state, the Pyramid of Djedefre holds significant historical, architectural, and cultural importance. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about visiting this intriguing site, from its historical background and architectural features to practical visitor information such as visiting hours, ticket prices, and travel tips. Whether you are a history enthusiast, an archaeologist, or a curious traveler, exploring the Pyramid of Djedefre will undoubtedly enrich your understanding of Egypt’s storied past.
Table of Contents
- [Introduction](#introductionintroduction)
- [Historical Background](#historical-backgroundhistorical-background)
- [Construction and Architectural Features](#construction-and-architectural-featuresconstruction-and-architectural-features)
- [Historical Significance](#historical-significancehistorical-significance)
- [Destruction and Current State](#destruction-and-current-statedestruction-and-current-state)
- [Archaeological Discoveries](#archaeological-discoveriesarchaeological-discoveries)
- [Cultural and Religious Significance](#cultural-and-religious-significancecultural-and-religious-significance)
- [Visitor Information](#visitor-informationvisitor-information)
- [Visiting Hours and Tickets](#visiting-hours-and-ticketsvisiting-hours-and-tickets)
- [Travel Tips and Accessibility](#travel-tips-and-accessibilitytravel-tips-and-accessibility)
- [Nearby Attractions](#nearby-attractionsnearby-attractions)
- [Preservation and Modern-Day Relevance](#preservation-and-modern-day-relevancepreservation-and-modern-day-relevance)
- [FAQ](#faqfaq)
- [What are the visiting hours for the Pyramid of Djedefre?](#what-are-the-visiting-hours-for-the-pyramid-of-djedefrewhat-are-the-visiting-hours-for-the-pyramid-of-djedefre)
- [How much are the tickets to visit the Pyramid of Djedefre?](#how-much-are-the-tickets-to-visit-the-pyramid-of-djedefrehow-much-are-the-tickets-to-visit-the-pyramid-of-djedefre)
- [What is the best way to reach the Pyramid of Djedefre?](#what-is-the-best-way-to-reach-the-pyramid-of-djedefrewhat-is-the-best-way-to-reach-the-pyramid-of-djedefre)
- [Are there any nearby attractions?](#are-there-any-nearby-attractionsare-there-any-nearby-attractions)
- [Is the site accessible for visitors with mobility issues?](#is-the-site-accessible-for-visitors-with-mobility-issuesis-the-site-accessible-for-visitors-with-mobility-issues)
- [Conclusion](#conclusionconclusion)
Historical Background
Construction and Architectural Features
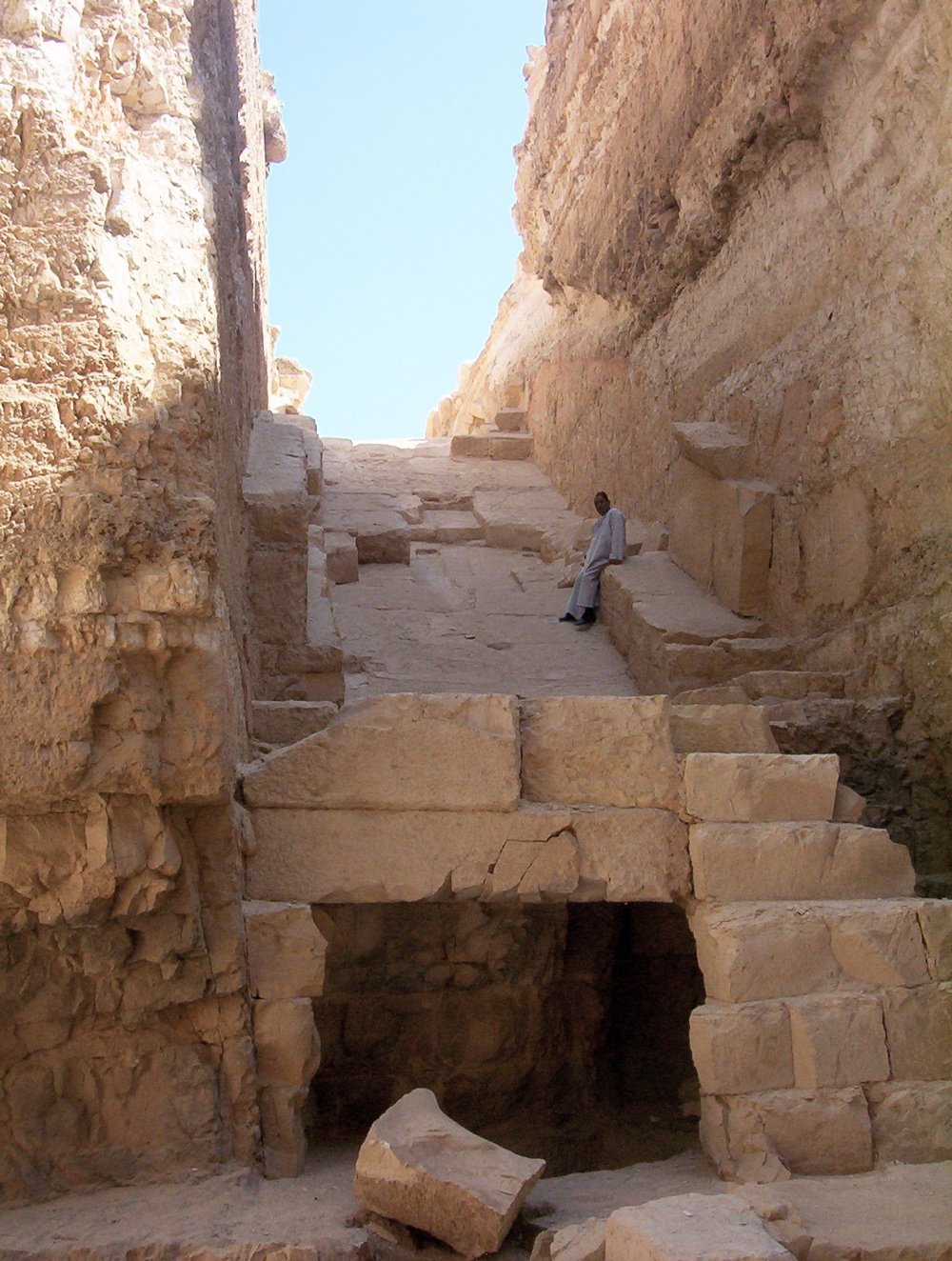
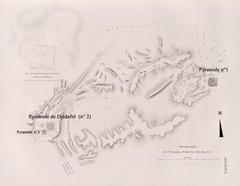
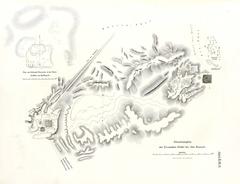
The Pyramid of Djedefre, also known as ‘Djedefre’s Starry Sky,’ was constructed during the Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt, specifically between 2566 and 2558 BC. This pyramid was intended to be the final resting place of Pharaoh Djedefre, the son of Khufu, who is renowned for building the Great Pyramid of Giza. Djedefre’s pyramid is located at Abu Rawash, which is Egypt’s northernmost pyramid site (Egypt Tours Portal).
The pyramid was built on a rocky outcrop and utilized third-dynasty building techniques, similar to the Step Pyramid of Djoser. The construction featured a descending corridor leading to an antechamber and burial chamber. A foundation deposit, including a copper axe blade, was buried in the corridor. The lower layers of the pyramid were clad in pink granite, while the upper courses likely used stone cladding set at an angle, forming a true pyramid with a slope of approximately fifty degrees (Ancient Egypt Online).
Historical Significance
Djedefre’s reign marked a significant period in ancient Egyptian history. He introduced the royal title ‘Sa-Rê,’ meaning ‘Son of Ra,’ and linked his cartouche name with the sun god Ra, showcasing a deep connection to divine symbolism. This was a notable departure from the practices of his predecessors and highlighted his efforts to establish a unique legacy (Egypt Tours Portal).
Despite his relatively short reign, Djedefre aimed to carve out his legacy through his pyramid. The pyramid’s unconventional construction materials, such as the use of mudbrick for the core, deviated from the traditional limestone or limestone casing. This departure from traditional construction methods raises questions about Djedefre’s motivations and the reasons behind this unorthodox choice (Egypt Tours Expert).
Destruction and Current State
The pyramid of Djedefre has suffered significant damage over the centuries. The destruction began at the end of the New Kingdom (1550-1050 BC) and continued throughout the Roman Christian era. During this time, the pyramid served as a stone quarry, with stones being hauled away by camels at the rate of three hundred loads a day. This extensive quarrying contributed to the pyramid’s current ruined state (Egypt Tours Portal).
Recent excavations from 1995 to 2005 have unveiled a different narrative, showcasing that Djedefre’s pyramid was indeed completed during his reign. However, the ravages of time and human activity have left the pyramid mostly in ruins. Statues of the king were smashed as late as the 2nd century AD, further contributing to the pyramid’s diminished stature today (Egypt Tours Portal).
Archaeological Discoveries
The pyramid complex includes several standard features of the time: the main pyramid, a satellite pyramid, a mortuary temple, a boat pit, an enclosure wall, and a causeway. However, no trace of a valley temple has been discovered to date. The main pyramid was built on a rocky outcrop and was constructed in stone. Djedefre echoed third-dynasty building techniques by excavating a trench in the north wall, which descends to meet a vertical shaft instead of building a pyramid and then cutting into the bedrock to create a chamber (Ancient Egypt Online).
A trench pit on the east side of the pyramid is generally thought to have been the boat pit, although the remains of a boat have not actually been found there. Instead, fragments of around one hundred and twenty statues of Djedefre were dumped here. These statues were likely intentionally defaced, probably by Romans and Christians. The attribution of this pit as a boat pit is fairly secure, as traces of the covering slabs have been found on a bench located between the pit and the enclosure wall, and the pit itself is curved to accommodate the hull and the prow of the boat (Ancient Egypt Online).
Cultural and Religious Significance
Djedefre’s pyramid holds significant cultural and religious importance. The pyramid’s name, ‘Djedefre’s Starry Sky,’ reflects the pharaoh’s connection to the divine and the celestial. Djedefre’s introduction of the title ‘Sa-Rê’ and his association with the sun god Ra highlight his efforts to establish a unique and divine legacy. This connection to the divine is further emphasized by the pyramid’s architectural features and the use of pink granite, which was considered a sacred material in ancient Egypt (Egypt Tours Portal).
The pyramid’s alignment also deviates from the traditional north-south orientation of other pyramids. Instead, it is oriented to the east-west. This deviation is believed to have been intentional, signifying a break from tradition and past pharaohs. This unique alignment further underscores Djedefre’s desire to establish his individuality and break away from the legacy of his father, Khufu (EgyptaTours).
Visitor Information
Visiting Hours and Tickets
The Pyramid of Djedefre is accessible to visitors year-round. Typical visiting hours are from 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM, although it is advisable to check for any changes in schedule on official tourism websites or local guides. Ticket prices may vary, but an average entry fee is around 100 Egyptian pounds (approximately $6 USD). It’s recommended to purchase tickets in advance during peak tourist seasons to avoid long queues.
Travel Tips and Accessibility
The site is located in Abu Rawash, about 8 kilometers northwest of Giza. Visitors can reach the pyramid by taxi or organized tours from Cairo. The terrain around the pyramid can be rocky and uneven, so wearing comfortable walking shoes is advisable. The site is not fully accessible for visitors with mobility issues, so planning accordingly is essential.
Nearby Attractions
While visiting the Pyramid of Djedefre, consider exploring other nearby historical sites. The Great Pyramid of Giza, the Sphinx, and the Solar Boat Museum are all within a short driving distance. These sites offer a broader understanding of Egypt’s rich history and architectural prowess.
Preservation and Modern-Day Relevance
Despite its ruined state, the Pyramid of Djedefre remains an important archaeological site. It provides valuable insights into the architectural innovations and cultural practices of ancient Egypt. The pyramid’s unique construction techniques, use of materials, and alignment offer a glimpse into the complexities of ancient Egyptian engineering and religious beliefs.
Modern-day excavations and research continue to uncover new information about the pyramid and its significance. The site remains a subject of interest for historians, archaeologists, and tourists alike. Visiting the Pyramid of Djedefre offers a unique opportunity to explore a lesser-known but historically significant monument and gain a deeper understanding of ancient Egyptian civilization (Egypt Tours Expert).
FAQ
What are the visiting hours for the Pyramid of Djedefre?
The typical visiting hours are from 8:00 AM to 4:00 PM. However, it’s best to check for any updates or changes in schedule.
How much are the tickets to visit the Pyramid of Djedefre?
The average entry fee is around 100 Egyptian pounds (approximately $6 USD).
What is the best way to reach the Pyramid of Djedefre?
The site is located in Abu Rawash, about 8 kilometers northwest of Giza. Visitors can reach the pyramid by taxi or organized tours from Cairo.
Are there any nearby attractions?
Yes, visitors can explore other nearby historical sites such as the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Sphinx, and the Solar Boat Museum.
Is the site accessible for visitors with mobility issues?
The site is not fully accessible for visitors with mobility issues. The terrain around the pyramid can be rocky and uneven.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Pyramid of Djedefre stands as a testament to the ambitious architectural legacy of Pharaoh Djedefre. Despite the challenges of time and human activity, the pyramid continues to intrigue and inspire those who seek to uncover the mysteries of ancient Egypt. Recent excavations and research have provided new insights into its construction and historical significance, highlighting Djedefre’s efforts to establish a unique legacy through innovative architectural techniques and deep religious symbolism (Ancient Egypt Online, Egypt Tours Portal).
Visiting the Pyramid of Djedefre offers a unique opportunity to explore a lesser-known but historically significant monument. Its unique construction methods, use of materials, and alignment offer valuable insights into the complexities of ancient Egyptian engineering and religious beliefs. Whether you are exploring the site for its historical value or its cultural significance, the Pyramid of Djedefre remains an important archaeological site that continues to captivate historians, archaeologists, and tourists alike (Egypt Tours Expert).
References
- Egypt Tours Portal. Pyramid of Djedefre. Retrieved from https://www.egypttoursportal.com/en-us/blog/egyptian-pyramids/pyramid-of-djedefre/
- Ancient Egypt Online. Pyramid of Djedefre. Retrieved from https://ancientegyptonline.co.uk/djedefre-pyramid/
- Egypt Tours Expert. Pyramid of Djedefre: Unveiling the Legacy of a Forgotten Pharaoh. Retrieved from https://egypttoursexpert.com/pyramid-of-djedefre-unveiling-the-legacy-of-a-forgotten-pharaoh/
- Wikipedia. Pyramid of Djedefre. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyramid_of_Djedefre
- EgyptaTours. Pyramid of Djedefre. Retrieved from https://egyptatours.com/pyramid-of-djedefre/
- Touristlink. Pyramid of Djedefre Overview. Retrieved from https://www.touristlink.com/egypt/pyramid-of-djedefre/overview.html